






For more than a decade now, research studies, proof of concept work, and clinical trials have endeavored to understand how mesenchymal stem cells might be used to help protect, repair, and/or regenerate damaged brain tissue following stroke. To date, the majority of studies have not demonstrated significant improvements in either morbidity or medium-long-term outcome, although safety has been relatively well proven. Limitations are likely to be linked to the pathobiological complexity and seriousness of stroke tissue damage, low efficacy of treatment, and short half-life of bio-active proteins released by stem cells. This article will highlight the heterogeneity and limitation of completed studies and the current status of ongoing work. At the same time, the potential of other combinational type treatments, such as drug-loading and targeting, and the use of hydrogels is discussed.
For more than a decade now, research studies, proof of concept work, and clinical trials have endeavored to understand how mesenchymal stem cells might be used to help protect, repair, and/or regenerate damaged brain tissue following stroke. To date, the majority of studies have not demonstrated significant improvements in either morbidity or medium-long-term outcome, although safety has been relatively well proven. Limitations are likely to be linked to the pathobiological complexity and seriousness of stroke tissue damage, low efficacy of treatment, and short half-life of bio-active proteins released by stem cells. This article will highlight the heterogeneity and limitation of completed studies and the current status of ongoing work. At the same time, the potential of other combinational type treatments, such as drug-loading and targeting, and the use of hydrogels is discussed.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/en.2023.00015

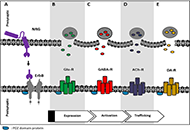
Globally, the incidence of Parkinson’s disease (PD) is increasing faster than other neurodegenerative disorders. Neuropathologically, PD is characterized by the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta due to the accumulation of aggregates of misfolded α-synuclein (α-Syn) in the cytoplasm of these neurons, forming Lewy bodies. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are associated with the spread of α-Syn to different brain areas. However, at the same time that these EVs contribute to the pathophysiology of PD, they can also be explored as therapeutic, serving as a vehicle to deliver specific molecules, since these vesicles can easily cross the blood-brain barrier. Thus, this review summarizes the recent progress in EVs as a therapeutic strategy for PD, focusing on their delivery to the brain, and discusses the potential challenges and future directions in this field.
Globally, the incidence of Parkinson’s disease (PD) is increasing faster than other neurodegenerative disorders. Neuropathologically, PD is characterized by the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta due to the accumulation of aggregates of misfolded α-synuclein (α-Syn) in the cytoplasm of these neurons, forming Lewy bodies. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are associated with the spread of α-Syn to different brain areas. However, at the same time that these EVs contribute to the pathophysiology of PD, they can also be explored as therapeutic, serving as a vehicle to deliver specific molecules, since these vesicles can easily cross the blood-brain barrier. Thus, this review summarizes the recent progress in EVs as a therapeutic strategy for PD, focusing on their delivery to the brain, and discusses the potential challenges and future directions in this field.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/en.2023.00016

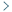
Earth’s rotation generates the basic circadian rhythm of day and night to which all living organisms must adapt to survive. In mammals, this happens thanks to a central clock located in the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) of the hypothalamus and to peripheral clock genes at the cellular level. The main environmental cue capable of synchronizing such clocks is light sensed by retinal ganglion cells signaling through a complex nervous pathway to the pineal gland which ultimately regulates melatonin synthesis that occurs during the night, darkness hours in all mammals. The central clock synchronized by melatonin drives the circadian oscillation of the sympathetic nervous system (SNS) adrenergic activity which in turn controls glucocorticoid production in the adrenal glands. These oscillations are integrated with peripheral cellular clocks by still not completely understood mechanisms and drive the homeostatic control of activity-rest (sleep) cycles, cardiovascular activity, body temperature, and immune-hematopoietic functions. The neuronal and hormonal mechanisms governing the circadian oscillation of hematopoiesis and immunity will be addressed in this review focusing on those offering therapeutic perspectives.
Earth’s rotation generates the basic circadian rhythm of day and night to which all living organisms must adapt to survive. In mammals, this happens thanks to a central clock located in the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) of the hypothalamus and to peripheral clock genes at the cellular level. The main environmental cue capable of synchronizing such clocks is light sensed by retinal ganglion cells signaling through a complex nervous pathway to the pineal gland which ultimately regulates melatonin synthesis that occurs during the night, darkness hours in all mammals. The central clock synchronized by melatonin drives the circadian oscillation of the sympathetic nervous system (SNS) adrenergic activity which in turn controls glucocorticoid production in the adrenal glands. These oscillations are integrated with peripheral cellular clocks by still not completely understood mechanisms and drive the homeostatic control of activity-rest (sleep) cycles, cardiovascular activity, body temperature, and immune-hematopoietic functions. The neuronal and hormonal mechanisms governing the circadian oscillation of hematopoiesis and immunity will be addressed in this review focusing on those offering therapeutic perspectives.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/en.2023.00017
This article belongs to the special issue Circadian Rhythm and Melatonin

