Editor's Picks
Articles
Latest
Most Viewed
Most Downloaded
Most Cited
Open Access
Systematic Review
Role of artificial intelligence in healthcare insurance: systematic literature review
Ahmed Ali Alkhelb, Salah Alshagrawi
Published: April 21, 2025 Explor Digit Health Technol. 2025;3:101145
Open Access
Letter to the Editor
AI in biomedical science: innovations, challenges, and ethical perspectives
Aynur Aliyeva
Published: April 08, 2025 Explor Digit Health Technol. 2025;3:101144

Open Access
Mini Review
AI-based treatment of psychological conditions: the potential use, benefits and drawbacks
Michael Baber, Barbara Baker
Published: April 03, 2025 Explor Digit Health Technol. 2025;3:101143
This article belongs to the special issue Digital Health Innovations in the Battle Against Psychological Problems: Progress, Hurdles, and Prospects

Open Access
Original Article
Digital modeling by biomedical informatics analysis predicts suppression of COVID-19 infectivity via ‘targeting oligonucleotide-directed devolution’
Frank-Un Hong ... Klaus D. Linse
Published: March 20, 2025 Explor Digit Health Technol. 2025;3:101142

Open Access
Perspective
Genomics vs. AI-enhanced electrocardiogram: predicting atrial fibrillation in the era of precision medicine
Jean-Marie Grégoire ... Stéphane Carlier
Published: February 24, 2025 Explor Digit Health Technol. 2025;3:101141
This article belongs to the special issue Wearable Technologies and Application of Machine Learning in Healthcare
Open Access
Letter to the Editor
Leveraging AI for early cholera detection and response: transforming public health surveillance in Nigeria
Adamu Muhammad Ibrahim ... Don Eliso Lucero-Prisno
Published: February 16, 2025 Explor Digit Health Technol. 2025;3:101140

Open Access
Original Article
Use of responsible artificial intelligence to predict health insurance claims in the USA using machine learning algorithms
Ashrafe Alam, Victor R. Prybutok
Published: February 28, 2024 Explor Digit Health Technol. 2024;2:30–45
This article belongs to the special issue Data-informed Decision Making in Healthcare
Open Access
Original Article
Digital health and mobile health: a bibliometric analysis of the 100 most cited papers and their contributing authors
Andy Wai Kan Yeung ... Atanas G. Atanasov
Published: April 22, 2024 Explor Digit Health Technol. 2024;2:86–100
Open Access
Perspective
Turbulence at Twitter with leadership change: implications for health research and science communication
Ronan Lordan, Hari Prasad Devkota
Published: November 01, 2023 Explor Digit Health Technol. 2023;1:4–10
This article belongs to the special issue Social Media Applications in Biomedical Research

Open Access
Systematic Review
Do you need a blockchain in healthcare data sharing? A tertiary review
Kun Li ... Visara Urovi
Published: June 14, 2024 Explor Digit Health Technol. 2024;2:101–123
This article belongs to the special issue Data-informed Decision Making in Healthcare
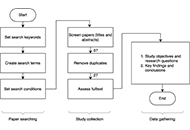
Open Access
Perspective
Science communication on X (formerly Twitter): A picture is worth a thousand characters?
Himel Mondal ... Harald Willschke
Published: November 28, 2023 Explor Digit Health Technol. 2023;1:28–34
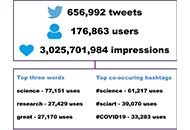
Open Access
Commentary
Identifying children’s environmental health risks, needs, misconceptions, and opportunities for research translation using social media
Andrew Larkin ... Perry Hystad
Published: April 08, 2024 Explor Digit Health Technol. 2024;2:59–66
This article belongs to the special issue Social Media Applications in Biomedical Research

Open Access
Original Article
Digital health and mobile health: a bibliometric analysis of the 100 most cited papers and their contributing authors
Andy Wai Kan Yeung ... Atanas G. Atanasov
Published: April 22, 2024 Explor Digit Health Technol. 2024;2:86–100

Open Access
Original Article
Use of responsible artificial intelligence to predict health insurance claims in the USA using machine learning algorithms
Ashrafe Alam, Victor R. Prybutok
Published: February 28, 2024 Explor Digit Health Technol. 2024;2:30–45
This article belongs to the special issue Data-informed Decision Making in Healthcare

Open Access
Perspective
Turbulence at Twitter with leadership change: implications for health research and science communication
Ronan Lordan, Hari Prasad Devkota
Published: November 01, 2023 Explor Digit Health Technol. 2023;1:4–10
This article belongs to the special issue Social Media Applications in Biomedical Research

