



Aim:
Atherosclerosis and diabetes mellitus (DM) often lead to severe conditions, such as acute ischemic stroke (AIS), cardiovascular disease (CVD), and chronic kidney disease (CKD). Some cancers are also associated with atherosclerosis. Therefore, identifying novel autoantibody biomarkers associated with atherosclerosis-related conditions is crucial for improving early diagnosis and risk assessment.
Methods:
We used an array of 9,480 proteins to detect IgG antibodies in the serum of patients with atherosclerosis. Following this screening, we quantified the antibody levels using an amplified luminescent proximity homogeneous assay-linked immunosorbent assay (AlphaLISA) with recombinant antigen proteins.
Results:
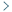
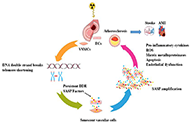
Ubiquitin conjugating enzyme E2 E3 (UBE2E3) was identified as a candidate antigen recognized by IgG antibodies in the sera of individuals diagnosed with atherosclerosis. Compared with healthy donors, significantly higher serum antibody levels against UBE2E3 were found in patients with AIS, DM, CVD, CKD, esophageal cancer (EC), and gastric cancer (GC), but not in those with colorectal cancer (CRC). Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis revealed that the higher areas under the ROC curves for anti-UBE2E3 antibodies were observed in DM- or nephrosclerosis-associated CKD than in the others. Spearman’s correlation analysis revealed that serum anti-UBE2E3 antibody (s-UBE2E3-Ab) levels were associated with the plaque score, maximum intima-media thickness, and cardio-ankle vascular index, which are typical indices of atherosclerosis and stenosis. In the survival analysis of GC and CRC, patients who were s-UBE2E3-Ab-positive had significantly poorer prognoses than patients who were s-UBE2E3-Ab-negative. The difference became more prominent when s-UBE2E3-Abs were combined with anti-differential screening-selected gene aberrant in neuroblastoma antibody (DAN-Ab) or sclerostin domain-containing protein 1 (SOSTDC1), which are bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) antagonists.
Conclusions:
The s-UBE2E3-Ab marker is highly associated with atherosclerosis-related diseases, such as AIS, CVD, DM, CKD, and digestive tract cancers, suggesting the involvement of BMP signals.
Aim:
Atherosclerosis and diabetes mellitus (DM) often lead to severe conditions, such as acute ischemic stroke (AIS), cardiovascular disease (CVD), and chronic kidney disease (CKD). Some cancers are also associated with atherosclerosis. Therefore, identifying novel autoantibody biomarkers associated with atherosclerosis-related conditions is crucial for improving early diagnosis and risk assessment.
Methods:
We used an array of 9,480 proteins to detect IgG antibodies in the serum of patients with atherosclerosis. Following this screening, we quantified the antibody levels using an amplified luminescent proximity homogeneous assay-linked immunosorbent assay (AlphaLISA) with recombinant antigen proteins.
Results:
Ubiquitin conjugating enzyme E2 E3 (UBE2E3) was identified as a candidate antigen recognized by IgG antibodies in the sera of individuals diagnosed with atherosclerosis. Compared with healthy donors, significantly higher serum antibody levels against UBE2E3 were found in patients with AIS, DM, CVD, CKD, esophageal cancer (EC), and gastric cancer (GC), but not in those with colorectal cancer (CRC). Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis revealed that the higher areas under the ROC curves for anti-UBE2E3 antibodies were observed in DM- or nephrosclerosis-associated CKD than in the others. Spearman’s correlation analysis revealed that serum anti-UBE2E3 antibody (s-UBE2E3-Ab) levels were associated with the plaque score, maximum intima-media thickness, and cardio-ankle vascular index, which are typical indices of atherosclerosis and stenosis. In the survival analysis of GC and CRC, patients who were s-UBE2E3-Ab-positive had significantly poorer prognoses than patients who were s-UBE2E3-Ab-negative. The difference became more prominent when s-UBE2E3-Abs were combined with anti-differential screening-selected gene aberrant in neuroblastoma antibody (DAN-Ab) or sclerostin domain-containing protein 1 (SOSTDC1), which are bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) antagonists.
Conclusions:
The s-UBE2E3-Ab marker is highly associated with atherosclerosis-related diseases, such as AIS, CVD, DM, CKD, and digestive tract cancers, suggesting the involvement of BMP signals.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ec.2025.101258

DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ec.2023.00001

The clinical manifestations of COVID-19 which mainly involve the respiratory system may however affect also cardiovascular system. There are a lot and still increasing numbers of reports revealing cardiovascular complications of COVID-19, which may occur in the acute phase as well as during longer follow-up period. The most clinically important diseases include: pulmonary embolism (PE), myocarditis, and acute coronary syndromes (ACS) as well as arrhythmias with the very common atrial fibrillation (AF) and pericarditis. In this review, cardiac imaging options in patients with and after coronavirus infection are presented, showing potential utility for expanding and improving the full and accurate diagnosis of potential complications. Echocardiography, magnetic resonance imaging, and computed tomography (CT) are considered in turn, highlighting their best advantages in patients affected by COVID.
The clinical manifestations of COVID-19 which mainly involve the respiratory system may however affect also cardiovascular system. There are a lot and still increasing numbers of reports revealing cardiovascular complications of COVID-19, which may occur in the acute phase as well as during longer follow-up period. The most clinically important diseases include: pulmonary embolism (PE), myocarditis, and acute coronary syndromes (ACS) as well as arrhythmias with the very common atrial fibrillation (AF) and pericarditis. In this review, cardiac imaging options in patients with and after coronavirus infection are presented, showing potential utility for expanding and improving the full and accurate diagnosis of potential complications. Echocardiography, magnetic resonance imaging, and computed tomography (CT) are considered in turn, highlighting their best advantages in patients affected by COVID.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ec.2023.00008