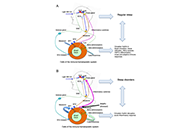
The gut microbiota and dysbiosis have been implicated in various metabolic diseases and gastrointestinal disorders. Recently, there has been growing evidence suggesting the influence of gut microbiota on neurological disorders, including autism. Although the number of children diagnosed with autism is increasing, the exact cause of the disease remains unknown. Numerous factors, such as genetics, environment, and diet, appear to contribute to its onset. Nevertheless, a degree of general consensus exists regarding the notion that the disease’s progression likely demands the participation of multiple factors. Among the potential causes, the role of the microbiota is particularly intriguing. The gut and brain have extensive connections, with a significant number of neuronal cells in the gut, and autism is often associated with gastrointestinal issues. In this review, the most recent information available on autism and microbiota has been analyzed. Findings of this study indicate that: (1) the microbiota is clearly altered in individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD); (2) microbiota transplantation appears to be effective in reducing the severity of autism symptoms; (3) while the microbiota is not solely responsible for the onset of autism, it likely plays a significant role. Considering all the available information, it is suggested that modifying the gut microbiota may have a positive impact on individuals with autism. This opens up possibilities for the use of pre- or probiotics in the treatment of children with ASD, as well as the potential use of fecal microbiota transfer.
The gut microbiota and dysbiosis have been implicated in various metabolic diseases and gastrointestinal disorders. Recently, there has been growing evidence suggesting the influence of gut microbiota on neurological disorders, including autism. Although the number of children diagnosed with autism is increasing, the exact cause of the disease remains unknown. Numerous factors, such as genetics, environment, and diet, appear to contribute to its onset. Nevertheless, a degree of general consensus exists regarding the notion that the disease’s progression likely demands the participation of multiple factors. Among the potential causes, the role of the microbiota is particularly intriguing. The gut and brain have extensive connections, with a significant number of neuronal cells in the gut, and autism is often associated with gastrointestinal issues. In this review, the most recent information available on autism and microbiota has been analyzed. Findings of this study indicate that: (1) the microbiota is clearly altered in individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD); (2) microbiota transplantation appears to be effective in reducing the severity of autism symptoms; (3) while the microbiota is not solely responsible for the onset of autism, it likely plays a significant role. Considering all the available information, it is suggested that modifying the gut microbiota may have a positive impact on individuals with autism. This opens up possibilities for the use of pre- or probiotics in the treatment of children with ASD, as well as the potential use of fecal microbiota transfer.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/en.2023.00018

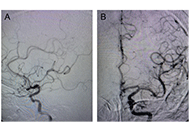
Several bare metals, self-expanding stents have been approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to treat carotid stenosis, but no covered stents have been particularly examined or approved for carotid or cerebrovascular applications. Nonetheless, there are a number of potentially useful applications for covered stents in the brachiocephalic, carotid, and even intracranial arteries. As with currently accepted applications for bare metal carotid stents, the use of covered stents in carotid arteries has been reserved for patients who are at high risk for complications with open surgical management of their specific problem. The present case report emphasizes the safety and efficacy of covered stent in complex carotid artery reconstruction entailing stenosis and aneurysmal dilatation and through light on its impact on minimizing the risk of ischemic complications associated with endovascular or surgical carotid sacrifice.
Several bare metals, self-expanding stents have been approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to treat carotid stenosis, but no covered stents have been particularly examined or approved for carotid or cerebrovascular applications. Nonetheless, there are a number of potentially useful applications for covered stents in the brachiocephalic, carotid, and even intracranial arteries. As with currently accepted applications for bare metal carotid stents, the use of covered stents in carotid arteries has been reserved for patients who are at high risk for complications with open surgical management of their specific problem. The present case report emphasizes the safety and efficacy of covered stent in complex carotid artery reconstruction entailing stenosis and aneurysmal dilatation and through light on its impact on minimizing the risk of ischemic complications associated with endovascular or surgical carotid sacrifice.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/en.2023.00019

