Editor's Picks
Articles
Latest
Most Viewed
Most Downloaded
Most Cited
Open Access
Review
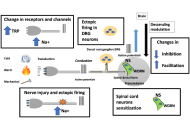
Neuropathic pain: proposal of a mechanism-based treatment
Laura Demartini, Cesare Bonezzi
Published: April 27, 2025 Explor Neurosci. 2025;4:100686
This article belongs to the special issue Neuropathic Pain
Open Access
Original Article
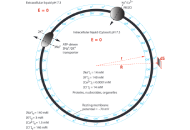
Application of TELC model to better elucidate neural stimulation by touch
James Weifu Lee
Published: April 26, 2025 Explor Neurosci. 2025;4:100685
Open Access
Original Article
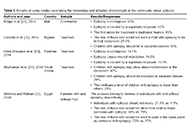
Correlation between self-perceived cognitive problems and objective cognitive impairment in non-CNS cancer patients in a resource-constrained health setting in South Africa
Antonio G. Lentoor, Tiro B. Motsamai
Published: April 16, 2025 Explor Neurosci. 2025;4:100684

Open Access
Perspective
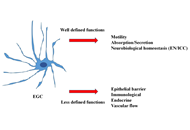
Moving forward: may some of “functional” gut disorders be reclassified as enteric neuro-gliopathies?
Gabrio Bassotti
Published: April 11, 2025 Explor Neurosci. 2025;4:100683
This article belongs to the special issue Enteric Neuro-Gliopathies: Ready for Prime Time?
Open Access
Mini Review
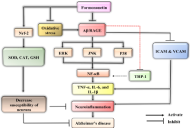
Mechanisms of action of formononetin, an extract from Astragalus membranaceus medicinal plant, in ameliorating Alzheimer’s disease
Manpreet Kaur ... Anish Singh
Published: April 02, 2025 Explor Neurosci. 2025;4:100682
This article belongs to the special issue Medicinal Plants and Bioactive Phytochemicals in Neuroprotection
Open Access
Review
Translocator protein (TSPO) in glioma: implications for diagnosis, disease progression monitoring, and targeted therapies
Julius Mulumba ... Yong Yang
Published: April 01, 2025 Explor Neurosci. 2025;4:100681
This article belongs to the special issue Current Approaches to Malignant Tumors of the Nervous System
Open Access
Review