Open Access
Commentary
Identifying children’s environmental health risks, needs, misconceptions, and opportunities for research translation using social media
Andrew Larkin ... Perry Hystad
Published: April 08, 2024 Explor Digit Health Technol. 2024;2:59–66
This article belongs to the special issue Social Media Applications in Biomedical Research

Open Access
Systematic Review
Do you need a blockchain in healthcare data sharing? A tertiary review
Kun Li ... Visara Urovi
Published: June 14, 2024 Explor Digit Health Technol. 2024;2:101–123
This article belongs to the special issue Data-informed Decision Making in Healthcare

Open Access
Editorial
Exploration of Digital Health Technologies
Atanas G. Atanasov
Published: November 01, 2023 Explor Digit Health Technol. 2023;1:1–3
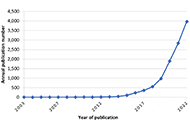
Open Access
Perspective
Turbulence at Twitter with leadership change: implications for health research and science communication
Ronan Lordan, Hari Prasad Devkota
Published: November 01, 2023 Explor Digit Health Technol. 2023;1:4–10
This article belongs to the special issue Social Media Applications in Biomedical Research

Open Access
Letter to the Editor
Harnessing the untapped potential of digital twin technology in digital public health interventions
Salman Khan ... ArunSundar MohanaSundaram
Published: November 01, 2023 Explor Digit Health Technol. 2023;1:11–16
This article belongs to the special issue Social Media Applications in Biomedical Research
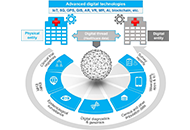
Open Access
Systematic Review
Do you need a blockchain in healthcare data sharing? A tertiary review
Kun Li ... Visara Urovi
Published: June 14, 2024 Explor Digit Health Technol. 2024;2:101–123
This article belongs to the special issue Data-informed Decision Making in Healthcare

Open Access
Original Article
Digital health and mobile health: a bibliometric analysis of the 100 most cited papers and their contributing authors
Andy Wai Kan Yeung ... Atanas G. Atanasov
Published: April 22, 2024 Explor Digit Health Technol. 2024;2:86–100

Open Access
Original Article
Use of responsible artificial intelligence to predict health insurance claims in the USA using machine learning algorithms
Ashrafe Alam, Victor R. Prybutok
Published: February 28, 2024 Explor Digit Health Technol. 2024;2:30–45
This article belongs to the special issue Data-informed Decision Making in Healthcare

Open Access
Perspective
Science communication on X (formerly Twitter): A picture is worth a thousand characters?
Himel Mondal ... Harald Willschke
Published: November 28, 2023 Explor Digit Health Technol. 2023;1:28–34

Special Issues
Ongoing Special lssues
Completed Special lssues
Expert Opinions on Digital Health Innovations
Prof. Marco Tatullo
August 31, 2025
Published Articles: 0

Digital Health Technologies for the Early Detection of Oral Cancer
Saman Warnakulasuriya
August 31, 2025
Published Articles: 9

Digital Health Innovations in the Battle Against Psychological Problems: Progress, Hurdles, and Prospects
Pasquale Caponnetto Mirko Casu
August 31, 2025
Published Articles: 1

Deep Learning Methods and Applications for Biomedical Imaging
Robertas Damaševičius
August 31, 2025
Published Articles: 1

Telepsychiatry in Low-and Middle-income Countries: an Update
Subho Chakrabarti
August 31, 2025
Published Articles: 1

Data-informed Decision Making in Healthcare
Sil Aarts
August 31, 2025
Published Articles: 5

Cancer Diagnosis in the Digital Age
Mohammad Reza Saeb
August 31, 2025
Published Articles: 1

Wearable Technologies and Application of Machine Learning in Healthcare
Shariful Islam
August 31, 2025
Published Articles: 3

Biosensors for Bioactive Molecules
J. G. Manjunatha Chaudhery Mustansar Hussain
August 31, 2025
Published Articles: 2

Social Media Applications in Biomedical Research
Devesh Tewari
May 31, 2025
Published Articles: 7

Journal Information
Journal Indexing
Journal Metrics
Article Usage (total)
Views: 182,499
Downloads: 10,558








 Title: Unravelling the interplaybetween #Harmattan wind andbaroreflex functions: implicationon environmental health andcardiovascular #pathophys
Title: Unravelling the interplaybetween #Harmattan wind andbaroreflex functions: implicationon environmental health andcardiovascular #pathophys


