Editor's Picks
Articles
Latest
Most Viewed
Most Downloaded
Most Cited
Open Access
Original Article
Synthesis and antitumoral activity of novel biaryl hydroxy-triazole and fluorene-triazole hybrids
David Chafi Zeitune ... Camilla Djenne Buarque
Published: April 21, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. 2025;3:1008107
Open Access
Review
Natural products targeting cancer stem cells: a promising therapeutic approach
Julia K. Opara ... Shrikant Anant
Published: April 18, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. 2025;3:1008106
This article belongs to the special issue Remedial benefits of natural products in inflammation and cancer
Open Access
Review
A narrative review on the role of gut microbiome, dietary strategies, and supplements in managing metabolic syndrome
Sunil Chopra ... Ramendra Pati Pandey
Published: April 14, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. 2025;3:1008105
This article belongs to the special issue Preventive and Therapeutic Potential of Nutraceuticals in Non-communicable Diseases
Open Access
Original Article
Revolutionizing diabetes treatment: computational insights into 4-hydroxy isoleucine derivatives and advanced molecular screening for antidiabetic compounds
Lakshmi Mounika Kelam ... M. Elizabeth Sobhia
Published: April 10, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. 2025;3:1008104
This article belongs to the special issue Bioactive Molecules from Natural Sources
Open Access
Review
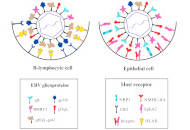
The use of peptides for deciphering the mechanism of EBV, HPV, and HCV invasion of human cells
Daniela Perdomo-Joven ... Mauricio Urquiza-Martinez
Published: March 26, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. 2025;3:1008103
This article belongs to the special issue Bioactive Peptides: Pioneering Innovations in Latin American Research
Open Access
Review
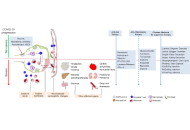
Novel progression on clinical therapy of COVID-19: Western and Traditional Chinese Medicines
Yongjia Xiong ... Feiyue Xing
Published: March 26, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. 2025;3:1008102
Open Access
Editorial
Drug discovery: a multifactorial ecosystem
Fernando Albericio
Published: January 01, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. 2023;1:1–5
Open Access
Review
Approved antibacterial drugs in the last 10 years: from the bench to the clinic
Miguel García-Castro ... Juan Manuel López-Romero
Published: June 30, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. 2023;1:180–209
This article belongs to the special issue Exploring Potential Drugs from Natural Products
Open Access
Review
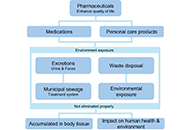
A review of the effects of pharmaceutical pollutants on humans and aquatic ecosystem
Jaya Vinny Eapen ... Jayesh Antony
Published: August 28, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. 2024;2:484–507
Open Access
Review
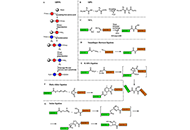
Nature-inspired and medicinally relevant short peptides
Maria G. Ciulla ... Kamal Kumar
Published: June 27, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. 2023;1:140–171
This article belongs to the special issue Exploring Potential Drugs from Natural Products
Open Access
Review
Seaweed: a sustainable solution for greening drug manufacturing in the pursuit of sustainable healthcare
Leonel Pereira, João Cotas
Published: February 27, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. 2024;2:50–84
This article belongs to the special issue Greening Drug Manufacturing for a Sustainable Healthcare

Open Access
Review
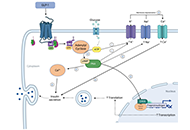
The protective role of GLP-1 in neuro-ophthalmology
Sohum Sheth ... Brandon Lucke-Wold
Published: August 28, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. 2023;1:221–238
Open Access
Review
Approved antibacterial drugs in the last 10 years: from the bench to the clinic
Miguel García-Castro ... Juan Manuel López-Romero
Published: June 30, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. 2023;1:180–209
This article belongs to the special issue Exploring Potential Drugs from Natural Products

Open Access
Review
Nature-inspired and medicinally relevant short peptides
Maria G. Ciulla ... Kamal Kumar
Published: June 27, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. 2023;1:140–171
This article belongs to the special issue Exploring Potential Drugs from Natural Products

Open Access
Review
A review of the effects of pharmaceutical pollutants on humans and aquatic ecosystem
Jaya Vinny Eapen ... Jayesh Antony
Published: August 28, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. 2024;2:484–507