Mitral valve prolapse (MVP) is a relatively common mitral valvulopathy and the most common cause of isolated primary mitral regurgitation (MR) requiring surgical repair. It affects about 1–3% of the general population. Although MVP is viewed as a benign condition, the association between MVP and sudden cardiac death (SCD) has been proven. Patients with MVP have a three times higher risk of SCD than the general population. The underlying mechanisms and predictors of arrhythmias, which occur in patients with MVP, are still poorly understood. However, some echocardiographic features such as mitral annulus disjunction (MAD), bileaflet MVP (biMVP), and papillary muscle (PM) fibrosis were frequently linked with increased number of arrhythmic events and are referred to as “arrhythmogenic” or “malignant”. Arrhythmogenic MVP (AMVP) has also been associated with other factors such as female sex, polymorphic premature ventricular contraction (PVC), abnormalities of T-waves, and Pickelhaube sign on tissue Doppler tracing of the lateral part of the mitral annulus. Cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging and speckle tracking echocardiography are new tools showing significant potential for detection of malignant features of AMVP. This paper presents various data coming from electrocardiography (ECG) analysis, echocardiography, and other imaging techniques as well as compilation of the recent studies on the subject of MVP.
Mitral valve prolapse (MVP) is a relatively common mitral valvulopathy and the most common cause of isolated primary mitral regurgitation (MR) requiring surgical repair. It affects about 1–3% of the general population. Although MVP is viewed as a benign condition, the association between MVP and sudden cardiac death (SCD) has been proven. Patients with MVP have a three times higher risk of SCD than the general population. The underlying mechanisms and predictors of arrhythmias, which occur in patients with MVP, are still poorly understood. However, some echocardiographic features such as mitral annulus disjunction (MAD), bileaflet MVP (biMVP), and papillary muscle (PM) fibrosis were frequently linked with increased number of arrhythmic events and are referred to as “arrhythmogenic” or “malignant”. Arrhythmogenic MVP (AMVP) has also been associated with other factors such as female sex, polymorphic premature ventricular contraction (PVC), abnormalities of T-waves, and Pickelhaube sign on tissue Doppler tracing of the lateral part of the mitral annulus. Cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging and speckle tracking echocardiography are new tools showing significant potential for detection of malignant features of AMVP. This paper presents various data coming from electrocardiography (ECG) analysis, echocardiography, and other imaging techniques as well as compilation of the recent studies on the subject of MVP.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ec.2023.00009
This article belongs to the special issue Common cardiovascular target for a wide gamut of contemporary health problems – thrombotic and arrhythmic sides of an inflammatory coin

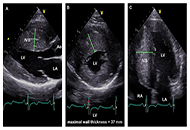
The use of echocardiography, a straightforward and widely available technique, allows for a comprehensive assessment of the patient with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) under both resting and stress conditions. The true prevalence of HCM has been redefined over time by this imaging approach, which has also made it feasible to pinpoint parameters that clinicians may use to stratify patients at risk for adverse cardiovascular events. The current and emerging prognostic predictors in HCM, assessed with transthoracic echocardiography at rest and during provocation, are discussed in this review.
The use of echocardiography, a straightforward and widely available technique, allows for a comprehensive assessment of the patient with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) under both resting and stress conditions. The true prevalence of HCM has been redefined over time by this imaging approach, which has also made it feasible to pinpoint parameters that clinicians may use to stratify patients at risk for adverse cardiovascular events. The current and emerging prognostic predictors in HCM, assessed with transthoracic echocardiography at rest and during provocation, are discussed in this review.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ec.2023.00010
This article belongs to the special issue Common cardiovascular target for a wide gamut of contemporary health problems – thrombotic and arrhythmic sides of an inflammatory coin

Aim:
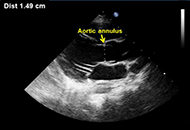
Transthoracic echocardiography is commonly used to assess coronary artery dilatation in Kawasaki disease (KD). However, existing criteria often miss early abnormalities. This study examines the utility of a new parameter, coronary external diameter index (CEDi), for early diagnosis and monitoring in KD.
Methods:
CEDi of left main (LM) and right coronary artery (RCA), calculated as the ratio of coronary artery external diameter (i.e., the distance between the outer coronary edges measured in the proximal segment of the artery) and the diameter of the aortic annulus, was evaluated in 34 patients (age 23 mouths ± 13 months) with KD at the hospital admission and after 2 weeks and 8 weeks of treatment. The control group consisted of 210 healthy children aged 20 months ± 13.4 months. Z-score charts for LM and RCA coronary external diameter (CED) were obtained.
Results:
Compared with controls, KD patients had a markedly higher mean value of LM CEDi (0.53 ± 0.06 vs. 0.33 ± 0.04; P < 0.0001) and RCA CEDi (0.48 ± 0.05 vs. 0.31 ± 0.04; P < 0.0001) at hospital admission. By ROC analysis, LM CEDi of 0.41, and RCA coronary artery thickness index (CATi) of 0.39 were the best cut-offs to confirm the clinical diagnosis of KD, both exhibiting 100% sensitivity and specificity. Mean LM CEDi and RCA CEDi values decreased significantly (P < 0.0001) after 2 weeks of follow-up and were similar to controls (P = 0.53 and P = 0.12, respectively) 8 weeks after admission.
Conclusions:
In patients with KD, CEDi of LM and RCA is an accurate parameter to evaluate coronary artery involvement in the early phase of the illness and during follow-up.
Aim:
Transthoracic echocardiography is commonly used to assess coronary artery dilatation in Kawasaki disease (KD). However, existing criteria often miss early abnormalities. This study examines the utility of a new parameter, coronary external diameter index (CEDi), for early diagnosis and monitoring in KD.
Methods:
CEDi of left main (LM) and right coronary artery (RCA), calculated as the ratio of coronary artery external diameter (i.e., the distance between the outer coronary edges measured in the proximal segment of the artery) and the diameter of the aortic annulus, was evaluated in 34 patients (age 23 mouths ± 13 months) with KD at the hospital admission and after 2 weeks and 8 weeks of treatment. The control group consisted of 210 healthy children aged 20 months ± 13.4 months. Z-score charts for LM and RCA coronary external diameter (CED) were obtained.
Results:
Compared with controls, KD patients had a markedly higher mean value of LM CEDi (0.53 ± 0.06 vs. 0.33 ± 0.04; P < 0.0001) and RCA CEDi (0.48 ± 0.05 vs. 0.31 ± 0.04; P < 0.0001) at hospital admission. By ROC analysis, LM CEDi of 0.41, and RCA coronary artery thickness index (CATi) of 0.39 were the best cut-offs to confirm the clinical diagnosis of KD, both exhibiting 100% sensitivity and specificity. Mean LM CEDi and RCA CEDi values decreased significantly (P < 0.0001) after 2 weeks of follow-up and were similar to controls (P = 0.53 and P = 0.12, respectively) 8 weeks after admission.
Conclusions:
In patients with KD, CEDi of LM and RCA is an accurate parameter to evaluate coronary artery involvement in the early phase of the illness and during follow-up.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ec.2023.00011

