Editor's Picks
Articles
Latest
Most Viewed
Most Downloaded
Most Cited
Open Access
Perspective
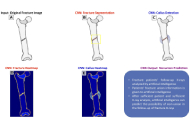
Can fracture non-union be predicted using deep learning?
Ali Yüce ... Abdülhamit Misir
Published: April 08, 2025 Explor Musculoskeletal Dis. 2025;3:100790
This article belongs to the special issue Innovation in Orthopedics
Open Access
Original Article
The prevalence and risk factors of gouty arthritis among fishermen in the Niger Delta region of Nigeria
Gogo James Owo ... Enyohwo Dennis Kpomah
Published: March 25, 2025 Explor Musculoskeletal Dis. 2025;3:100789

Open Access
Review
Urate lowering therapy in primary care: rheum for improvement
Emilie Schurenberg ... Kenneth G. Saag
Published: March 25, 2025 Explor Musculoskeletal Dis. 2025;3:100788
This article belongs to the special issue Pharmacological and Non-Pharmacological Management of Gout

Open Access
Commentary
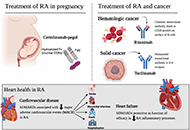
Highly effective treatment options for rheumatoid arthritis afforded by the availability of biosimilars
Leticia A. Shea, Jamshaid S. Ahmed
Published: March 03, 2025 Explor Musculoskeletal Dis. 2025;3:100787
This article belongs to the special issue Biosimilars: State of the Art in the Treatment of Rheumatic Diseases
Open Access
Commentary
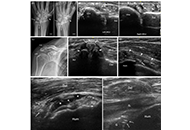
Re-conceptualizing structural damage in chronic calcium pyrophosphate crystal inflammatory arthritis through ultrasonography: a pictorial essay
Janeth Yinh ... Ali Guermazi
Published: February 24, 2025 Explor Musculoskeletal Dis. 2025;3:100786
This article belongs to the special issue Multifaceted Imaging in Rheumatic and Musculoskeletal Diseases
Open Access
Perspective
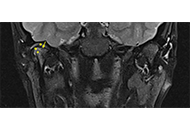
Perspective on clinical and imaging tools for early identification of temporomandibular joint involvement in juvenile idiopathic arthritis
Silvia Magni-Manzoni
Published: February 11, 2025 Explor Musculoskeletal Dis. 2025;3:100785
This article belongs to the special issue Multifaceted Imaging in Rheumatic and Musculoskeletal Diseases
Open Access
Case Report
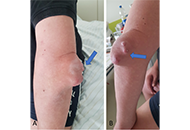
Similarities and differences between gouty arthritis and rheumatoid arthritis—an interesting case with a short look into the literature
David Kiefer ... Juergen Braun
Published: February 24, 2023 Explor Musculoskeletal Dis. 2023;1:11–19
Open Access
Case Report
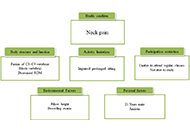
Physiotherapy management of a patient with neck pain having block vertebra: a case report
Sarah Quais, Ammar Suhail
Published: March 27, 2023 Explor Musculoskeletal Dis. 2023;1:31–36
Open Access
Case Report
Return-to-play decision-making following ankle injury: a comprehensive case analysis of the functional hop test
Michael Crinion ... Michael Agnone
Published: March 06, 2024 Explor Musculoskeletal Dis. 2024;2:75–81

Open Access
Review
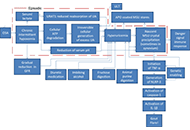
Premature mortality with gout and hyperuricemia may be reduced by early resolution of comorbid obstructive sleep apnea
Burton Abrams
Published: August 31, 2023 Explor Musculoskeletal Dis. 2023;1:106–120
This article belongs to the special issue Hyperuricemia current state and prospects
Open Access
Review
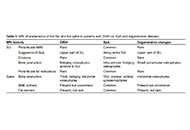
Is there a place for magnetic resonance imaging in diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis?
Iris Eshed
Published: April 27, 2023 Explor Musculoskeletal Dis. 2023;1:43–53
This article belongs to the special issue Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis- A common but neglected disease
Open Access
Review
Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis, beyond the musculoskeletal system
Fabiola Atzeni ... Reuven Mader
Published: December 04, 2023 Explor Musculoskeletal Dis. 2023;1:216–227
This article belongs to the special issue Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis- A common but neglected disease

Open Access
Review
Soft tissue sarcoma: clinical recognition and approach to the loneliest cancer
Sujan Shakya ... Xiang Zhou
Published: February 06, 2024 Explor Musculoskeletal Dis. 2024;2:56–68
Open Access
Review
Interstitial lung disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a narrative review
Gloria Candelas Rodríguez, Virginia Villaverde
Published: October 20, 2023 Explor Musculoskeletal Dis. 2023;1:128–142
This article belongs to the special issue Comorbidities in rheumatoid arthritis
Open Access
Case Report
Similarities and differences between gouty arthritis and rheumatoid arthritis—an interesting case with a short look into the literature
David Kiefer ... Juergen Braun
Published: February 24, 2023 Explor Musculoskeletal Dis. 2023;1:11–19