Over the past decade, knowledge of the pathophysiology and immunology of multiple sclerosis (MS) and depression, and the complex links to vitamin D (VitD) balance, has increased rapidly. Both diseases are characterized by an imbalance of proinflammatory and antiinflammatory cytokines, increased serum neurofilament light chains (sNfLs), disruption of the blood-brain barrier (BBB), abolition of the physiological function of the various types of microglia (MG), decreased calcidiol-serum levels, and disorders of the gut microbiome in combination with hyperactivity of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA)-axis/microbiome-gut-brain-axis characterized. In depression, stress initiates cellular and molecular changes in the brain via increased cortisol release in the HPA-axis. Microglial activation and neuronal damage as well as dysregulation of neuroplastic and neurotrophic factors complete the spectrum of pathological damage. It is shown that gut dysbiosis leads to increased gut permeability, which favors endotoxemia and ultimately paves the way to systemic inflammation. A VitD supplementation could restore the balance of microorganisms in the intestine and reduce the inflammatory processes at various levels. VitD promotes regulatory T cell (Treg) proliferation, inhibits the expression of T helper 1 (Th1) cells and Th17 immune cells, and inhibits proinflammatory interleukin-17 (IL-17). 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 [1,25(OH)2D3] reduces also the secretion of interferon-γ (IFN-γ) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α). Increased calcitriol levels lead to a reduction in MG activation, oxidative stress, and lower BBB permeability. An early, permanent, daily sufficient VitD supplementation as an add-on therapy under control of the serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D [s25(OH)D] levels is an essential therapeutic tool to slow down the disability caused by MS and thereby primarily prevent or reduce the stress and subsequently the manifestation of depression. Through the future continuous measurement of the biomarkers serum neurofilament ligth chains and glial fibrillary acidic proteins as well as the s25(OH)D level in MS and comorbidity depression, future therapy successes or failures can be avoided.
Over the past decade, knowledge of the pathophysiology and immunology of multiple sclerosis (MS) and depression, and the complex links to vitamin D (VitD) balance, has increased rapidly. Both diseases are characterized by an imbalance of proinflammatory and antiinflammatory cytokines, increased serum neurofilament light chains (sNfLs), disruption of the blood-brain barrier (BBB), abolition of the physiological function of the various types of microglia (MG), decreased calcidiol-serum levels, and disorders of the gut microbiome in combination with hyperactivity of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA)-axis/microbiome-gut-brain-axis characterized. In depression, stress initiates cellular and molecular changes in the brain via increased cortisol release in the HPA-axis. Microglial activation and neuronal damage as well as dysregulation of neuroplastic and neurotrophic factors complete the spectrum of pathological damage. It is shown that gut dysbiosis leads to increased gut permeability, which favors endotoxemia and ultimately paves the way to systemic inflammation. A VitD supplementation could restore the balance of microorganisms in the intestine and reduce the inflammatory processes at various levels. VitD promotes regulatory T cell (Treg) proliferation, inhibits the expression of T helper 1 (Th1) cells and Th17 immune cells, and inhibits proinflammatory interleukin-17 (IL-17). 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 [1,25(OH)2D3] reduces also the secretion of interferon-γ (IFN-γ) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α). Increased calcitriol levels lead to a reduction in MG activation, oxidative stress, and lower BBB permeability. An early, permanent, daily sufficient VitD supplementation as an add-on therapy under control of the serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D [s25(OH)D] levels is an essential therapeutic tool to slow down the disability caused by MS and thereby primarily prevent or reduce the stress and subsequently the manifestation of depression. Through the future continuous measurement of the biomarkers serum neurofilament ligth chains and glial fibrillary acidic proteins as well as the s25(OH)D level in MS and comorbidity depression, future therapy successes or failures can be avoided.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/en.2023.00020
This article belongs to the special issue Novel Therapeutic Approaches for the Treatment of Depression

Brain development, a complex process, consisting of several phases, starting as early as two weeks after conception, and continuing through childhood till early adolescence, is crucial for the development of properly functioning body systems, behavioral traits, and neurocognitive abilities. Infancy and childhood are recognized as important periods for initial brain formation, however in later stages of life, such as childhood and adulthood, experiences, together with environmental exposures, can still influence brain physiology. The developing brain is particularly susceptible to epigenetic changes with many factors being proposed as modifiers by directly impacting DNA methylation as well as histone and chromatin modifications within genes implicated in development. These factors include: maternal stress and diet, exposure to pollutants, sleep quality, as well as dietary habits. Evidence indicates exposures to environmental threats can lead to inappropriate neurological, metabolic, and endocrine functioning often mediated by epigenetic mechanisms with symptoms manifesting themselves as early as childhood or in later stages of life. Therefore, the main aim of this review is to evaluate the current studies focused on negative environmental exposures and their consequences on the developing brain directed by epigenetic mechanisms.
Brain development, a complex process, consisting of several phases, starting as early as two weeks after conception, and continuing through childhood till early adolescence, is crucial for the development of properly functioning body systems, behavioral traits, and neurocognitive abilities. Infancy and childhood are recognized as important periods for initial brain formation, however in later stages of life, such as childhood and adulthood, experiences, together with environmental exposures, can still influence brain physiology. The developing brain is particularly susceptible to epigenetic changes with many factors being proposed as modifiers by directly impacting DNA methylation as well as histone and chromatin modifications within genes implicated in development. These factors include: maternal stress and diet, exposure to pollutants, sleep quality, as well as dietary habits. Evidence indicates exposures to environmental threats can lead to inappropriate neurological, metabolic, and endocrine functioning often mediated by epigenetic mechanisms with symptoms manifesting themselves as early as childhood or in later stages of life. Therefore, the main aim of this review is to evaluate the current studies focused on negative environmental exposures and their consequences on the developing brain directed by epigenetic mechanisms.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/en.2023.00021

Life is the highest form of adaptation to the environment which is based on energy metabolism. To maintain life, the neuromuscular system must constantly interact with the environment. The striatal muscles are the main energy consumer and their access to energy fuel is mainly limited by the brain’s needs. In the state of wakefulness, the brain must continuously process streams of sensory signals and respond to them with motor actions. At the same time, the brain to be efficient must memorize the sensory-movement relationships. Brain memory networking requires additional energy allocation, and due to limited systemic energy resources, the processes of memorization are completed during the sleep phase when the inactive muscular system allows allocating the energy fuel to the brain functions such as memory trace formation and the removal of the activity-dependent waste products. Both physiological processes can be completed during sleep only, and consequently, chronic sleep disorder leads to pathological changes in brain functioning and escalation of neurodegenerative processes. Consequently, sleep disorders become the main cause of dementia which is the prodrome of Alzheimer’s disease.
Life is the highest form of adaptation to the environment which is based on energy metabolism. To maintain life, the neuromuscular system must constantly interact with the environment. The striatal muscles are the main energy consumer and their access to energy fuel is mainly limited by the brain’s needs. In the state of wakefulness, the brain must continuously process streams of sensory signals and respond to them with motor actions. At the same time, the brain to be efficient must memorize the sensory-movement relationships. Brain memory networking requires additional energy allocation, and due to limited systemic energy resources, the processes of memorization are completed during the sleep phase when the inactive muscular system allows allocating the energy fuel to the brain functions such as memory trace formation and the removal of the activity-dependent waste products. Both physiological processes can be completed during sleep only, and consequently, chronic sleep disorder leads to pathological changes in brain functioning and escalation of neurodegenerative processes. Consequently, sleep disorders become the main cause of dementia which is the prodrome of Alzheimer’s disease.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/en.2023.00022
This article belongs to the special issue Alzheimer’s Disease

