Open Access
Original Article
A dextrorotatory residues-incorporated bioactive dodecapeptide against enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli
Ping Zeng ... Lanhua Yi
Published: June 30, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. 2023;1:210–220
This article belongs to the special issue Bioactive Peptides discovery and development

Open Access
Retraction
Retraction: Controlled release of dexamethasone phosphate from modified mesoporous biocompatible silica nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization, and kinetic studies
Juan Manuel Galdopórpora ... María Victoria Tuttolomondo
Published: March 17, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. 2025;3:100896

Open Access
Correction
Correction: Antioxidants from microalgae and their potential impact on human well-being
Leonel Pereira ... Ana Valado
Published: December 03, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. 2024;2:875
Open Access
Review
Nature-inspired and medicinally relevant short peptides
Maria G. Ciulla ... Kamal Kumar
Published: June 27, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. 2023;1:140–171
This article belongs to the special issue Exploring Potential Drugs from Natural Products
Open Access
Original Article
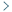
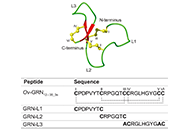
Identification of an inter-cysteine loop potentially involved in the activity of Opisthorchis viverrini-granulin-1
Rozita Takjoo ... Norelle L. Daly
Published: June 30, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. 2023;1:172–179
This article belongs to the special issue Exploring Potential Drugs from Natural Products
Open Access
Review
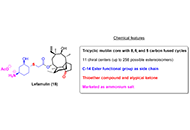
Approved antibacterial drugs in the last 10 years: from the bench to the clinic
Miguel García-Castro ... Juan Manuel López-Romero
Published: June 30, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. 2023;1:180–209
This article belongs to the special issue Exploring Potential Drugs from Natural Products
Open Access
Review
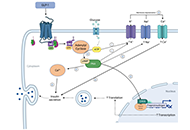
The protective role of GLP-1 in neuro-ophthalmology
Sohum Sheth ... Brandon Lucke-Wold
Published: August 28, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. 2023;1:221–238
Open Access
Review
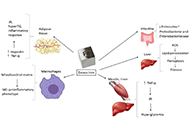
Iron depletion in “metabolic fatty liver syndromes”: a strong biological rationale with disappointing liver outcomes
Amedeo Lonardo
Published: August 28, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. 2023;1:239–252
Open Access
Review
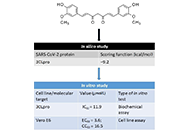
Natural compounds from medicinal plants against COVID-19
Anton Kolodnitsky ... Vladimir Poroikov
Published: August 28, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. 2023;1:253–275
This article belongs to the special issue Exploring Potential Drugs from Natural Products
Open Access
Original Article
In silico study about β-amyloid’s role in Alzheimer’s disease and glaucoma and prediction of its interactions with glaucoma related proteins
Nancy Maurya
Published: August 29, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. 2023;1:276–286
This article belongs to the special issue Machine Learning for Drug Science
Open Access
Commentary
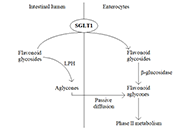
Could flavonoid aglycones prevent the absorption of flavonoid glycosides by inhibiting sodium-dependent glucose transporter-1 in the small intestine?
Katrin Sak
Published: August 30, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. 2023;1:287–291

Open Access
Case Report
Single or multiple treatments with lusutrombopag in subjects with thrombocytopenia and chronic liver disease needing an invasive procedure
Davide Scalabrini ... Pietro Andreone
Published: August 30, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. 2023;1:292–298
This article belongs to the special issue Innovative Therapeutics in Hepato-Gastroenterology
Open Access
Original Article
Electrochemical properties of hydroxyapatite immobilization material for potential cytosensor fabrication
Dennis Adusei ... Elvis K. Tiburu
Published: September 21, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. 2023;1:299–311

Open Access
Case Report
Grade IV oral mucositis treatment with Brazilian green propolis mucoadherent gel
Diogo Alvarenga Silva ... Vagner Rodrigues Santos
Published: October 9, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. 2023;1:312–321
Open Access
Original Article
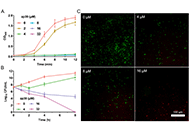
Late-stage diversification strategy for the synthesis of peptide acids and amides using hydrazides
Shoko Tanaka ... Kohei Sato
Published: October 09, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. 2023;1:322–335
This article belongs to the special issue Bioactive Peptides discovery and development
Open Access
Editorial
Drug discovery: a multifactorial ecosystem
Fernando Albericio
Published: January 01, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. 2023;1:1–5
Open Access
Original Article
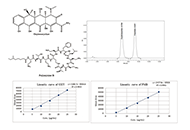
Convenient estimation of oxytetracycline and polymyxin B by a novel high-performance liquid chromatography method: development and validation
Tanu Chaudhary ... Dilpreet Singh
Published: February 24, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. 2023;1:6–17
Open Access
Original Article
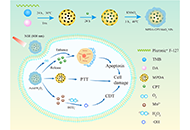
Surface functionalized mesoporous polydopamine nanocomposites for killing tumor cells through collaborative chemo/photothermal/chemodynamic treatment
Yi Ouyang ... Hui Liu
Published: February 27, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. 2023;1:18–30
Open Access
Review
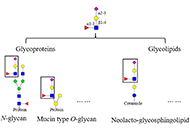
Essential functions, syntheses and detection of sialyl Lewis X on glycoproteins
Qiushi Chen ... Xuechen Li
Published: February 28, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. 2023;1:31–54
This article belongs to the special issue Bioactive Peptides discovery and development

Open Access
Systematic Review
Utilizing the Ethereum blockchain for retrieving and archiving augmented reality surgical navigation data
Sai Batchu ... Brandon Lucke-Wold
Published: February 28, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. 2023;1:55–63