-
78 results in Exploration of Asthma & AllergySort byMost Cited
 Impact of the standardization unit’s definition on the in vitro biological potency of allergen extractsOpen AccessLetter to the EditorIn Europe, allergen products from different manufacturers can be labeled using the same unit with yet different definitions of that unit, which may cause confusion, as is the case for the index of r [...] Read more.Thierry Batard ... Laurent MascarellPublished: August 27, 2023 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2023;1:107–114
Impact of the standardization unit’s definition on the in vitro biological potency of allergen extractsOpen AccessLetter to the EditorIn Europe, allergen products from different manufacturers can be labeled using the same unit with yet different definitions of that unit, which may cause confusion, as is the case for the index of r [...] Read more.Thierry Batard ... Laurent MascarellPublished: August 27, 2023 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2023;1:107–114
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eaa.2023.00012 Catching your breath: unraveling the intricate connection between panic disorder and asthmaOpen AccessReviewRespiratory changes are often associated with anxiety disorders, particularly panic disorder (PD). Individuals experiencing PD are subjected to unexpected panic attacks, marked by overwhelming anxie [...] Read more.Graziella Chiara PrezzaventoPublished: April 08, 2024 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2024;2:97–110
Catching your breath: unraveling the intricate connection between panic disorder and asthmaOpen AccessReviewRespiratory changes are often associated with anxiety disorders, particularly panic disorder (PD). Individuals experiencing PD are subjected to unexpected panic attacks, marked by overwhelming anxie [...] Read more.Graziella Chiara PrezzaventoPublished: April 08, 2024 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2024;2:97–110
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eaa.2024.00032
This article belongs to the special issue Asthma and its Relationship with Psychological and Psychopathological Factors Management of asthma using probioticsOpen AccessReviewAsthma is one of the most common respiratory diseases in humans throughout the world. The illness continues to be the most prevalent cause of respiratory morbidity and affects both adults and childr [...] Read more.Amar P. Garg ... Bajeerao PatilPublished: February 20, 2024 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2024;2:9–32
Management of asthma using probioticsOpen AccessReviewAsthma is one of the most common respiratory diseases in humans throughout the world. The illness continues to be the most prevalent cause of respiratory morbidity and affects both adults and childr [...] Read more.Amar P. Garg ... Bajeerao PatilPublished: February 20, 2024 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2024;2:9–32
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eaa.2024.00026
This article belongs to the special issue Asthma and its Relationship with Psychological and Psychopathological Factors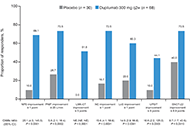 Dupilumab improved objective and patient-reported outcomes in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps and complete nasal obstructionOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The impact of complete bilateral nasal obstruction [nasal polyp score (NPS) = 8/8] on treatment outcomes in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP) is unclear. This post hoc analys [...] Read more.Martin Wagenmann ... Juby A. Jacob-NaraPublished: July 30, 2024 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2024;2:363–372
Dupilumab improved objective and patient-reported outcomes in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps and complete nasal obstructionOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The impact of complete bilateral nasal obstruction [nasal polyp score (NPS) = 8/8] on treatment outcomes in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP) is unclear. This post hoc analys [...] Read more.Martin Wagenmann ... Juby A. Jacob-NaraPublished: July 30, 2024 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2024;2:363–372
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eaa.2024.00051
This article belongs to the special issue Update on Chronic RhinoSinusitis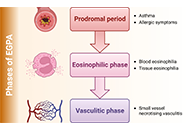 New therapeutic approaches with biological drugs for eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitisOpen AccessReviewEosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA) is a multiorganic syndrome that affects the cardiovascular, neurologic, renal, and gastrointestinal systems with an incidence ranging from 0 case [...] Read more.Alejandra Carrón-Herrero ... Giovanni PaolettiPublished: June 08, 2023 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2023;1:31–48
New therapeutic approaches with biological drugs for eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitisOpen AccessReviewEosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA) is a multiorganic syndrome that affects the cardiovascular, neurologic, renal, and gastrointestinal systems with an incidence ranging from 0 case [...] Read more.Alejandra Carrón-Herrero ... Giovanni PaolettiPublished: June 08, 2023 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2023;1:31–48