Congenital heart defects (CHD) represent the most frequent congenital anomalies among newborns, as well as the leading cause of spontaneous abortion, stillbirth, neonatal and infant death. CHD have been recognized as multifactorial diseases, with environmental contaminants as potential contributors to the etiopathogenesis of CHD. Toxic elements, such as arsenic (As), cadmium (Cd), lead (Pb), and mercury (Hg) are known to be associated with adverse reproductive outcomes and certain congenital anomalies, however their association with the risk for CHD remains inconsistent. This review summarizes the updated evidence on the CHD-associated risk related to exposure to As, Cd, Hg, Pb during pregnancy, reporting the main findings from epidemiological and experimental studies and the underlying molecular mechanisms. Additionally, being diet the major source of these elements in the general population, after having identified the main vectors of toxic metals in food, possible remediation strategies to reduce diet-related risks are also described. Among these, a novel, consumer-centered approach in developing new foods is discussed, considering not only the nutritional characteristics of edible compounds foods are made up of, but also their organoleptic features, making the food even more appealing to the consumer. Overall, current data support the association of maternal exposure to As and Pb with increased risk for CHD, although significant associations have only been observed for total and/or specific subgroups. On the other hand, the evidence of association for Cd and Hg exposure in pregnancy with CHD in the offspring remains, yet, quite speculative. Further large prospective cohort studies and insights into the molecular and biomolecular processes of these relationships are warranted to further explore and/or verify these findings.
Congenital heart defects (CHD) represent the most frequent congenital anomalies among newborns, as well as the leading cause of spontaneous abortion, stillbirth, neonatal and infant death. CHD have been recognized as multifactorial diseases, with environmental contaminants as potential contributors to the etiopathogenesis of CHD. Toxic elements, such as arsenic (As), cadmium (Cd), lead (Pb), and mercury (Hg) are known to be associated with adverse reproductive outcomes and certain congenital anomalies, however their association with the risk for CHD remains inconsistent. This review summarizes the updated evidence on the CHD-associated risk related to exposure to As, Cd, Hg, Pb during pregnancy, reporting the main findings from epidemiological and experimental studies and the underlying molecular mechanisms. Additionally, being diet the major source of these elements in the general population, after having identified the main vectors of toxic metals in food, possible remediation strategies to reduce diet-related risks are also described. Among these, a novel, consumer-centered approach in developing new foods is discussed, considering not only the nutritional characteristics of edible compounds foods are made up of, but also their organoleptic features, making the food even more appealing to the consumer. Overall, current data support the association of maternal exposure to As and Pb with increased risk for CHD, although significant associations have only been observed for total and/or specific subgroups. On the other hand, the evidence of association for Cd and Hg exposure in pregnancy with CHD in the offspring remains, yet, quite speculative. Further large prospective cohort studies and insights into the molecular and biomolecular processes of these relationships are warranted to further explore and/or verify these findings.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ec.2023.00012
This article belongs to the special issue Environmental Cardiology

DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ec.2023.00013
This article belongs to the special issue Environmental Cardiology

Atherosclerosis is a chronic disease, characterized by chronic inflammation, endothelial dysfunction, and lipid deposition in the vessel. Although many major, well-identified risk factors for atherosclerosis [e.g., hyperlipidemia, hypertension, type 2 diabetes (T2D), smoking habit, and obesity] explain a lot about the risk, there is a considerable number of patients who develop atherosclerotic damage and undergo adverse events without presenting any of these established modifiable risk factors. This observation has stimulated an urgent need to expand knowledge towards the identification of additional, less established risk factors that may help in the assessment of risk and fill the gap of knowledge in the cardiovascular (CV) setting. Among them, the hypothesis of a possible relationship between viral infectious agents and atherosclerosis has risen since the early 1900s. However, there is still a great deal of debate regarding the onset and progression of CV disease in relation to the roles of the pathogens (as active inducers or bystanders), host genomic counterparts, and environmental triggers, affecting both virus abundance and the composition of viral communities. Accordingly, the aim of this review is to discuss the current state of knowledge on infectious agents in the atherosclerotic process, with particular focus on two environmental-related viruses, as examples of familiar (influenza) and unfamiliar [severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2)] disease triggers.
Atherosclerosis is a chronic disease, characterized by chronic inflammation, endothelial dysfunction, and lipid deposition in the vessel. Although many major, well-identified risk factors for atherosclerosis [e.g., hyperlipidemia, hypertension, type 2 diabetes (T2D), smoking habit, and obesity] explain a lot about the risk, there is a considerable number of patients who develop atherosclerotic damage and undergo adverse events without presenting any of these established modifiable risk factors. This observation has stimulated an urgent need to expand knowledge towards the identification of additional, less established risk factors that may help in the assessment of risk and fill the gap of knowledge in the cardiovascular (CV) setting. Among them, the hypothesis of a possible relationship between viral infectious agents and atherosclerosis has risen since the early 1900s. However, there is still a great deal of debate regarding the onset and progression of CV disease in relation to the roles of the pathogens (as active inducers or bystanders), host genomic counterparts, and environmental triggers, affecting both virus abundance and the composition of viral communities. Accordingly, the aim of this review is to discuss the current state of knowledge on infectious agents in the atherosclerotic process, with particular focus on two environmental-related viruses, as examples of familiar (influenza) and unfamiliar [severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2)] disease triggers.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ec.2023.00014
This article belongs to the special issue Environmental Cardiology

