Editor's Picks
Articles
Latest
Most Viewed
Most Downloaded
Most Cited
Open Access
Review
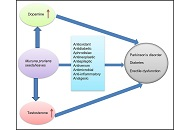
Efficacy of Mucuna pruriens (L.) DC. in treating diabetes, Parkinson’s disease, and erectile dysfunction—a review of clinical and preclinical trials
Ravindra Verma ... Prakash S. Bisen
Published: April 23, 2025 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2025;3:101083
This article belongs to the special issue Natural Products in Health and Disease
Open Access
Review
Agriculture, food security, and sustainability: a review
Shahidul Islam
Published: April 14, 2025 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2025;3:101082

Open Access
Review
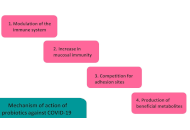
Importance of probiotics and prebiotics and their mechanism of immune action against COVID-19: a narrative review
Norma Angélica Santiesteban-López ... Juan Chávez Medina
Published: April 14, 2025 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2025;3:101081
Open Access
Original Article
Reproducibility of the visual palatability of the crumb of bread and a novel sensory evaluation method using images presented on a screen
Yukinori Sato
Published: April 01, 2025 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2025;3:101080

Open Access
Review
Therapeutic effects of ketogenic diets on physiological and mental health
Alejandro Borrego-Ruiz, Juan J. Borrego
Published: March 25, 2025 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2025;3:101079
This article belongs to the special issue Ketogenic Diet as Medical Nutrition Therapy
Open Access
Original Article
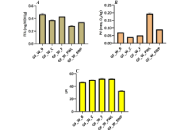
Sustainable insect proteins vs. conventional proteins as fillings in gluten-free oat-based breakfast wraps: nutritional, microbial, and sensory quality
Olamide Akande ... Daniel Ajewole
Published: March 18, 2025 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2025;3:101078
This article belongs to the special issue The food (r)evolution towards food quality/security and human nutrition
Open Access
Review
AI-powered revolution in plant sciences: advancements, applications, and challenges for sustainable agriculture and food security
Deependra Kumar Gupta ... Ajay Kumar Singh
Published: August 06, 2024 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2024;2:443–459

Open Access
Review
Olive oil, fruit and leaves in diabetes mellitus type 2 treatment
Mario Nosić ... Ines Banjari
Published: October 29, 2023 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2023;1:192–205
This article belongs to the special issue Natural Products in Health and Disease

Open Access
Perspective
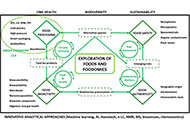
Future trends in Food Science and Foodomics: a perspective view by the Editorial Team of Exploration of Foods and Foodomics
Elena Ibáñez ... Alejandro Cifuentes
Published: November 28, 2024 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2024;2:707–766
Open Access
Review
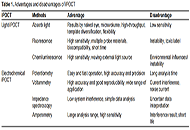
Intelligent point of care test for food safety via a smartphone
Le Zhang ... Zhaowei Zhang
Published: August 30, 2023 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2023;1:143–161
Open Access
Review
Atlantic algae as food and their extracts
Leonel Pereira
Published: April 27, 2023 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2023;1:15–31
This article belongs to the special issue The food (r)evolution towards food quality/security and human nutrition

Open Access
Review
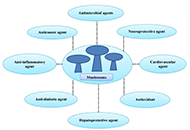
A concise review: edible mushroom and their medicinal significance
Jaya P. Ambhore ... Bhavana A. Shende
Published: May 17, 2024 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2024;2:183–194
Open Access
Perspective
Future trends in Food Science and Foodomics: a perspective view by the Editorial Team of Exploration of Foods and Foodomics
Elena Ibáñez ... Alejandro Cifuentes
Published: November 28, 2024 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2024;2:707–766

Open Access
Review
AI-powered revolution in plant sciences: advancements, applications, and challenges for sustainable agriculture and food security
Deependra Kumar Gupta ... Ajay Kumar Singh
Published: August 06, 2024 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2024;2:443–459