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eaa.2023.00006
This article belongs to the special issue The Era of Biologics in Allergy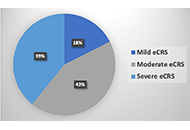 Assessing chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps severity by “Japanese epidemiological survey of refractory eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis” algorithmOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP) is a complex disease with different subtypes that affect patients’ quality of life. This study aim to evaluate the severity of CRSwNP and [...] Read more.Sérgio Duarte Dortas ... Solange Oliveira Rodrigues VallePublished: June 16, 2023 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2023;1:49–54
Assessing chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps severity by “Japanese epidemiological survey of refractory eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis” algorithmOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP) is a complex disease with different subtypes that affect patients’ quality of life. This study aim to evaluate the severity of CRSwNP and [...] Read more.Sérgio Duarte Dortas ... Solange Oliveira Rodrigues VallePublished: June 16, 2023 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2023;1:49–54
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eaa.2023.00007
This article belongs to the special issue Precision Medicine in Allergy and Rhinology Eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders: new perspectives and the emerging role of biological therapiesOpen AccessReviewThe advent of biological drugs has opened up new therapeutic possibilities in the field of eosinophilic gastro-intestinal diseases (EGIDs). EGIDs are chronic inflammatory diseases of the gastrointes [...] Read more.Francesca Losa, Arianna CingolaniPublished: June 30, 2023 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2023;1:60–72
Eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders: new perspectives and the emerging role of biological therapiesOpen AccessReviewThe advent of biological drugs has opened up new therapeutic possibilities in the field of eosinophilic gastro-intestinal diseases (EGIDs). EGIDs are chronic inflammatory diseases of the gastrointes [...] Read more.Francesca Losa, Arianna CingolaniPublished: June 30, 2023 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2023;1:60–72
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eaa.2023.00009
This article belongs to the special issue The Era of Biologics in Allergy Small airway dysfunction and obesity in asthmatic patients: a dangerous liaison?Open AccessReviewAsthma is a chronic condition characterized by inflammation throughout the entire bronchial airways. Recent findings suggest that ventilation inhomogeneity and small airway dysfunction (SAD) play a [...] Read more.Jack Pepys ... Marcello CottiniPublished: August 15, 2023 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2023;1:73–88
Small airway dysfunction and obesity in asthmatic patients: a dangerous liaison?Open AccessReviewAsthma is a chronic condition characterized by inflammation throughout the entire bronchial airways. Recent findings suggest that ventilation inhomogeneity and small airway dysfunction (SAD) play a [...] Read more.Jack Pepys ... Marcello CottiniPublished: August 15, 2023 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2023;1:73–88
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eaa.2023.00010 Evaluation of ongoing mepolizumab treatment in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polypsOpen AccessReviewChronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP) is a multifactorial inflammatory disease of the mucous membranes of the nose and paranasal sinuses. Eosinophilic inflammation is described as a comm [...] Read more.Ludger Klimek ... Claus BachertPublished: February 22, 2024 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2024;2:33–48
Evaluation of ongoing mepolizumab treatment in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polypsOpen AccessReviewChronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP) is a multifactorial inflammatory disease of the mucous membranes of the nose and paranasal sinuses. Eosinophilic inflammation is described as a comm [...] Read more.Ludger Klimek ... Claus BachertPublished: February 22, 2024 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2024;2:33–48
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eaa.2024.00027
This article belongs to the special issue Update on Chronic RhinoSinusitis Predictive value of skin testing with excipients for COVID-19 vaccinesOpen AccessReviewCoronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) was declared a global pandemic by the World Health Organization (WHO) in March 2020. Despite the availability of therapies and the adoption of security measures, [...] Read more.Fabio Viggiani ... Eustachio NettisPublished: February 27, 2024 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2024;2:49–64
Predictive value of skin testing with excipients for COVID-19 vaccinesOpen AccessReviewCoronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) was declared a global pandemic by the World Health Organization (WHO) in March 2020. Despite the availability of therapies and the adoption of security measures, [...] Read more.Fabio Viggiani ... Eustachio NettisPublished: February 27, 2024 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2024;2:49–64