Aim:
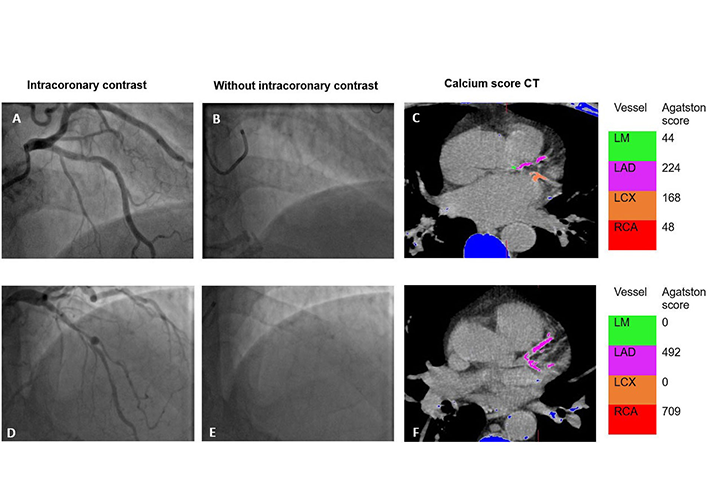
The pattern and severity of coronary artery calcification (CAC) can influence prognosis and outcome in percutaneous coronary intervention. An objective assessment of CAC during invasive angiography may provide additional prognostic information. This study aimed to assess the correlation between the angiographic Birmingham calcium score (BCS) and the Agatston coronary calcium score (CCS) performed as part of single-photon emission computed tomography myocardial perfusion imaging (SPECT-MPI).
Methods:
In this retrospective observational study, patients undergoing SPECT-MPI and invasive coronary angiography as part of their routine management were included. BCS was calculated by reviewing angiography images in retrospect by an observer blinded to the SPECT-MPI calcium score. Spearman’s correlation was used to analyze the correlation between BCS and SPECT-MPI. Receiver operating characteristic curve was used to detect cut-off for BCS that would detect clinically significant CAC [> 400 Agatston units (AU)]. Kaplan-Meier was used to report on outcomes at 5 years follow-up.
Results:
In this cohort of 151 patients, there was a positive correlation between BCS and CCS [Spearman correlation coefficient (r) = 0.558, P < 0.001]. Cumulative BCS of 1 was able to identify clinically significant CAC [area under the curve 0.788, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.714–0.863]. Cumulative BCS ≥ 3 was associated with major adverse outcomes at 5 years follow-up (log rank P = 0.013).
Conclusion:
BCS correlates well with established higher CCS. Application of BCS during invasive coronary angiography will aid risk stratification, management, and follow-up with no extra patient involvement, radiation, or costs.
Aim:
The pattern and severity of coronary artery calcification (CAC) can influence prognosis and outcome in percutaneous coronary intervention. An objective assessment of CAC during invasive angiography may provide additional prognostic information. This study aimed to assess the correlation between the angiographic Birmingham calcium score (BCS) and the Agatston coronary calcium score (CCS) performed as part of single-photon emission computed tomography myocardial perfusion imaging (SPECT-MPI).
Methods:
In this retrospective observational study, patients undergoing SPECT-MPI and invasive coronary angiography as part of their routine management were included. BCS was calculated by reviewing angiography images in retrospect by an observer blinded to the SPECT-MPI calcium score. Spearman’s correlation was used to analyze the correlation between BCS and SPECT-MPI. Receiver operating characteristic curve was used to detect cut-off for BCS that would detect clinically significant CAC [> 400 Agatston units (AU)]. Kaplan-Meier was used to report on outcomes at 5 years follow-up.
Results:
In this cohort of 151 patients, there was a positive correlation between BCS and CCS [Spearman correlation coefficient (r) = 0.558, P < 0.001]. Cumulative BCS of 1 was able to identify clinically significant CAC [area under the curve 0.788, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.714–0.863]. Cumulative BCS ≥ 3 was associated with major adverse outcomes at 5 years follow-up (log rank P = 0.013).
Conclusion:
BCS correlates well with established higher CCS. Application of BCS during invasive coronary angiography will aid risk stratification, management, and follow-up with no extra patient involvement, radiation, or costs.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ec.2024.00022

Drawing insights from a spectrum of in vitro, in vivo experimental, and clinical studies, this review illuminates the underlying mechanism by which iodinated contrast media (ICM) exerts an indirect genotoxic effect. The mechanism involves the photoelectric effect induced by iodine molecules, thereby augmenting radiation attenuation and subsequently elevating the locally absorbed radiation dose. The ensuing generation of secondary electrons from each photoelectric absorption interaction triggers molecular reactions, culminating in discernible DNA damage, notably in the form of DNA double-strand breaks. A convergence of evidence from in vitro, experimental, and clinical investigations underscores a consistent pattern: the addition of iodine contrast linearly heightens the absorbed radiation dose and associated DNA damage. This quantification was evident through alterations in attenuation and the manifestation of double-strand breaks in circulating lymphocytes, serving as an intermediate endpoint and a potential long-term indicator of cancer. The observed surplus of DNA damage in contrast-enhanced images compared to non-contrast images ranged notably from +30% to +200%. This broad range accentuates a substantial amplification effect on radiation-induced damage, particularly noteworthy at clinically relevant iodine doses. Crucially, this effect remains unaffected by brands or manufacturers and exhibits a robust, exclusive correlation with the concentration of iodine in the bloodstream. The significant augmentation of absorbed dose and genotoxic impact of X-rays due to the use of contrast agents warrants critical attention within the medical community. This often-unacknowledged genotoxic influence may play a pivotal role in elevating cancer risks among patients undergoing radiation-based procedures, necessitating a reconsideration of risk assessment protocols and clinical practices.
Drawing insights from a spectrum of in vitro, in vivo experimental, and clinical studies, this review illuminates the underlying mechanism by which iodinated contrast media (ICM) exerts an indirect genotoxic effect. The mechanism involves the photoelectric effect induced by iodine molecules, thereby augmenting radiation attenuation and subsequently elevating the locally absorbed radiation dose. The ensuing generation of secondary electrons from each photoelectric absorption interaction triggers molecular reactions, culminating in discernible DNA damage, notably in the form of DNA double-strand breaks. A convergence of evidence from in vitro, experimental, and clinical investigations underscores a consistent pattern: the addition of iodine contrast linearly heightens the absorbed radiation dose and associated DNA damage. This quantification was evident through alterations in attenuation and the manifestation of double-strand breaks in circulating lymphocytes, serving as an intermediate endpoint and a potential long-term indicator of cancer. The observed surplus of DNA damage in contrast-enhanced images compared to non-contrast images ranged notably from +30% to +200%. This broad range accentuates a substantial amplification effect on radiation-induced damage, particularly noteworthy at clinically relevant iodine doses. Crucially, this effect remains unaffected by brands or manufacturers and exhibits a robust, exclusive correlation with the concentration of iodine in the bloodstream. The significant augmentation of absorbed dose and genotoxic impact of X-rays due to the use of contrast agents warrants critical attention within the medical community. This often-unacknowledged genotoxic influence may play a pivotal role in elevating cancer risks among patients undergoing radiation-based procedures, necessitating a reconsideration of risk assessment protocols and clinical practices.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ec.2024.00023