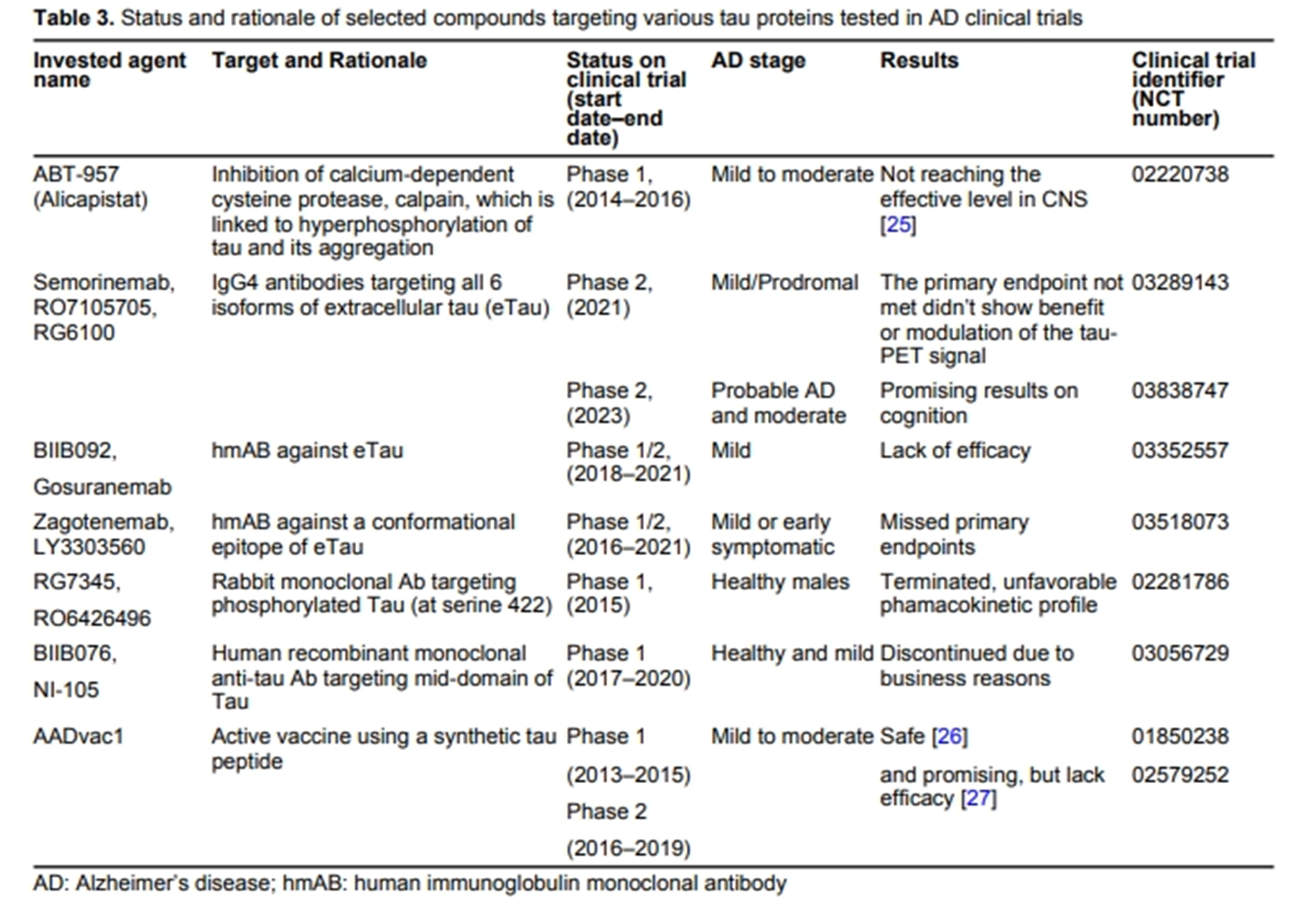
Current therapeutics for Alzheimer’s disease and clinical trials
Danqing Xiao, Chen Zhang
Published: June 27, 2024 Explor Neurosci. 2024;3:255–271
This article belongs to the special issue Alzheimer’s Disease
Open Access
Review
Negative environmental influences on the developing brain mediated by epigenetic modifications
Maya Komar-Fletcher ... Joanna Michalina Jurek
Published: September 28, 2023 Explor Neurosci. 2023;2:193–211
Open Access
Review
Impact of circadian clock dysfunction on human health
Saptadip Samanta, Sk Asif Ali
Published: September 29, 2022 Explor Neurosci. 2022;1:4–30
This article belongs to the special issue Circadian Rhythm and Melatonin
Open Access
Review
Effects mediated by melatonin and cortisol of artificial light and noise, alone and in combination, on sleep and health
Nahum M. Gabinet
Published: September 13, 2024 Explor Neurosci. 2024;3:382–417
This article belongs to the special issue Circadian Rhythm and Melatonin
Open Access
Review
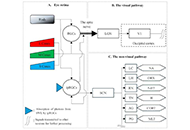
Stigma and psychosocial problems in patients with epilepsy
Kubra Yeni
Published: December 06, 2023 Explor Neurosci. 2023;2:251–263
This article belongs to the special issue Epilepsy
Open Access
Review
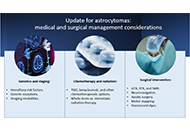
Update for astrocytomas: medical and surgical management considerations
Matthew Willman ... Brandon Lucke-Wold
Published: February 23, 2023 Explor Neurosci. 2023;2:1–26
Open Access
Mini Review
Nutritional treatment with the ketogenic diet in children with refractory epilepsy: a narrative review
Srilaxmi Vityala ... Swathi Nenavath
Published: October 30, 2023 Explor Neurosci. 2023;2:245–250
This article belongs to the special issue Epilepsy

Open Access
Review
Current therapeutics for Alzheimer’s disease and clinical trials
Danqing Xiao, Chen Zhang
Published: June 27, 2024 Explor Neurosci. 2024;3:255–271
This article belongs to the special issue Alzheimer’s Disease