As the average lifespan has increased, memory disorders have become a more pressing public health concern. However, dementia in the elderly population is often neglected in light of other health priorities. Therefore, expanding the knowledge surrounding the pathology of dementia will allow more informed decision-making regarding treatment within elderly and older adult populations. An important emerging avenue in dementia research is understanding the vascular contributors to dementia. This review summarizes potential causes of vascular cognitive impairment like stroke, microinfarction, hypertension, atherosclerosis, blood-brain barrier dysfunction, and cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Also, this review address treatments that target these vascular impairments that also show promising results in reducing patient’s risk for and experience of dementia.
As the average lifespan has increased, memory disorders have become a more pressing public health concern. However, dementia in the elderly population is often neglected in light of other health priorities. Therefore, expanding the knowledge surrounding the pathology of dementia will allow more informed decision-making regarding treatment within elderly and older adult populations. An important emerging avenue in dementia research is understanding the vascular contributors to dementia. This review summarizes potential causes of vascular cognitive impairment like stroke, microinfarction, hypertension, atherosclerosis, blood-brain barrier dysfunction, and cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Also, this review address treatments that target these vascular impairments that also show promising results in reducing patient’s risk for and experience of dementia.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/en.2023.00023

Aim:
Apolipoprotein E (ApoE) isoforms, especially the ApoE4 isoform, are genetic risk factors for Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Moreover, the APOE ε4 haplotype has a dose-dependent association with an increased risk of amyloid-related imaging abnormalities (ARIA) in individuals receiving disease-modifying therapy for AD. Therefore, the importance of APOE genotyping or proteotyping has been highlighted. Here, the authors developed fully automated chemiluminescence enzyme-immunoassay kit for ApoE4 and Pan-ApoE, and evaluated their diagnostic concordance with the APOE genotyping.
Methods:
One hundred seventy-eight specimens were analyzed using the Lumipulse® G ApoE4 and Pan-ApoE for the ApoE proteotype and evaluated its diagnostic concordance with the APOE genotype.
Results:
The ApoE4 kit specifically detected the ApoE4 concentration in plasma samples, and the polymorphism could be classified clearly by the ratio of ApoE4 and Pan-ApoE amount in plasma.
Conclusions:
The combination of Pan-ApoE and ApoE4-specific chemiluminescent enzyme immunoassay (CLEIA) assay is useful for predicting APOE ε4 allele status.
Aim:
Apolipoprotein E (ApoE) isoforms, especially the ApoE4 isoform, are genetic risk factors for Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Moreover, the APOE ε4 haplotype has a dose-dependent association with an increased risk of amyloid-related imaging abnormalities (ARIA) in individuals receiving disease-modifying therapy for AD. Therefore, the importance of APOE genotyping or proteotyping has been highlighted. Here, the authors developed fully automated chemiluminescence enzyme-immunoassay kit for ApoE4 and Pan-ApoE, and evaluated their diagnostic concordance with the APOE genotyping.
Methods:
One hundred seventy-eight specimens were analyzed using the Lumipulse® G ApoE4 and Pan-ApoE for the ApoE proteotype and evaluated its diagnostic concordance with the APOE genotype.
Results:
The ApoE4 kit specifically detected the ApoE4 concentration in plasma samples, and the polymorphism could be classified clearly by the ratio of ApoE4 and Pan-ApoE amount in plasma.
Conclusions:
The combination of Pan-ApoE and ApoE4-specific chemiluminescent enzyme immunoassay (CLEIA) assay is useful for predicting APOE ε4 allele status.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/en.2023.00024
This article belongs to the special issue Alzheimer's Disease

DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/en.2022.00001

All living organisms exhibit circadian rhythms. Humans show circadian rhythm of the different physiological functions such as sleep-wake cycle, core body temperature, feeding behavior, metabolic activity, heart rate variability, hormone secretion, and others. The hypothalamic suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) acts as a primary circadian pacemaker. Peripheral tissues have an endogenous circadian clock; however, SCN synchronizes the circadian activity of the peripheral clocks. The retinohypothalamic tract (RHT) from retinal ganglionic cells carries the photic signal into the SCN that regulates the rhythmic expression of the core clock genes through the feedback loop. At the output level, the SCN connects with the pineal gland and the peripheral tissues with the help of neuroendocrine mediators. Disruption of circadian clock functions is detrimental to health. Shift work, night work, chronic or acute jet lag, and light-at-night have adverse effects on circadian functions. Misalignment of circadian rhythm alters the expression of core clock genes, leading to deregulation of cellular activity and metabolic functions. Circadian rhythm dysfunction causes many pathologic conditions, including sleep disorders, cardiovascular problems, metabolic dysfunction, infertility, poor physical performance, as well as cancer. The present work has reviewed the relationship between circadian clock dysfunction and impaired physiological activities.
All living organisms exhibit circadian rhythms. Humans show circadian rhythm of the different physiological functions such as sleep-wake cycle, core body temperature, feeding behavior, metabolic activity, heart rate variability, hormone secretion, and others. The hypothalamic suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) acts as a primary circadian pacemaker. Peripheral tissues have an endogenous circadian clock; however, SCN synchronizes the circadian activity of the peripheral clocks. The retinohypothalamic tract (RHT) from retinal ganglionic cells carries the photic signal into the SCN that regulates the rhythmic expression of the core clock genes through the feedback loop. At the output level, the SCN connects with the pineal gland and the peripheral tissues with the help of neuroendocrine mediators. Disruption of circadian clock functions is detrimental to health. Shift work, night work, chronic or acute jet lag, and light-at-night have adverse effects on circadian functions. Misalignment of circadian rhythm alters the expression of core clock genes, leading to deregulation of cellular activity and metabolic functions. Circadian rhythm dysfunction causes many pathologic conditions, including sleep disorders, cardiovascular problems, metabolic dysfunction, infertility, poor physical performance, as well as cancer. The present work has reviewed the relationship between circadian clock dysfunction and impaired physiological activities.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/en.2022.00002
This article belongs to the special issue Circadian Rhythm and Melatonin

Neuregulins (NRGs) and their cognate ErbB receptors (ErbB2–ErbB4) constitute a vast group of proteins encoded by six different genes (NRG1–6) and many isoforms with critical roles in the development and functioning of the nervous system. NRGs are known to regulate important processes in the nervous system like neural development, neuronal differentiation, neurite outgrowth, and specification. These factors are involved in the regulation of neurotransmission pathways and the modulation of several forms of synaptic plasticity. Due to NRGs’ role in synaptic plasticity, defects in their normal functioning are translated into altered signaling networks, which have been linked to susceptibility to developing psychiatric disorders like schizophrenia (SZ), autism, depression, and bipolar disorders. Additionally, deviation of the NRG normal functioning is involved in neurological diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. Contrastingly, NRG/ErbB signaling is also involved in the recovery after traumatic brain injuries (e.g., ischemic stroke). The NRG/ErbB signaling complex is highly unusual because the ligands (mainly NRG1–NRG3, with their multiple isoforms) and receptors (ErbB2–ErbB4) can orchestrate vast signaling complexes, with a wide reach within the processes that govern the development and appropriate function of the nervous system. This may explain why NRGs and ErbB receptor genes have been linked to complex brain disorders, like SZ. This review, are discussed important aspects of NRG and their relevance for nervous system functioning, including 1) subcellular localization, 2) signaling pathways involved in neuronal functions, 3) effect on neurite development and synapse formation, 4) modulation of some mechanisms of synaptic plasticity [long-term potentiation (LTP), depotentiation, long-term depression (LTD)] and 5) roles of NRGs in some neurological diseases. This review intends to present a summary of the main findings about this family of proteins, which might position them as one of the master regulators of brain functioning.
Neuregulins (NRGs) and their cognate ErbB receptors (ErbB2–ErbB4) constitute a vast group of proteins encoded by six different genes (NRG1–6) and many isoforms with critical roles in the development and functioning of the nervous system. NRGs are known to regulate important processes in the nervous system like neural development, neuronal differentiation, neurite outgrowth, and specification. These factors are involved in the regulation of neurotransmission pathways and the modulation of several forms of synaptic plasticity. Due to NRGs’ role in synaptic plasticity, defects in their normal functioning are translated into altered signaling networks, which have been linked to susceptibility to developing psychiatric disorders like schizophrenia (SZ), autism, depression, and bipolar disorders. Additionally, deviation of the NRG normal functioning is involved in neurological diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. Contrastingly, NRG/ErbB signaling is also involved in the recovery after traumatic brain injuries (e.g., ischemic stroke). The NRG/ErbB signaling complex is highly unusual because the ligands (mainly NRG1–NRG3, with their multiple isoforms) and receptors (ErbB2–ErbB4) can orchestrate vast signaling complexes, with a wide reach within the processes that govern the development and appropriate function of the nervous system. This may explain why NRGs and ErbB receptor genes have been linked to complex brain disorders, like SZ. This review, are discussed important aspects of NRG and their relevance for nervous system functioning, including 1) subcellular localization, 2) signaling pathways involved in neuronal functions, 3) effect on neurite development and synapse formation, 4) modulation of some mechanisms of synaptic plasticity [long-term potentiation (LTP), depotentiation, long-term depression (LTD)] and 5) roles of NRGs in some neurological diseases. This review intends to present a summary of the main findings about this family of proteins, which might position them as one of the master regulators of brain functioning.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/en.2022.00003