While authorship practices can vary across different disciplines, authorship should reflect the individuals who have made a substantial contribution to the research project, take public responsibility for the paper’s content, and agree to its submission for publication. In real life, the article is usually authored by at least one truly genuine author and some parasitic authors. The first author and the last author are especially important. The middle authors are less important, and their participation is often wrongly seen as an inconsequential decorative favor. The honorary author, a gift or guest author, is added as a bonus to please someone higher in the hierarchy than the submitting author. This practice is believed to enhance the chances of publication, but usually, the excess of honorary authors will make reviewers more critical. A ghost author contributed substantially but it does not appear in the list of authors to avoid declaring an overt conflict of interest. The gold author is someone paid by a third party in direct or indirect forms, and capable of writing and signing everything asked by the payer, including overstating the merits of a new drug or ignoring its drawbacks. A fake author does not exist, and while it may seem humorous it is a breach of scientific integrity and can lead to serious consequences for the individuals involved. With Chat-generative pre-trained transformer (Chat-GPT), artificial intelligence may contribute decisively to the article content and presentation. Overall, it is important to maintain high standards of integrity and transparency in authorship practices to ensure that research findings are trustworthy and reliable. The reputation of your work is in the hands of your coauthors, so choose them carefully and make sure they share your commitment to scientific integrity.
While authorship practices can vary across different disciplines, authorship should reflect the individuals who have made a substantial contribution to the research project, take public responsibility for the paper’s content, and agree to its submission for publication. In real life, the article is usually authored by at least one truly genuine author and some parasitic authors. The first author and the last author are especially important. The middle authors are less important, and their participation is often wrongly seen as an inconsequential decorative favor. The honorary author, a gift or guest author, is added as a bonus to please someone higher in the hierarchy than the submitting author. This practice is believed to enhance the chances of publication, but usually, the excess of honorary authors will make reviewers more critical. A ghost author contributed substantially but it does not appear in the list of authors to avoid declaring an overt conflict of interest. The gold author is someone paid by a third party in direct or indirect forms, and capable of writing and signing everything asked by the payer, including overstating the merits of a new drug or ignoring its drawbacks. A fake author does not exist, and while it may seem humorous it is a breach of scientific integrity and can lead to serious consequences for the individuals involved. With Chat-generative pre-trained transformer (Chat-GPT), artificial intelligence may contribute decisively to the article content and presentation. Overall, it is important to maintain high standards of integrity and transparency in authorship practices to ensure that research findings are trustworthy and reliable. The reputation of your work is in the hands of your coauthors, so choose them carefully and make sure they share your commitment to scientific integrity.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ec.2024.00024

Left ventricular (LV) function is typically evaluated through LV ejection fraction (EF), a robust indicator of risk, showing a nonlinear increase in mortality rates below 40%. Conversely, excessively high EF values (> 65%) also correlate with elevated mortality, following a U-shaped curve, with its nadir observed between 50% and 65%. This underscores the necessity for improved identification of the hypercontractile phenotype. However, EF is not synonymous with LV contraction function, as it can fluctuate independently of contractility due to variations in afterload, preload, heart rate, and ventricular-arterial coupling. Assessing the contractile status of the LV requires more specific metrics, such as LV elastance (or contractile force) and global longitudinal strain. Current guidelines outline various parameters for a more precise characterization of LV contractility, yet further research is warranted for validation. The true hypercontractile phenotype is evident in cardiac pathologies such as hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, ischemia with angiographically normal coronary arteries, Tako-tsubo syndrome, heart failure with preserved EF, and may also stem from systemic disorders including anemia, hyperthyroidism, liver, kidney, or pulmonary diseases. The hypercontractile phenotype constitutes a distinctive hemodynamic substrate underlying clinical manifestations such as angina, dyspnea, or arrhythmias, presenting a target for intervention through beta-blockers or specific cardiac myosin inhibitors. While EF remains pivotal for clinical classification, risk stratification, and therapeutic decision-making, integrating it with other indices of LV function can enhance the characterization of the hypercontractile phenotype.
Left ventricular (LV) function is typically evaluated through LV ejection fraction (EF), a robust indicator of risk, showing a nonlinear increase in mortality rates below 40%. Conversely, excessively high EF values (> 65%) also correlate with elevated mortality, following a U-shaped curve, with its nadir observed between 50% and 65%. This underscores the necessity for improved identification of the hypercontractile phenotype. However, EF is not synonymous with LV contraction function, as it can fluctuate independently of contractility due to variations in afterload, preload, heart rate, and ventricular-arterial coupling. Assessing the contractile status of the LV requires more specific metrics, such as LV elastance (or contractile force) and global longitudinal strain. Current guidelines outline various parameters for a more precise characterization of LV contractility, yet further research is warranted for validation. The true hypercontractile phenotype is evident in cardiac pathologies such as hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, ischemia with angiographically normal coronary arteries, Tako-tsubo syndrome, heart failure with preserved EF, and may also stem from systemic disorders including anemia, hyperthyroidism, liver, kidney, or pulmonary diseases. The hypercontractile phenotype constitutes a distinctive hemodynamic substrate underlying clinical manifestations such as angina, dyspnea, or arrhythmias, presenting a target for intervention through beta-blockers or specific cardiac myosin inhibitors. While EF remains pivotal for clinical classification, risk stratification, and therapeutic decision-making, integrating it with other indices of LV function can enhance the characterization of the hypercontractile phenotype.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ec.2024.00025