Open Access
Review
Stigma and psychosocial problems in patients with epilepsy
Kubra Yeni
Published: December 06, 2023 Explor Neurosci. 2023;2:251–263
This article belongs to the special issue Epilepsy

Open Access
Review
Impact of circadian clock dysfunction on human health
Saptadip Samanta, Sk Asif Ali
Published: September 29, 2022 Explor Neurosci. 2022;1:4–30
This article belongs to the special issue Circadian Rhythm and Melatonin

Open Access
Review
Negative environmental influences on the developing brain mediated by epigenetic modifications
Maya Komar-Fletcher ... Joanna Michalina Jurek
Published: September 28, 2023 Explor Neurosci. 2023;2:193–211

Open Access
Review
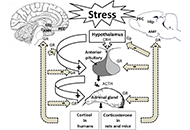
Cellular and molecular mechanisms of stress-induced memory impairment
Ameneh Rezayof ... Shiva Hashemizadeh
Published: December 30, 2022 Explor Neurosci. 2022;1:100–119
This article belongs to the special issue Neuroinflammation in the Ageing and the Injured Brain
Open Access
Review
Stigma and psychosocial problems in patients with epilepsy
Kubra Yeni
Published: December 06, 2023 Explor Neurosci. 2023;2:251–263
This article belongs to the special issue Epilepsy

Open Access
Review
Neuropharmacologic modulation of the melatonergic system
Utku Aykan ... Canan Uluoglu
Published: December 22, 2023 Explor Neurosci. 2023;2:287–306
This article belongs to the special issue Circadian Rhythm and Melatonin
Open Access
Review
Connecting the ends: signaling via receptor tyrosine kinases and cytoskeletal degradation in neurodegeneration
Priyanka Sengupta ... Debashis Mukhopadhyay
Published: February 20, 2024 Explor Neurosci. 2024;3:1–26
This article belongs to the special issue Alzheimer’s Disease

Open Access
Review
Effects mediated by melatonin and cortisol of artificial light and noise, alone and in combination, on sleep and health
Nahum M. Gabinet
Published: September 13, 2024 Explor Neurosci. 2024;3:382–417
This article belongs to the special issue Circadian Rhythm and Melatonin

Open Access
Review
Updates in mechanical thrombectomy
Kevin Pierre ... Brandon Lucke-Wold
Published: December 30, 2022 Explor Neurosci. 2022;1:83–99

Open Access
Review
Update for astrocytomas: medical and surgical management considerations
Matthew Willman ... Brandon Lucke-Wold
Published: February 23, 2023 Explor Neurosci. 2023;2:1–26

Special Issues
Ongoing Special lssues
Completed Special lssues
Medicinal Plants and Bioactive Phytochemicals in Neuroprotection
Prof. Marcello Iriti
June 30, 2025
Published Articles: 4

Neuropathic Pain
Giustino Varrassi
December 31, 2024
Published Articles: 7

Alzheimer's Disease
Ryszard Pluta
March 31, 2025
Published Articles: 8

Novel Therapeutic Approaches for the Treatment of Depression
Prof. Dirk M. Hermann Dr. Ayan Mohamud Yusuf
June 20, 2024
Published Articles: 6

Cerebral Ischemia, Genetics, Comorbidities, Risk Factors and New Therapeutic Options for Neurorestoration
Prof. Aurel Popa-Wagner
March 31, 2025
Published Articles: 5

Circadian Rhythm and Melatonin
Prof. Ertugrul Kilic
June 30, 2024
Published Articles: 7

Neuroinflammation in the Ageing and the Injured Brain
Prof. Ameneh Rezayof Dr. Maryam Sardari
June 30, 2025
Published Articles: 3

Extracellular Vesicles as Cell-based Therapeutics
Prof. Dirk M. Hermann Dr. Chen Wang
June 30, 2025
Published Articles: 3

Journal Information
Journal Indexing
Journal Metrics
Article Usage (total)
Views: 226,181
Downloads: 4,630









 Title: Unravelling the interplaybetween #Harmattan wind andbaroreflex functions: implicationon environmental health andcardiovascular #pathophys
Title: Unravelling the interplaybetween #Harmattan wind andbaroreflex functions: implicationon environmental health andcardiovascular #pathophys