Open Access
Review
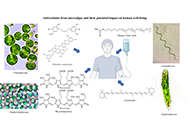
Antioxidants from microalgae and their potential impact on human well-being
Leonel Pereira ... Ana Valado
Published: May 31, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. 2024;2:292–321
This article belongs to the special issue Greening Drug Manufacturing for a Sustainable Healthcare
Open Access
Review
The protective role of GLP-1 in neuro-ophthalmology
Sohum Sheth ... Brandon Lucke-Wold
Published: August 28, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. 2023;1:221–238

Open Access
Review
Seaweed: a sustainable solution for greening drug manufacturing in the pursuit of sustainable healthcare
Leonel Pereira, João Cotas
Published: February 27, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. 2024;2:50–84
This article belongs to the special issue Greening Drug Manufacturing for a Sustainable Healthcare

Open Access
Review
A review of the effects of pharmaceutical pollutants on humans and aquatic ecosystem
Jaya Vinny Eapen ... Jayesh Antony
Published: August 28, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. 2024;2:484–507

Open Access
Review
Antioxidants from microalgae and their potential impact on human well-being
Leonel Pereira ... Ana Valado
Published: May 31, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. 2024;2:292–321
This article belongs to the special issue Greening Drug Manufacturing for a Sustainable Healthcare

Open Access
Review
Seaweed: a sustainable solution for greening drug manufacturing in the pursuit of sustainable healthcare
Leonel Pereira, João Cotas
Published: February 27, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. 2024;2:50–84
This article belongs to the special issue Greening Drug Manufacturing for a Sustainable Healthcare

Open Access
Review
Harnessing the power of seaweed: unveiling the potential of marine algae in drug discovery
Leonel Pereira, Ana Valado
Published: December 28, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. 2023;1:475–496
Open Access
Review
Approved antibacterial drugs in the last 10 years: from the bench to the clinic
Miguel García-Castro ... Juan Manuel López-Romero
Published: June 30, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. 2023;1:180–209
This article belongs to the special issue Exploring Potential Drugs from Natural Products

Open Access
Systematic Review
Utilizing the Ethereum blockchain for retrieving and archiving augmented reality surgical navigation data
Sai Batchu ... Brandon Lucke-Wold
Published: February 28, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. 2023;1:55–63

Special Issues
Ongoing Special lssues
Completed Special lssues
Essential Oils: Insights into Pharmacology, In Vivo, In Vitro and In Silico Studies
Prof. Mozaniel Santana de Oliveira
October 31, 2025
Published Articles: 0

Drug Repurposing: Accelerating Cancer Therapeutic Discoveries
Prof. Wei-Lin Jin Dr. Jin-Min Ma
August 31, 2025
Published Articles: 0