Metabolic syndrome (MetS) is known as a non-communicable disease (NCD) that affects more and more individuals. MetS is closely related to type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), cardiovascular disease (CVD), obesity and inflammation. It is associated with T2DM due to the disturbance in insulin secretion/effect, eventually leading to insulin resistance (IR). The link between MetS and CVD is due to accelerated atherosclerosis in response to chronic inflammation. This literature review was based on a search in the PubMed database. All selected articles are written in English and cover a period of approximately 10 years (January 2014 to May 2023). The first selection used MeSH terms such as: “metabolic syndrome”, “type 2 diabetes mellitus”, “obesity”, “inflammation”, and “insulin resistance” and different associations between them. Titles and abstracts were analyzed. In the end, 44 articles were selected, 4 of which were meta-analysis studies. Currently, an individual is considered to have MetS if they present 3 of the following changes: increased waist circumference, increased triglycerides (TG), reduced high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), increased fasting blood glucose and hypertension. We believe this can often lead to a false diagnosis. The objective of this paper is to compile what we consider to be an appropriate panel of MetS indicators. The markers that stand out in this review are the lipid profile, anti- and pro-inflammatory function and oxidative stress. Considering the research, we believe that a complete panel, to correlate the most characteristic conditions of MetS, should include the following markers: TG/HDL-C ratio, small dense low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (SdLDL-C), lipid peroxidation markers, leptin/adiponectin ratio, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1), activin-A and ferritin levels. Finally, it is important to expand research on the pathophysiology of MetS and confirm the most appropriate markers as well as discover new ones to correctly diagnose this condition.
Metabolic syndrome (MetS) is known as a non-communicable disease (NCD) that affects more and more individuals. MetS is closely related to type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), cardiovascular disease (CVD), obesity and inflammation. It is associated with T2DM due to the disturbance in insulin secretion/effect, eventually leading to insulin resistance (IR). The link between MetS and CVD is due to accelerated atherosclerosis in response to chronic inflammation. This literature review was based on a search in the PubMed database. All selected articles are written in English and cover a period of approximately 10 years (January 2014 to May 2023). The first selection used MeSH terms such as: “metabolic syndrome”, “type 2 diabetes mellitus”, “obesity”, “inflammation”, and “insulin resistance” and different associations between them. Titles and abstracts were analyzed. In the end, 44 articles were selected, 4 of which were meta-analysis studies. Currently, an individual is considered to have MetS if they present 3 of the following changes: increased waist circumference, increased triglycerides (TG), reduced high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), increased fasting blood glucose and hypertension. We believe this can often lead to a false diagnosis. The objective of this paper is to compile what we consider to be an appropriate panel of MetS indicators. The markers that stand out in this review are the lipid profile, anti- and pro-inflammatory function and oxidative stress. Considering the research, we believe that a complete panel, to correlate the most characteristic conditions of MetS, should include the following markers: TG/HDL-C ratio, small dense low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (SdLDL-C), lipid peroxidation markers, leptin/adiponectin ratio, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1), activin-A and ferritin levels. Finally, it is important to expand research on the pathophysiology of MetS and confirm the most appropriate markers as well as discover new ones to correctly diagnose this condition.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ec.2024.00026
This article belongs to the special issue Molecular Mechanisms of Cardiovascular Aging

Adventitial crosslinking is a method in current investigational stage for preventing the rupture of aortic aneurysms. It is based on the photochemical crosslinking of adventitial collagen by exposure to ultraviolet A radiation. Essentially, an adventitial top layer is generated that displays enhanced mechanical properties and imparts additional strength and stiffness to the aneurysmal wall. Looking back upon the history of aortic surgery during 1940s, the aortic film wrapping, then dubbed “cellophane wrapping”, also was a procedure employed for delaying the aneurysmal rupture. In principle, the two procedures are similar in that both result in laminar composites, although the top layers differ fundamentally from each other. This review discussed in some detail the use and clinical outcomes of the aortic wrapping with artificial films, also mentioning the contemporary procedures still grouped under this umbrella term. The focus of the review was a comparative view on two procedures, the aortic film wrapping and adventitial crosslinking. It was concluded that the methods are different in many aspects, including the mechanisms of action. In fact, the promoters of adventitial crosslinking were not aware of the prior existence of aortic film wrapping. However, the achievements of the classical wrapping, by now regarded as merely historical episodes, did not discard prior knowledge, but repurposed it in a process that led to innovative strategies.
Adventitial crosslinking is a method in current investigational stage for preventing the rupture of aortic aneurysms. It is based on the photochemical crosslinking of adventitial collagen by exposure to ultraviolet A radiation. Essentially, an adventitial top layer is generated that displays enhanced mechanical properties and imparts additional strength and stiffness to the aneurysmal wall. Looking back upon the history of aortic surgery during 1940s, the aortic film wrapping, then dubbed “cellophane wrapping”, also was a procedure employed for delaying the aneurysmal rupture. In principle, the two procedures are similar in that both result in laminar composites, although the top layers differ fundamentally from each other. This review discussed in some detail the use and clinical outcomes of the aortic wrapping with artificial films, also mentioning the contemporary procedures still grouped under this umbrella term. The focus of the review was a comparative view on two procedures, the aortic film wrapping and adventitial crosslinking. It was concluded that the methods are different in many aspects, including the mechanisms of action. In fact, the promoters of adventitial crosslinking were not aware of the prior existence of aortic film wrapping. However, the achievements of the classical wrapping, by now regarded as merely historical episodes, did not discard prior knowledge, but repurposed it in a process that led to innovative strategies.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ec.2024.00027

Lipoprotein(a) [Lp(a)] is composed of a low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and glycoprotein (a)—apolipoprotein(a) [apo(a)]. The size and concentration of Lp(a) in serum can vary among individuals and is determined by genetic factors. The environmental factors, diet, and physical activity have a negligible effect on Lp(a) level. Observational, epidemiological, and genetic studies improved that high levels of Lp(a) > 50 mg/dL (> 125 nmol/L) have been associated with an increased risk of myocardial infarction (MI), stroke, and calcific aortic valve stenosis (CAVS). It is recommended to measure Lp(a) at least once in adults to identify individuals with a high cardiovascular risk. This screening is particularly important in certain populations, including: youth with a history of ischemic stroke or a family history of premature atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (CVD; ASCVD) or high Lp(a), individuals with recurrent cardiovascular events despite optimal hypolipemic treatment and no other identifiable risk factors or patients with familial hypercholesterolemia (FH). Considering Lp(a) levels in the evaluation of cardiovascular risk can provide valuable information for risk stratification and management decisions. However, it’s important to note that the treatments of elevated level of Lp(a) are limited. In recent years, there has been ongoing research and development of new drugs targeting Lp(a): pelacarsen—antisense oligonucleotide (ASO), and olpasiran—a small interfering RNA (siRNA).
Lipoprotein(a) [Lp(a)] is composed of a low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and glycoprotein (a)—apolipoprotein(a) [apo(a)]. The size and concentration of Lp(a) in serum can vary among individuals and is determined by genetic factors. The environmental factors, diet, and physical activity have a negligible effect on Lp(a) level. Observational, epidemiological, and genetic studies improved that high levels of Lp(a) > 50 mg/dL (> 125 nmol/L) have been associated with an increased risk of myocardial infarction (MI), stroke, and calcific aortic valve stenosis (CAVS). It is recommended to measure Lp(a) at least once in adults to identify individuals with a high cardiovascular risk. This screening is particularly important in certain populations, including: youth with a history of ischemic stroke or a family history of premature atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (CVD; ASCVD) or high Lp(a), individuals with recurrent cardiovascular events despite optimal hypolipemic treatment and no other identifiable risk factors or patients with familial hypercholesterolemia (FH). Considering Lp(a) levels in the evaluation of cardiovascular risk can provide valuable information for risk stratification and management decisions. However, it’s important to note that the treatments of elevated level of Lp(a) are limited. In recent years, there has been ongoing research and development of new drugs targeting Lp(a): pelacarsen—antisense oligonucleotide (ASO), and olpasiran—a small interfering RNA (siRNA).
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ec.2023.00015
This article belongs to the special issue Common cardiovascular target for a wide gamut of contemporary health problems – thrombotic and arrhythmic sides of an inflammatory coin