This brief statement describes some recent achievements of neuropathological research, with the focus on Alzheimer’s and other age-related diseases, neurodegenerative disorders (tauopathies, synucleinopathies), multimorbidity of the aged brain, multiple sclerosis (MS), and other neuroinflammatory disorders, including central nervous system involvement by coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), as well as new developments in neurovascular diseases, neurooncology, and myopathies. Although neuropathology, using modern technologies, such as cryo-electron microscopy, proteomic and experimental methods, has helped to increase diagnostic accuracy and provided insight into the pathogenesis of many neurological disorders, future studies in co-operation with clinical and other neurosciences should overcome the challenges of disease-influencing therapeutic approaches.
This brief statement describes some recent achievements of neuropathological research, with the focus on Alzheimer’s and other age-related diseases, neurodegenerative disorders (tauopathies, synucleinopathies), multimorbidity of the aged brain, multiple sclerosis (MS), and other neuroinflammatory disorders, including central nervous system involvement by coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), as well as new developments in neurovascular diseases, neurooncology, and myopathies. Although neuropathology, using modern technologies, such as cryo-electron microscopy, proteomic and experimental methods, has helped to increase diagnostic accuracy and provided insight into the pathogenesis of many neurological disorders, future studies in co-operation with clinical and other neurosciences should overcome the challenges of disease-influencing therapeutic approaches.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/en.2022.00004

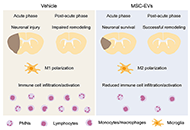
Ischemic stroke is a highly prevalent condition that frequently results in life-long disability and death. Considerable efforts have been made to establish treatments that prevent secondary ischemic damage and promote stroke recovery. Until now, the recanalization of occluded blood vessels via thrombolysis and thrombectomy, although highly potent, remains the only treatment in humans that enhances stroke outcome. Small extracellular vesicles are non-replicating, nano-sized (70–150 nm) lipid bilayer-enclosed vesicles, which have shown remarkable biological activities in various physiological and pathophysiological contexts. When administered post-stroke, mesenchymal stromal cell-derived extracellular vesicles (MSC-EVs) induce neuroprotection, promote brain remodeling and plasticity, and enhance neurological recovery in rodents and non-human primates via mechanisms that involve immunomodulation and anti-inflammation. In this review, experimental studies on the therapeutic actions of MSC-EVs in animal stroke models are summarized and perspectives for clinical translation are outlined.
Ischemic stroke is a highly prevalent condition that frequently results in life-long disability and death. Considerable efforts have been made to establish treatments that prevent secondary ischemic damage and promote stroke recovery. Until now, the recanalization of occluded blood vessels via thrombolysis and thrombectomy, although highly potent, remains the only treatment in humans that enhances stroke outcome. Small extracellular vesicles are non-replicating, nano-sized (70–150 nm) lipid bilayer-enclosed vesicles, which have shown remarkable biological activities in various physiological and pathophysiological contexts. When administered post-stroke, mesenchymal stromal cell-derived extracellular vesicles (MSC-EVs) induce neuroprotection, promote brain remodeling and plasticity, and enhance neurological recovery in rodents and non-human primates via mechanisms that involve immunomodulation and anti-inflammation. In this review, experimental studies on the therapeutic actions of MSC-EVs in animal stroke models are summarized and perspectives for clinical translation are outlined.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/en.2022.00005

The therapy of many neurological disorders has advanced markedly during recent decades. Not so for neurodegenerative disorders. Early detection, deep individual genotyping and phenotyping, and personalized therapies have been suggested as the way forward. However, we still do not know enough about the aetiology and molecular basics of these diseases. In fact, the term neurodegenerative disorder may be a misleading categorization that constitutes a major cognitive barrier against better characterization and understanding of these disorders. Therefore, we need to go back to the basics and employ novel, open-minded observational study protocols that combine very extensive and robust clinical, molecular and epidemiological data collection methods. Moreover, we need to reconsider our basic orientation towards these diseases to increase our chances of finding out what we are actually trying to care for and cure.
The therapy of many neurological disorders has advanced markedly during recent decades. Not so for neurodegenerative disorders. Early detection, deep individual genotyping and phenotyping, and personalized therapies have been suggested as the way forward. However, we still do not know enough about the aetiology and molecular basics of these diseases. In fact, the term neurodegenerative disorder may be a misleading categorization that constitutes a major cognitive barrier against better characterization and understanding of these disorders. Therefore, we need to go back to the basics and employ novel, open-minded observational study protocols that combine very extensive and robust clinical, molecular and epidemiological data collection methods. Moreover, we need to reconsider our basic orientation towards these diseases to increase our chances of finding out what we are actually trying to care for and cure.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/en.2022.00006

Stroke is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality. The advent of mechanical thrombectomy has largely improved patient outcomes. This article reviews the features and outcomes associated with aspiration, stent retrievers, and combination catheters used in current practice. There is also a discussion on clinical considerations based on anatomical features and clot composition. The reperfusion grading scale and outcome metrics commonly used following thrombectomy when a patient is still in the hospital are reviewed. Lastly, there are proposed discharge and outpatient follow-up goals in caring for patients hospitalized for a stroke.
Stroke is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality. The advent of mechanical thrombectomy has largely improved patient outcomes. This article reviews the features and outcomes associated with aspiration, stent retrievers, and combination catheters used in current practice. There is also a discussion on clinical considerations based on anatomical features and clot composition. The reperfusion grading scale and outcome metrics commonly used following thrombectomy when a patient is still in the hospital are reviewed. Lastly, there are proposed discharge and outpatient follow-up goals in caring for patients hospitalized for a stroke.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/en.2022.00007

