Open Access
Review
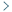
AS1411-functionalized delivery nanosystems for targeted cancer therapy
Pooria Safarzadeh Kozani ... Mohammad Tariq Malik
Published: April 30, 2021 Explor Med. 2021;2:146–166
This article belongs to the special issue Nanomedicine and Cancer Immunotherapy
Open Access
Review
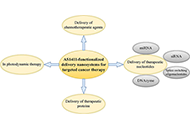
Nanomedicine in cancer therapy: promises and hurdles of polymeric nanoparticles
Carmen Paus ... Alessandra Cambi
Published: April 30, 2021 Explor Med. 2021;2:167–185
This article belongs to the special issue Nanomedicine and Cancer Immunotherapy
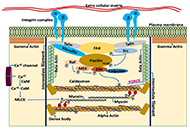
Open Access
Perspective
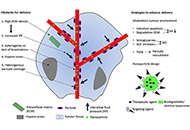
Vascular aging, the vascular cytoskeleton and aortic stiffness
Lova Prasadareddy Kajuluri ... Kathleen G Morgan
Published: June 30, 2021 Explor Med. 2021;2:186–197
This article belongs to the special issue Exploring Aortic Disease
Open Access
Review
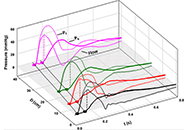
Wave propagation and reflection in the aorta and implications of the aortic Windkessel
John V. Tyberg
Published: June 30, 2021 Explor Med. 2021;2:198–207
This article belongs to the special issue Exploring Aortic Disease
Open Access
Review
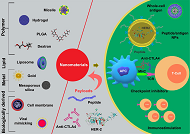
Emerging nanomaterials for cancer immunotherapy
Sureshbabu Ram Kumar Pandian ... Krishnan Sundar
Published: June 30, 2021 Explor Med. 2021;2:208–231
This article belongs to the special issue Nanomedicine and Cancer Immunotherapy

Open Access
Original Article
Neuropsychological test validation of speech markers of cognitive impairment in the Framingham Cognitive Aging Cohort
Larry Zhang ... Reza Hosseini Ghomi
Published: June 30, 2021 Explor Med. 2021;2:232–252
This article belongs to the special issue Digital Biomarkers: The New Frontier for Medicine and Research
Open Access
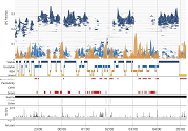
Original Article
Digital sleep measures and white matter health in the Framingham Heart Study
Robert Joseph Thomas ... Rhoda Au
Published: June 30, 2021 Explor Med. 2021;2:253–267
This article belongs to the special issue Digital Biomarkers: The New Frontier for Medicine and Research
Open Access
Review
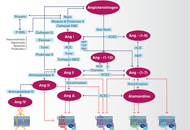
Angiotensin-(1-7) and Mas receptor in the brain
Natalia L. Rukavina Mikusic ... Mariela M. Gironacci
Published: June 30, 2021 Explor Med. 2021;2:268–293
This article belongs to the special issue Angiotensins—A Century of Progress
Open Access
Review
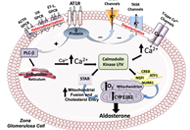
Angiotensin peptides in the regulation of adrenal cortical function
Gian Paolo Rossi ... Teresa Maria Seccia
Published: June 30, 2021 Explor Med. 2021;2:294–304
This article belongs to the special issue Angiotensins—A Century of Progress
Open Access
Commentary
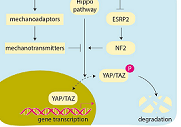
An engineered mayhem: YAP/TAZ mechanosignaling and hepatocarcinogenesis in NAFLD
Gyorgy Baffy
Published: August 31, 2021 Explor Med. 2021;2:305–310
This article belongs to the special issue Exploring Chronic Liver Disease
Open Access
Review
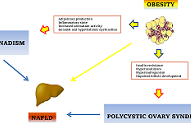
Sex hormones abnormalities in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: pathophysiological and clinical implications
Angelo Di Vincenzo ... Marco Rossato
Published: August 31, 2021 Explor Med. 2021;2:311–323
This article belongs to the special issue Exploring NAFLD/NASH
Open Access
Case Report
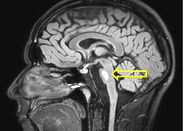
Central pontine myelinolysis secondary to glycemic variability in type 1 diabetes: a case report and a systematic review of the literature
Stefania Di Agostino ... Mauro Maurantonio
Published: August 31, 2021 Explor Med. 2021;2:324–332
Open Access
Review
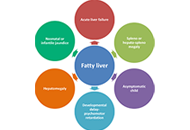
Pediatric vs. adult NAFLD to MAFLD transition: a welcome but tangled path
Angelo Colucci ... Claudia Mandato
Published: August 31, 2021 Explor Med. 2021;2:333–342
This article belongs to the special issue Exploring NAFLD/NASH
Open Access
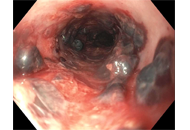
Case Report
Submucosal esophageal hematomas in a critically ill patient on anticoagulation
Hassam Ali, Maliha Naseer
Published: August 31, 2021 Explor Med. 2021;2:343–347
Open Access
Review
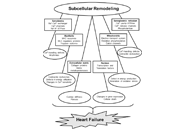
Role of angiotensin II in the development of subcellular remodeling in heart failure
Sukhwinder K. Bhullar ... Naranjan S. Dhalla
Published: August 31, 2021 Explor Med. 2021;2:352–371
This article belongs to the special issue Angiotensins—A Century of Progress

Open Access
Original Article
High prevalence of false positive SARS-CoV2 serology in a cohort of patients with liver autoimmune diseases
Maria Giulia Cornacchia ... Gaetano Serviddio
Published: August 31, 2021 Explor Med. 2021;2:372–377
This article belongs to the special issue Exploring Chronic Liver Disease

Open Access
Perspective
Why the aortic dissection detection risk score is problematic in emergency departments
Anne-Maree Kelly
Published: August 31, 2021 Explor Med. 2021;2:348–351
This article belongs to the special issue Exploring Aortic Disease
Open Access
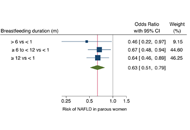
Commentary
Breastfeeding duration and reduced risk of NAFLD in midlife of parous women
Alessandro Mantovani ... Andrea Dalbeni
Published: October 31, 2021 Explor Med. 2021;2:378–381
This article belongs to the special issue Exploring Chronic Liver Disease
Open Access
Original Article
Objective measurement of sleep by smartphone application: comparison with actigraphy and relation to self-reported sleep
Taylor Maynard ... Sandy Neargarder
Published: October 31, 2021 Explor Med. 2021;2:382–391
This article belongs to the special issue Digital Biomarkers: The New Frontier for Medicine and Research

Open Access
Review
Exploring evidence-based innovative therapy for the treatment of chronic HBV infection: experimental and clinical
Sheikh Mohammad Fazle Akbar ... Yoichi Hiasa
Published: October 31, 2021 Explor Med. 2021;2:392–409
This article belongs to the special issue Exploring Chronic Liver Disease