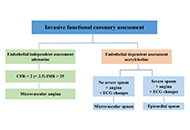
Coronary vasospasm stands as a widely acknowledged and frequent culprit behind chest pain, acute coronary syndrome, and sudden cardiac death, yet it remains a challenging diagnosis. Current guidelines recommend invasive coronary function testing to assess pathophysiology and mechanisms and to define treatment. In reality, this protocol is rarely applied, because it necessitates extended occupation of the cath lab, repetitive administration of nephrotoxic iodine contrast agents, the need for repeated testing on both coronary arteries leading to considerable radiation exposure, and significant direct expenses. The promising perspective for vasospasm testing is a noninvasive approach with advanced echocardiographic techniques, such as transthoracic Doppler echocardiography, with more sensitive indicators of ischemia. Hyperventilation and exercise tests are used for vasospasm directed testing, with assessment of the new parameters: coronary flow velocities and reserve, allowing to see deeper into macro and microvascular pathophysiology. Association between coronary flow, global longitudinal strain and microvascular dysfunction (MVD) and impaired values at hyperemia was previously demonstrated. Reduction in coronary flow velocity (CFV) despite heightened myocardial oxygen consumption and double product during hyperventilation are indicative of coronary vasospasm. Normal coronary angiography finding in patients with documented evidence of ischemia should initiate additional diagnostic testing in order to increase the yield of specific diagnosis in patients with suspected vasospasm, which could help to personalize treatment and prognosis. In order to achieve this, non-invasive provocative stress echocardiography tests should be included in the diagnostic workup. This approach, characterized by its simplicity, feasibility, safety, and efficacy, is currently undergoing extensive testing on a large scale.
Coronary vasospasm stands as a widely acknowledged and frequent culprit behind chest pain, acute coronary syndrome, and sudden cardiac death, yet it remains a challenging diagnosis. Current guidelines recommend invasive coronary function testing to assess pathophysiology and mechanisms and to define treatment. In reality, this protocol is rarely applied, because it necessitates extended occupation of the cath lab, repetitive administration of nephrotoxic iodine contrast agents, the need for repeated testing on both coronary arteries leading to considerable radiation exposure, and significant direct expenses. The promising perspective for vasospasm testing is a noninvasive approach with advanced echocardiographic techniques, such as transthoracic Doppler echocardiography, with more sensitive indicators of ischemia. Hyperventilation and exercise tests are used for vasospasm directed testing, with assessment of the new parameters: coronary flow velocities and reserve, allowing to see deeper into macro and microvascular pathophysiology. Association between coronary flow, global longitudinal strain and microvascular dysfunction (MVD) and impaired values at hyperemia was previously demonstrated. Reduction in coronary flow velocity (CFV) despite heightened myocardial oxygen consumption and double product during hyperventilation are indicative of coronary vasospasm. Normal coronary angiography finding in patients with documented evidence of ischemia should initiate additional diagnostic testing in order to increase the yield of specific diagnosis in patients with suspected vasospasm, which could help to personalize treatment and prognosis. In order to achieve this, non-invasive provocative stress echocardiography tests should be included in the diagnostic workup. This approach, characterized by its simplicity, feasibility, safety, and efficacy, is currently undergoing extensive testing on a large scale.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ec.2024.00016

Aim:
There is a lack of studies that analyzed factors influencing on feasibility of coronary flow velocity reserve (CFVR) during exercise stress echocardiography (SE). The aim of the study was to define the feasibility of assessment of CFVR during exercise through SE depending on experience, techniques, and clinical factors.
Methods:
This is a single-center study. SE was performed using three generations of echo systems in five consecutive cohorts of patients by experienced and novice specialists. All patients performed a supine bicycle testing. CFVR was calculated in the middle/middle-distal parts of the left anterior descending artery (LAD). Three different adjustment settings were used for LAD visualization.
Results:
The study included 3,014 patients (59 years old ± 11 years old, 54% males). Age [odds ratio (OR) 0.98, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.96–0.99, P < 0.01], body mass index (BMI; OR 0.95, 95% CI 0.91–0.98, P < 0.003), rest heart rate (OR 0.98, 95% CI 0.97–0.99, P < 0.0005) and doctor’s experience (OR 2.7, 95% CI 1.57–4.53, P < 0.0003) were independent factors that influence on feasibility. The feasibility of CFVR assessment during exercise SE in the whole population by experienced doctors was 89.4%. The feasibility of CFVR assessment of LAD in obese patients performed by experienced doctors using modern echo machines and new techniques was high (86.0%).
Conclusions:
Coronary artery velocity reserve during supine exercise SE is a feasible, non-invasive available tool. The new generation echo machine and the new techniques provide a good feasibility of CFVR assessment, even in novice doctors. Despite a lower level of possibility to assess CFVR in obese patients or with a higher resting heart rate, this method is feasible in a great majority of such patients.
Aim:
There is a lack of studies that analyzed factors influencing on feasibility of coronary flow velocity reserve (CFVR) during exercise stress echocardiography (SE). The aim of the study was to define the feasibility of assessment of CFVR during exercise through SE depending on experience, techniques, and clinical factors.
Methods:
This is a single-center study. SE was performed using three generations of echo systems in five consecutive cohorts of patients by experienced and novice specialists. All patients performed a supine bicycle testing. CFVR was calculated in the middle/middle-distal parts of the left anterior descending artery (LAD). Three different adjustment settings were used for LAD visualization.
Results:
The study included 3,014 patients (59 years old ± 11 years old, 54% males). Age [odds ratio (OR) 0.98, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.96–0.99, P < 0.01], body mass index (BMI; OR 0.95, 95% CI 0.91–0.98, P < 0.003), rest heart rate (OR 0.98, 95% CI 0.97–0.99, P < 0.0005) and doctor’s experience (OR 2.7, 95% CI 1.57–4.53, P < 0.0003) were independent factors that influence on feasibility. The feasibility of CFVR assessment during exercise SE in the whole population by experienced doctors was 89.4%. The feasibility of CFVR assessment of LAD in obese patients performed by experienced doctors using modern echo machines and new techniques was high (86.0%).
Conclusions:
Coronary artery velocity reserve during supine exercise SE is a feasible, non-invasive available tool. The new generation echo machine and the new techniques provide a good feasibility of CFVR assessment, even in novice doctors. Despite a lower level of possibility to assess CFVR in obese patients or with a higher resting heart rate, this method is feasible in a great majority of such patients.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ec.2024.00017