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eaa.2024.00028 Allergen-specific immunotherapy for allergic asthma: What’s new?Open AccessMini ReviewAllergen-specific immunotherapy for inhalant allergies, using allergen extracts of proven value, is highly effective in selected patients with allergic rhinoconjunctivitis and allergic asthma. Both [...] Read more.Chiara Asperti ... Stephen R. DurhamPublished: February 29, 2024 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2024;2:76–84
Allergen-specific immunotherapy for allergic asthma: What’s new?Open AccessMini ReviewAllergen-specific immunotherapy for inhalant allergies, using allergen extracts of proven value, is highly effective in selected patients with allergic rhinoconjunctivitis and allergic asthma. Both [...] Read more.Chiara Asperti ... Stephen R. DurhamPublished: February 29, 2024 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2024;2:76–84
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eaa.2024.00030
This article belongs to the special issue Precision Medicine in Allergy and Rhinology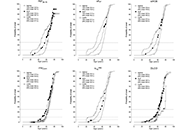 Small airway disease assessed by parameters of small airway dysfunction in patients with asthma, asthma-chronic obstructive pulmonary disease-overlap, and chronic obstructive pulmonary diseaseOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: There is an increasing interest in defining the role of small airway disease (SAD) in asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and asthma with coexisting COPD. Based on the spec [...] Read more.Richard Kraemer, Heinrich MatthysPublished: April 02, 2024 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2024;2:85–96
Small airway disease assessed by parameters of small airway dysfunction in patients with asthma, asthma-chronic obstructive pulmonary disease-overlap, and chronic obstructive pulmonary diseaseOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: There is an increasing interest in defining the role of small airway disease (SAD) in asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and asthma with coexisting COPD. Based on the spec [...] Read more.Richard Kraemer, Heinrich MatthysPublished: April 02, 2024 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2024;2:85–96
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eaa.2024.00031 Renewing the Australian asthma agenda: lessons from the Finnish 10-year Asthma ProgramOpen AccessReviewThe Finnish Asthma Program, which ran between 1994 and 2004, has long been heralded as a benchmark of success in how to improve management and reduce asthma-related health service utilization. In Au [...] Read more.Kristin Carson-Chahhoud ... Tari HaahtelaPublished: May 20, 2024 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2024;2:161–169
Renewing the Australian asthma agenda: lessons from the Finnish 10-year Asthma ProgramOpen AccessReviewThe Finnish Asthma Program, which ran between 1994 and 2004, has long been heralded as a benchmark of success in how to improve management and reduce asthma-related health service utilization. In Au [...] Read more.Kristin Carson-Chahhoud ... Tari HaahtelaPublished: May 20, 2024 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2024;2:161–169
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eaa.2024.00037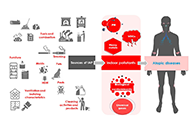 Indoor air pollution and atopic diseases: a comprehensive frameworkOpen AccessReviewIndoor air pollution (IAP) is an important cause of concern for human health, leading to millions of deaths worldwide each year. Since people spend most of their time indoor the quality of the air i [...] Read more.Erminia Ridolo ... Francesca NicolettaPublished: May 31, 2024 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2024;2:170–185
Indoor air pollution and atopic diseases: a comprehensive frameworkOpen AccessReviewIndoor air pollution (IAP) is an important cause of concern for human health, leading to millions of deaths worldwide each year. Since people spend most of their time indoor the quality of the air i [...] Read more.Erminia Ridolo ... Francesca NicolettaPublished: May 31, 2024 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2024;2:170–185
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eaa.2024.00038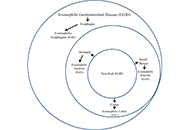 Eosinophilic gastrointestinal diseases: current perspectives on pathogenesis and managementOpen AccessReviewEosinophilic gastrointestinal diseases (EGIDs) are a group of chronic conditions, characterized by an excessive accumulation of eosinophils in various areas of the mucosal of the gastrointestinal (G [...] Read more.Georgia Papaiakovou ... Nikoletta RovinaPublished: June 07, 2024 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2024;2:205–218
Eosinophilic gastrointestinal diseases: current perspectives on pathogenesis and managementOpen AccessReviewEosinophilic gastrointestinal diseases (EGIDs) are a group of chronic conditions, characterized by an excessive accumulation of eosinophils in various areas of the mucosal of the gastrointestinal (G [...] Read more.Georgia Papaiakovou ... Nikoletta RovinaPublished: June 07, 2024 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2024;2:205–218