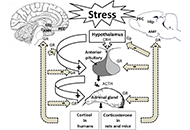
Exposure to stressful conditions plays a critical role in brain processes, including neural plasticity, synaptic transmission, and cognitive functions. Since memory-related brain regions, the hippocampus (Hip), the amygdala, and the prefrontal cortex, express high glucocorticoid receptors (GRs), these areas are the potential targets of stress hormones. Stress affects memory encoding, consolidation, and retrieval, which may depend on many factors such as the type, duration, the intensity of the stressor or the brain region. Here, this review mainly focused on the mechanisms involved in stress-induced memory impairment. Acute/chronic stress induces structural and functional changes in neurons and glial cells. Dendritic arborization, reduction of dendritic spine density, and alteration in glutamatergic-mediated synaptic transmission via N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) and α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionic acid (AMPA) receptors are mechanisms that stress affect long-term memory formation. Exposure to acute or chronic stress could interplay with multiple neurotransmitter signaling, modulating the neuronal circuits involved in memory impairment or state-dependent learning. Stress hormones also modulate the expression of microRNAs in the specific brain regions responsible for stress-induced behaviors. Because of expressing GRs in astrocytes and microglial cells, stress could affect the morphology, structure, and functions of these glial cells in memory-related brain regions. Astrocytes play a crucial role in stress-induced aversive or fear memory formation. Over-activation of the microglial cells enhances the release of inflammatory cytokines, which results in neuronal injury. Stress has a prominent role in cognitive decline to induces memory problems, particularly in older adults. Due to the issue’s importance, here the provided overview attempted to address the question of how stress alters neuronal epigenetic regulators, synaptic transmissions, and glial activity in the brain.
Exposure to stressful conditions plays a critical role in brain processes, including neural plasticity, synaptic transmission, and cognitive functions. Since memory-related brain regions, the hippocampus (Hip), the amygdala, and the prefrontal cortex, express high glucocorticoid receptors (GRs), these areas are the potential targets of stress hormones. Stress affects memory encoding, consolidation, and retrieval, which may depend on many factors such as the type, duration, the intensity of the stressor or the brain region. Here, this review mainly focused on the mechanisms involved in stress-induced memory impairment. Acute/chronic stress induces structural and functional changes in neurons and glial cells. Dendritic arborization, reduction of dendritic spine density, and alteration in glutamatergic-mediated synaptic transmission via N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) and α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionic acid (AMPA) receptors are mechanisms that stress affect long-term memory formation. Exposure to acute or chronic stress could interplay with multiple neurotransmitter signaling, modulating the neuronal circuits involved in memory impairment or state-dependent learning. Stress hormones also modulate the expression of microRNAs in the specific brain regions responsible for stress-induced behaviors. Because of expressing GRs in astrocytes and microglial cells, stress could affect the morphology, structure, and functions of these glial cells in memory-related brain regions. Astrocytes play a crucial role in stress-induced aversive or fear memory formation. Over-activation of the microglial cells enhances the release of inflammatory cytokines, which results in neuronal injury. Stress has a prominent role in cognitive decline to induces memory problems, particularly in older adults. Due to the issue’s importance, here the provided overview attempted to address the question of how stress alters neuronal epigenetic regulators, synaptic transmissions, and glial activity in the brain.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/en.2022.00008