Aim:
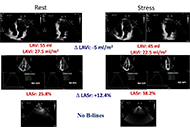
Left atrial volume index (LAVI), left atrial reservoir function through left atrial reservoir strain (LASr), and B-lines in lung ultrasound serve as supplementary indicators of left ventricular filling pressures. This study analyzes the interrelation between LAVI, LASr, and B-lines in both resting and peak vasodilator stress.
Methods:
Dipyridamole stress echocardiography (SE) was conducted on 252 individuals (180 males, 71%, age 65 years ± 10 years) with chronic coronary syndromes. LAVI was quantified using the biplane disk summation method; LASr was obtained using 2-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography; B-lines were evaluated through a simplified 4-site scan in the third intercostal space during lung ultrasound.
Results:
During SE, a reduction in LAVI (26 ml/m2 ± 14 ml/m2 vs. 24 ml/m2 ± 12 ml/m2, P < 0.001) and an increase in LASr from rest (33% ± 8% vs. 38% ± 10%, P < 0.001) were respectively observed from rest to stress. B-lines were increased significantly during SE, from 19 (7.5%) to 29 (11.5%), P < 0.001. A substantial, inverse linear correlation was identified between LAVI and LASr both at rest (r = –0.301, P < 0.001) and peak stress (r = –0.279, P < 0.001). At group analysis, peak B-lines showed a direct correlation with peak LAVI (r = 0.151, P = 0.017) and an inverse correlation with peak LASr (r = –0.234, P < 0.001). In individual assessments, 9.7% (20/207) of patients displayed stress B-lines with normal LAVI and preserved LASr, while 20% (9/45) exhibited stress B-lines with abnormalities in both LAVI and LASr.
Conclusions:
Vasodilator SE with combined left atrial and volume assessment, related to pulmonary congestion, is feasible with a high success rate. Pulmonary congestion is more frequent with dilated left atrium with reduced atrial contractile reserve (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT030.49995; NCT050.81115).
Aim:
Left atrial volume index (LAVI), left atrial reservoir function through left atrial reservoir strain (LASr), and B-lines in lung ultrasound serve as supplementary indicators of left ventricular filling pressures. This study analyzes the interrelation between LAVI, LASr, and B-lines in both resting and peak vasodilator stress.
Methods:
Dipyridamole stress echocardiography (SE) was conducted on 252 individuals (180 males, 71%, age 65 years ± 10 years) with chronic coronary syndromes. LAVI was quantified using the biplane disk summation method; LASr was obtained using 2-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography; B-lines were evaluated through a simplified 4-site scan in the third intercostal space during lung ultrasound.
Results:
During SE, a reduction in LAVI (26 ml/m2 ± 14 ml/m2 vs. 24 ml/m2 ± 12 ml/m2, P < 0.001) and an increase in LASr from rest (33% ± 8% vs. 38% ± 10%, P < 0.001) were respectively observed from rest to stress. B-lines were increased significantly during SE, from 19 (7.5%) to 29 (11.5%), P < 0.001. A substantial, inverse linear correlation was identified between LAVI and LASr both at rest (r = –0.301, P < 0.001) and peak stress (r = –0.279, P < 0.001). At group analysis, peak B-lines showed a direct correlation with peak LAVI (r = 0.151, P = 0.017) and an inverse correlation with peak LASr (r = –0.234, P < 0.001). In individual assessments, 9.7% (20/207) of patients displayed stress B-lines with normal LAVI and preserved LASr, while 20% (9/45) exhibited stress B-lines with abnormalities in both LAVI and LASr.
Conclusions:
Vasodilator SE with combined left atrial and volume assessment, related to pulmonary congestion, is feasible with a high success rate. Pulmonary congestion is more frequent with dilated left atrium with reduced atrial contractile reserve (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT030.49995; NCT050.81115).
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ec.2024.00018

Myocardial bridging is a congenital defect characterized by the course of a segment of the coronary arteries within the heart muscle most frequently affecting the left anterior descending coronary artery (LAD). Patients with myocardial bridging may present with episodes of exertional anginal chest pain. The gold standard for non-invasive diagnosis of myocardial bridge is coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA), which allows anatomical characterization. Coronary flow velocity reserve (CFVR) of the LAD on stress echocardiography (SE) can play an important role in the diagnosis of myocardial bridging of the LAD; a relationship between CVFR-LAD and coronary inflammation by estimating the attenuation of peri-coronary adipose tissue at CCTA has been demonstrated in patients without obstructive ischaemic heart disease. Therefore, coronary inflammation localized to the LAD has been assessed in patients diagnosed with myocardial bridging of the LAD and previous SE with CFVR-LAD in a case series.
Myocardial bridging is a congenital defect characterized by the course of a segment of the coronary arteries within the heart muscle most frequently affecting the left anterior descending coronary artery (LAD). Patients with myocardial bridging may present with episodes of exertional anginal chest pain. The gold standard for non-invasive diagnosis of myocardial bridge is coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA), which allows anatomical characterization. Coronary flow velocity reserve (CFVR) of the LAD on stress echocardiography (SE) can play an important role in the diagnosis of myocardial bridging of the LAD; a relationship between CVFR-LAD and coronary inflammation by estimating the attenuation of peri-coronary adipose tissue at CCTA has been demonstrated in patients without obstructive ischaemic heart disease. Therefore, coronary inflammation localized to the LAD has been assessed in patients diagnosed with myocardial bridging of the LAD and previous SE with CFVR-LAD in a case series.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ec.2024.00019