Open Access
Case Report
Return-to-play decision-making following ankle injury: a comprehensive case analysis of the functional hop test
Michael Crinion ... Michael Agnone
Published: March 06, 2024 Explor Musculoskeletal Dis. 2024;2:75–81

Open Access
Review
Uric acid in atherosclerosis and cardiovascular diseases: innocent bystander or ruthless killer?
Giovanni Cimmino ... Plinio Cirillo
Published: June 03, 2024 Explor Musculoskeletal Dis. 2024;2:189–207
This article belongs to the special issue Hyperuricemia: current state and prospects
Open Access
Systematic Review
Role and effectiveness of surface EMG feedback in sports and orthopedic rehabilitation: a systematic review
Thomas Haab ... Paul Burkey
Published: September 12, 2024 Explor Musculoskeletal Dis. 2024;2:391–407
Open Access
Review
How should we do in the selection and follow-up of systemic conventional treatments in psoriasis?
Sevgi Akarsu
Published: December 05, 2023 Explor Musculoskeletal Dis. 2023;1:241–256
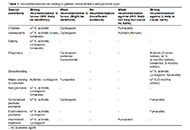
Open Access
Review
Rheumatoid arthritis and cardiovascular comorbidities
Uğur Özkan ... Murat Birtane
Published: December 06, 2023 Explor Musculoskeletal Dis. 2023;1:264–288
This article belongs to the special issue Comorbidities in rheumatoid arthritis
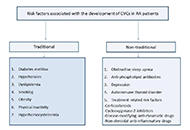
Open Access
Review
Interstitial lung disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a narrative review
Gloria Candelas Rodríguez, Virginia Villaverde
Published: October 20, 2023 Explor Musculoskeletal Dis. 2023;1:128–142
This article belongs to the special issue Comorbidities in rheumatoid arthritis

Open Access
Review
Work-related musculoskeletal disorders among surgeons: a bibliometric analysis from 1982 to 2024
Philippe Gorce, Julien Jacquier-Bret
Published: July 30, 2024 Explor Musculoskeletal Dis. 2024;2:317–335
This article belongs to the special issue Prevalence and Risk Factors of Work-related Musculoskeletal Disorders
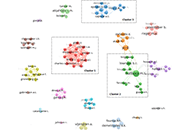
Open Access
Review
Psoriasis, bone and bowel: a comprehensive review and new insights
Fakhreddin Sabooniha
Published: January 18, 2024 Explor Musculoskeletal Dis. 2024;2:1–19

Open Access
Review
Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis and axial spondyloarthritis—similarities and differences
David Kiefer ... Xenofon Baraliakos
Published: November 20, 2023 Explor Musculoskeletal Dis. 2023;1:194–206
This article belongs to the special issue Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis- A common but neglected disease
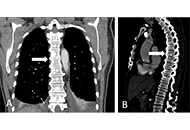
Special Issues
Ongoing Special lssues
Completed Special lssues
Innovation in Orthopedics
Prof. Ashok N. Johari Prof. Philippe Hernigou
October 31, 2025
Published Articles: 1

Evaluation and Outcomes in the Management of Gout
Prof. Fernando Pérez-Ruiz
October 31, 2025
Published Articles: 0

Macrophages and Fibrosis in the Rheumatic Diseases: from Pathophysiology to Treatment
Dr. Stefano Soldano
August 31, 2025
Published Articles: 0

Ultrasound as Outcome Measure in Rheumatic Diseases Trials
Dr. Andrea Di Matteo
August 31, 2025
Published Articles: 0

Biosimilars: State of the Art in the Treatment of Rheumatic Diseases
Prof. Valderilio Feijó Azevedo
August 31, 2025
Published Articles: 6

Multifaceted Imaging in Rheumatic and Musculoskeletal Diseases
Dr. Peter Mandl
August 31, 2025
Published Articles: 3

Pharmacological and Non-Pharmacological Management of Gout
Prof. George Nuki
January 31, 2025
Published Articles: 8

Prevalence and Risk Factors of Work-related Musculoskeletal Disorders
Prof. Philippe Gorce
August 31, 2025
Published Articles: 3

Cell Therapy and Tissue Engineering for Musculoskeletal Conditions: From Pre-clinical Studies to Clinical Trials
Prof. Elena Jones
March 31, 2024
Published Articles: 1
Calcium Pyrophosphate Deposition Disease
Prof. Jürgen Braun
August 31, 2025
Published Articles: 6

Hyperuricemia: current state and prospects
Dr. Blanka Stiburkova
August 31, 2024
Published Articles: 2

Journal Information
Journal Indexing
Journal Metrics
Article Usage (total)
Views: 164,550
Downloads: 2,796











 Title: Unravelling the interplaybetween #Harmattan wind andbaroreflex functions: implicationon environmental health andcardiovascular #pathophys
Title: Unravelling the interplaybetween #Harmattan wind andbaroreflex functions: implicationon environmental health andcardiovascular #pathophys