Open Access
Review
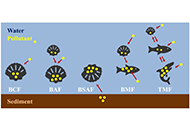
Bioaccumulation of environmental pollutants and marine toxins in bivalve molluscs: a review
Clara Ochoa-Esteso ... María Jesús Lerma-García
Published: December 03, 2024 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2024;2:788–809
This article belongs to the special issue Food Contaminants: Analysis, Occurrence and Risk Assessment
Open Access
Perspective
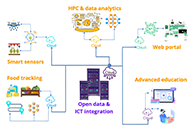
From data to nutrition: the impact of computing infrastructure and artificial intelligence
Pierpaolo Di Bitonto ... Sabina Tangaro
Published: December 03, 2024 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2024;2:810–829
This article belongs to the special issue Metrological Aspects in the Analysis of Nutrients, Functional Compounds, Additives and Contaminants in Food and Feed
Open Access
Original Article
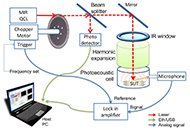
Exploring the potential of laser photoacoustic spectroscopy (LPAS) for predicting amylose content in rice flour
Florinda Artuso ... Fabio Pollastrone
Published: September 10, 2024 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2024;2:542–554
This article belongs to the special issue Metrological Aspects in the Analysis of Nutrients, Functional Compounds, Additives and Contaminants in Food and Feed
Open Access
Original Article
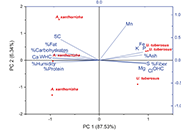
Proximal characteristics, phenolic compounds profile, and functional properties of Ullucus tuberosus and Arracacia xanthorrhiza
Steffanny Sanchez-Portillo ... Raúl Rodríguez-Herrera
Published: November 18, 2024 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2024;2:672–686
Open Access
Review
AI-powered revolution in plant sciences: advancements, applications, and challenges for sustainable agriculture and food security
Deependra Kumar Gupta ... Ajay Kumar Singh
Published: August 06, 2024 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2024;2:443–459

Open Access
Review
Pickering emulsions in food and nutraceutical technology: from delivering hydrophobic compounds to cutting-edge food applications
Lucía Cassani, Andrea Gomez-Zavaglia
Published: July 30, 2024 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2024;2:408–442
This article belongs to the special issue Delivery of Hydrophobic Compounds in Food Systems

Open Access
Original Article
Development of soy whey fortified orange juice beverages: their physicochemical, rheological, antioxidant, and sensory properties
Hilal Ahmad Punoo ... Andleeb Muzaffar
Published: October 29, 2023 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2023;1:206–220

Open Access
Review
Nutritional and bioactive characterization of pistachio—a review with special focus on health
Juliana Ripari Garrido ... María Victoria Salinas
Published: July 26, 2024 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2024;2:363–390
This article belongs to the special issue Delivery of Hydrophobic Compounds in Food Systems
Open Access
Review
Recent advances in nano-related natural antioxidants, their extraction methods and applications in the food industry
Ayla Elmi Kashtiban ... Sayna Zahedinia
Published: April 19, 2024 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2024;2:125–154
This article belongs to the special issue The food (r)evolution towards food quality/security and human nutrition
Open Access
Review
Agriculture, food security, and sustainability: a review
Shahidul Islam
Published: April 14, 2025 Explor Foods Foodomics. 2025;3:101082

Special Issues
Ongoing Special lssues
Completed Special lssues
Enhancing Food Production with Artificial Intelligence: Harnessing Industrial By-Products
Raquel Madureira Ana Lúcia da Silva Oliveira
September 02, 2025
Published Articles: 0

Organic and Inorganic Compounds in Foods and Plants from Latin America
Bruno Lemos Batista Bruno Alves Rocha Camila Neves Lange
September 02, 2025
Published Articles: 1

Metrological Aspects in the Analysis of Nutrients, Functional Compounds, Additives and Contaminants in Food and Feed
Maria Z. Tsimidou Nives Ogrinc Claudia Zoani
November 01, 2025
Published Articles: 13

Food Contaminants: Analysis, Occurrence and Risk Assessment
Olga Pardo Francesc A. Esteve-Turrillas
September 02, 2025
Published Articles: 3

Molecular Targets of Diet in Cancer Therapy and Prevention
Sabrina Battista
September 02, 2025
Published Articles: 0

Food Authenticity and Emerging Challenges of Novel Food
Di Wu Guoliang Li
September 02, 2025
Published Articles: 4

Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents in Food Chemistry and Advanced Food Materials
Maria Fernanda Silva Federico Gomez Maria de los Angeles Fernandez
September 02, 2025
Published Articles: 1

New Generation Analytical Technologies in Food Analysis
Bengi Uslu Cem Erkmen
September 02, 2025
Published Articles: 3

Ketogenic Diet as Medical Nutrition Therapy
Luca Rastrelli Giuseppe Castaldo
August 02, 2025
Published Articles: 6

The food (r)evolution towards food quality/security and human nutrition
José Pinela José Ignacio Alonso-Esteban
August 02, 2025
Published Articles: 8

Journal Information
Journal Indexing
Journal Metrics
Article Usage (total)
Views: 168,509
Downloads: 6,633










 Title: Unravelling the interplaybetween #Harmattan wind andbaroreflex functions: implicationon environmental health andcardiovascular #pathophys
Title: Unravelling the interplaybetween #Harmattan wind andbaroreflex functions: implicationon environmental health andcardiovascular #pathophys