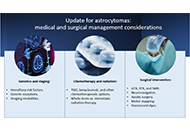
Astrocytomas include a wide range of tumors with unique mutations and varying grades of malignancy. These tumors all originate from the astrocyte, a star-shaped glial cell that plays a major role in supporting functions of the central nervous system (CNS), including blood-brain barrier (BBB) development and maintenance, water and ion regulation, influencing neuronal synaptogenesis, and stimulating the immunological response. In terms of epidemiology, glioblastoma (GB), the most common and malignant astrocytoma, generally occur with higher rates in Australia, Western Europe, and Canada, with the lowest rates in Southeast Asia. Additionally, significantly higher rates of GB are observed in males and non-Hispanic whites. It has been suggested that higher levels of testosterone observed in biological males may account for the increased rates of GB. Hereditary syndromes such as Cowden, Lynch, Turcot, Li-Fraumeni, and neurofibromatosis type 1 have been linked to increased rates of astrocytoma development. While there are a number of specific gene mutations that may influence malignancy or be targeted in astrocytoma treatment, O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (MGMT) gene function is an important predictor of astrocytoma response to chemotherapeutic agent temozolomide (TMZ). TMZ for primary and bevacizumab in the setting of recurrent tumor formation are two of the main chemotherapeutic agents currently approved in the treatment of astrocytomas. While stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) has debatable implications for increased survival in comparison to whole-brain radiotherapy (WBRT), SRS demonstrates increased precision with reduced radiation toxicity. When considering surgical resection of astrocytoma, the extent of resection (EoR) is taken into consideration. Subtotal resection (STR) spares the margins of the T1 enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) region, gross total resection (GTR) includes the margins, and supramaximal resection (SMR) extends beyond the margin of the T1 and into the T2 region. Surgical resection, radiation, and chemotherapy are integral components of astrocytoma treatment.
Hereditary risk factors, genetic mutations, and imaging modalities are discussed in reference to astrocytoma staging and mechanism of growth. In terms of the treatment of astrocytomas, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and strategic surgical interventions are discussed
Astrocytomas include a wide range of tumors with unique mutations and varying grades of malignancy. These tumors all originate from the astrocyte, a star-shaped glial cell that plays a major role in supporting functions of the central nervous system (CNS), including blood-brain barrier (BBB) development and maintenance, water and ion regulation, influencing neuronal synaptogenesis, and stimulating the immunological response. In terms of epidemiology, glioblastoma (GB), the most common and malignant astrocytoma, generally occur with higher rates in Australia, Western Europe, and Canada, with the lowest rates in Southeast Asia. Additionally, significantly higher rates of GB are observed in males and non-Hispanic whites. It has been suggested that higher levels of testosterone observed in biological males may account for the increased rates of GB. Hereditary syndromes such as Cowden, Lynch, Turcot, Li-Fraumeni, and neurofibromatosis type 1 have been linked to increased rates of astrocytoma development. While there are a number of specific gene mutations that may influence malignancy or be targeted in astrocytoma treatment, O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (MGMT) gene function is an important predictor of astrocytoma response to chemotherapeutic agent temozolomide (TMZ). TMZ for primary and bevacizumab in the setting of recurrent tumor formation are two of the main chemotherapeutic agents currently approved in the treatment of astrocytomas. While stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) has debatable implications for increased survival in comparison to whole-brain radiotherapy (WBRT), SRS demonstrates increased precision with reduced radiation toxicity. When considering surgical resection of astrocytoma, the extent of resection (EoR) is taken into consideration. Subtotal resection (STR) spares the margins of the T1 enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) region, gross total resection (GTR) includes the margins, and supramaximal resection (SMR) extends beyond the margin of the T1 and into the T2 region. Surgical resection, radiation, and chemotherapy are integral components of astrocytoma treatment.
Hereditary risk factors, genetic mutations, and imaging modalities are discussed in reference to astrocytoma staging and mechanism of growth. In terms of the treatment of astrocytomas, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and strategic surgical interventions are discussed
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/en.2023.00009

Aim:
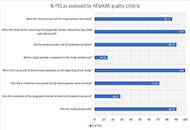
Stroke is one of the leading causes of death and disability worldwide. Plasma biomarkers have long been used to evaluate physiological or pathological processes and to make predictions about the outcome of stroke patients. The current systematic review is focused on genetic plasma biomarkers as a new potential prognostic indicator for post-stroke recovery. The aim of the present systematic review is to assess the potential of genetic plasma biomarkers associated with stroke to predict post-stroke recovery.
Methods:
The search strategy used PubMed and Web of Science databases to identified 166 studies that investigated genetic plasma biomarkers in patients with stroke between 2017 and 2021. However, only 21 of them met the inclusion criteria.
Results:
The identified genetic biomarkers can be divided into: (i) serum/plasma circular RNA (circRNA) associated with stroke onset or recurrence (5; 23.80%), (ii) genetic polymorphisms associated with the atherosclerotic process and stroke recurrence (6; 28.57%), (iii) serum/plasma long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) levels involved in immunity/inflammatory processes (4; 19.04%), (iv) marker of DNA methylation associated with stroke onset and outcome (3; 14.28%), and (v) proteins and pathways of stroke identified by serum/ plasma proteomics/genomics analysis (3; 14.28%).
Conclusions:
Overall, more than 100 potential biomarkers were found and the data suggest that combinations of plasma genetic biomarkers might be used as a better predictor for stroke.
Aim:
Stroke is one of the leading causes of death and disability worldwide. Plasma biomarkers have long been used to evaluate physiological or pathological processes and to make predictions about the outcome of stroke patients. The current systematic review is focused on genetic plasma biomarkers as a new potential prognostic indicator for post-stroke recovery. The aim of the present systematic review is to assess the potential of genetic plasma biomarkers associated with stroke to predict post-stroke recovery.
Methods:
The search strategy used PubMed and Web of Science databases to identified 166 studies that investigated genetic plasma biomarkers in patients with stroke between 2017 and 2021. However, only 21 of them met the inclusion criteria.
Results:
The identified genetic biomarkers can be divided into: (i) serum/plasma circular RNA (circRNA) associated with stroke onset or recurrence (5; 23.80%), (ii) genetic polymorphisms associated with the atherosclerotic process and stroke recurrence (6; 28.57%), (iii) serum/plasma long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) levels involved in immunity/inflammatory processes (4; 19.04%), (iv) marker of DNA methylation associated with stroke onset and outcome (3; 14.28%), and (v) proteins and pathways of stroke identified by serum/ plasma proteomics/genomics analysis (3; 14.28%).
Conclusions:
Overall, more than 100 potential biomarkers were found and the data suggest that combinations of plasma genetic biomarkers might be used as a better predictor for stroke.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/en.2023.00010
This article belongs to the special issue Cerebral Ischemia, Genetics, Comorbidities, Risk Factors and New Therapeutic Options for Neurorestoration