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eaa.2024.00041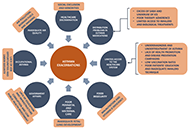 How to implement the anti-inflammatory reliever treatment proposed by the Global Initiative for Asthma in low- and middle-income countriesOpen AccessReviewThere are no plausible arguments to consider that the best evidence-based asthma treatment should be different in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs). A few decades ago, the recognition of asth [...] Read more.Carlos A. Torres-Duque ... Abraham Alí-MunivePublished: June 12, 2024 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2024;2:219–232
How to implement the anti-inflammatory reliever treatment proposed by the Global Initiative for Asthma in low- and middle-income countriesOpen AccessReviewThere are no plausible arguments to consider that the best evidence-based asthma treatment should be different in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs). A few decades ago, the recognition of asth [...] Read more.Carlos A. Torres-Duque ... Abraham Alí-MunivePublished: June 12, 2024 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2024;2:219–232
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eaa.2024.00042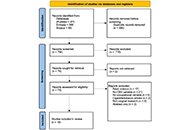 The impact of occupational exposures on chronic rhinosinusitis: a scoping reviewOpen AccessReviewChronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) is a prevalent and burdensome condition worldwide, characterized by inflammation of the paranasal sinuses. Ideally, instead of treating CRS, we would identify ways to pr [...] Read more.Aurelia S. Monk ... Adam J. KimplePublished: July 19, 2024 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2024;2:301–318
The impact of occupational exposures on chronic rhinosinusitis: a scoping reviewOpen AccessReviewChronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) is a prevalent and burdensome condition worldwide, characterized by inflammation of the paranasal sinuses. Ideally, instead of treating CRS, we would identify ways to pr [...] Read more.Aurelia S. Monk ... Adam J. KimplePublished: July 19, 2024 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2024;2:301–318
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eaa.2024.00046
This article belongs to the special issue Environment, Infectious Diseases, and Allergy Impulse oscillometry for the evaluation and management of pediatric asthmaOpen AccessReviewAsthma is the most common chronic disease during childhood. While most of characteristic structural changes in asthma have been identified in the large airways, there is a growing recognition of per [...] Read more.Pasquale Comberiati ... Diego PeroniPublished: December 19, 2023 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2023;1:219–229
Impulse oscillometry for the evaluation and management of pediatric asthmaOpen AccessReviewAsthma is the most common chronic disease during childhood. While most of characteristic structural changes in asthma have been identified in the large airways, there is a growing recognition of per [...] Read more.Pasquale Comberiati ... Diego PeroniPublished: December 19, 2023 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2023;1:219–229
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eaa.2023.00022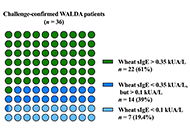 Omega-5-gliadin-specific immunoglobulin E-positive, but wheat-specific immunoglobulin E-negative wheat allergy dependent on augmentation factors—a frequent presentationOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Most patients with wheat allergy dependent on augmentation factors (WALDA) show specific immunoglobulin E (sIgE) to ω5-gliadin. However, some WALDA patients may show negative results when t [...] Read more.Valentina Faihs ... Knut BrockowPublished: December 28, 2023 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2023;1:230–238
Omega-5-gliadin-specific immunoglobulin E-positive, but wheat-specific immunoglobulin E-negative wheat allergy dependent on augmentation factors—a frequent presentationOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Most patients with wheat allergy dependent on augmentation factors (WALDA) show specific immunoglobulin E (sIgE) to ω5-gliadin. However, some WALDA patients may show negative results when t [...] Read more.Valentina Faihs ... Knut BrockowPublished: December 28, 2023 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2023;1:230–238
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eaa.2023.00023
This article belongs to the special issue The Different Faces of Food Allergy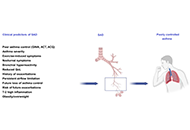 Small airway dysfunction and impulse oscillometry in adult patients with asthma: recent findingsOpen AccessMini ReviewAsthma is a respiratory disease affecting more than 300 million people around the world. Airflow obstruction and inflammation due to asthma usually involve large airways, but recently small airway i [...] Read more.Marcello Cottini ... Alvise BertiPublished: October 31, 2023 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2023;1:163–173
Small airway dysfunction and impulse oscillometry in adult patients with asthma: recent findingsOpen AccessMini ReviewAsthma is a respiratory disease affecting more than 300 million people around the world. Airflow obstruction and inflammation due to asthma usually involve large airways, but recently small airway i [...] Read more.Marcello Cottini ... Alvise BertiPublished: October 31, 2023 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2023;1:163–173
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eaa.2023.00017 -