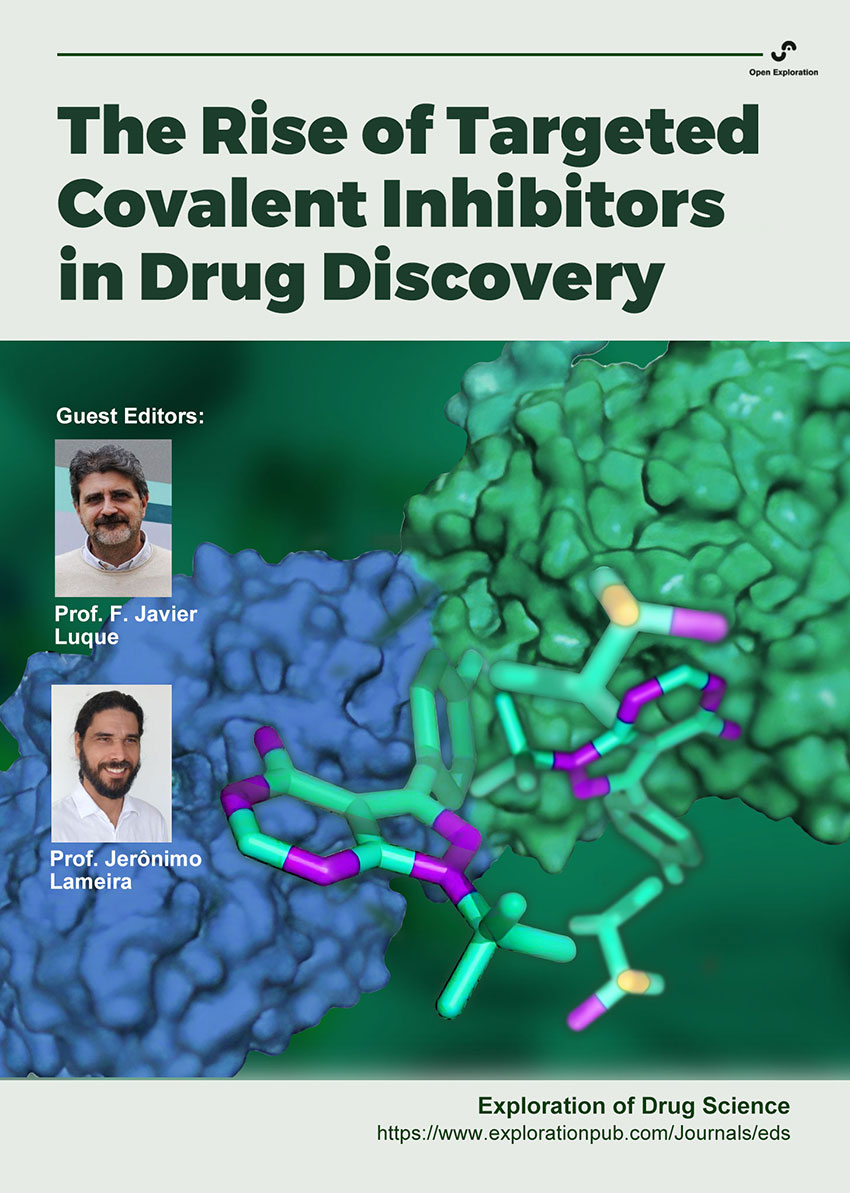
The Rise of Targeted Covalent Inhibitors in Drug Discovery
Prof. F. Javier Luque Prof. Jerônimo Lameira
September 30, 2025
Published Articles: 0
Bioactive Molecules from Natural Sources
Prof. Michio Kurosu
August 31, 2025
Published Articles: 1

Leveraging the FDA-Approved Kinase Inhibitors to Treat Neurological Disorders
Prof. Dazhi Liu
June 30, 2025
Published Articles: 2

Bioactive Peptides: Pioneering Innovations in Latin American Research
Fanny Guzmán Quimbayo Fernando Albericio
June 30, 2025
Published Articles: 9

Recent advances with investigational compounds and strategies to delay or reverse normal aging processes
Ricardo P. Garay, MD, PhD
June 30, 2025
Published Articles: 2

Discovery and development of new antibacterial compounds
Kamal Kumar
June 30, 2025
Published Articles: 3

Remedial benefits of natural products in inflammation and cancer
Noah Isakov Ruby John Anto
June 30, 2025
Published Articles: 6

Mimicking Nature: Biomimetics as Tools for Diagnosis and Therapeutics
Diego Núñez-Villanueva Rosario González-Muñiz
June 30, 2025
Published Articles: 3

Greening Drug Manufacturing for a Sustainable Healthcare
Prof. Alessandra Tolomelli Prof. Walter Cabri
June 30, 2025
Published Articles: 3

Innovative Therapeutics in Hepato-Gastroenterology
Prof. Amedeo Lonardo
June 30, 2025
Published Articles: 4

Preventive and Therapeutic Potential of Nutraceuticals in Non-communicable Diseases
Prof. Marcello Iriti
June 30, 2025
Published Articles: 2

Drug Discovery in Neuropsychiatric Diseases: therapeutic opportunities beyond the classic aminergic system
Prof. Santiago J. Ballaz Prof. Fernando Albericio
June 30, 2025
Published Articles: 0

Bioactive Peptides discovery and development
Prof. Xuechen Li
November 30, 2024
Published Articles: 10

Machine Learning for Drug Science
Prof. Walter Filgueira de Azevedo Jr.
May 31, 2025
Published Articles: 5

Emerging Nanomedicine Technologies for Enhanced Cancer Theranostics
Prof. Xiangyang Shi
April 30, 2025
Published Articles: 4

Journal Information
Journal Indexing
Journal Metrics
Article Usage (total)
Views: 229,365
Downloads: 5,479









 Title: Unravelling the interplaybetween #Harmattan wind andbaroreflex functions: implicationon environmental health andcardiovascular #pathophys
Title: Unravelling the interplaybetween #Harmattan wind andbaroreflex functions: implicationon environmental health andcardiovascular #pathophys


