-
35 results in Exploration of BioMat-XSort byMost Cited
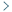
 Navigating regulatory challenges in molecularly tailored nanomedicineOpen AccessCommentaryNanomedicine, a convergence of nanotechnology and medical sciences, has unleashed transformative potential in healthcare. However, harnessing the benefits of nanomedicine requires a thorough underst [...] Read more.Ajay Vikram Singh ... Paolo ZamboniPublished: April 25, 2024 Explor BioMat-X. 2024;1:124–134
Navigating regulatory challenges in molecularly tailored nanomedicineOpen AccessCommentaryNanomedicine, a convergence of nanotechnology and medical sciences, has unleashed transformative potential in healthcare. However, harnessing the benefits of nanomedicine requires a thorough underst [...] Read more.Ajay Vikram Singh ... Paolo ZamboniPublished: April 25, 2024 Explor BioMat-X. 2024;1:124–134
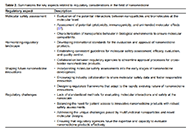
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ebmx.2024.00009 Unlocking the potential of circulating small extracellular vesicles in neurodegenerative disease through targeted biomarkers and advancements in biosensingOpen AccessReviewNeurodegenerative diseases (NDDs) gradually affect neurons impacting both their function and structure, and they afflict millions worldwide. Detecting these conditions before symptoms arise is cruci [...] Read more.Saqer Al Abdullah ... Kristen DellingerPublished: April 24, 2024 Explor BioMat-X. 2024;1:100–123
Unlocking the potential of circulating small extracellular vesicles in neurodegenerative disease through targeted biomarkers and advancements in biosensingOpen AccessReviewNeurodegenerative diseases (NDDs) gradually affect neurons impacting both their function and structure, and they afflict millions worldwide. Detecting these conditions before symptoms arise is cruci [...] Read more.Saqer Al Abdullah ... Kristen DellingerPublished: April 24, 2024 Explor BioMat-X. 2024;1:100–123
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ebmx.2024.00008 Exploration of biomaterials: a multidisciplinary ventureOpen AccessEditorialMaryam TabrizianPublished: January 01, 2024 Explor BioMat-X. 2024;1:1–4
Exploration of biomaterials: a multidisciplinary ventureOpen AccessEditorialMaryam TabrizianPublished: January 01, 2024 Explor BioMat-X. 2024;1:1–4
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ebmx.2023.00001 Fabrication and characterization of pHEMA hydrogel conduit containing GelMA-HaMA IPN for peripheral nerve regenerationOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Small defects after any injury to the periperal nerves results in self-regeneration. However, for larger defects, suturing or grafting are necessary, which may have limitations. Thus, resear [...] Read more.Damla Arslantunali Sahin ... Vasif HasirciPublished: February 26, 2024 Explor BioMat-X. 2024;1:34–57
Fabrication and characterization of pHEMA hydrogel conduit containing GelMA-HaMA IPN for peripheral nerve regenerationOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Small defects after any injury to the periperal nerves results in self-regeneration. However, for larger defects, suturing or grafting are necessary, which may have limitations. Thus, resear [...] Read more.Damla Arslantunali Sahin ... Vasif HasirciPublished: February 26, 2024 Explor BioMat-X. 2024;1:34–57
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ebmx.2024.00005
This article belongs to the special issue Nature-Based Biomaterials for Biomedical Applications A biomimetic approach to modulating the sustained release of fibroblast growth factor 2 from fibrin microthread scaffoldsOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The pleiotropic effect of fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2) on promoting myogenesis, angiogenesis, and innervation makes it an ideal growth factor for treating volumetric muscle loss (VML) i [...] Read more.Meagan E. Carnes ... George D. PinsPublished: April 23, 2024 Explor BioMat-X. 2024;1:58–83
A biomimetic approach to modulating the sustained release of fibroblast growth factor 2 from fibrin microthread scaffoldsOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The pleiotropic effect of fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2) on promoting myogenesis, angiogenesis, and innervation makes it an ideal growth factor for treating volumetric muscle loss (VML) i [...] Read more.Meagan E. Carnes ... George D. PinsPublished: April 23, 2024 Explor BioMat-X. 2024;1:58–83
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ebmx.2024.00006 Effects of cold plasma treatment on the biological performances of decellularized bovine pericardium extracellular matrix-based films for biomedical applicationsOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Since decades, decellularized extracellular matrix (dECM)-derived materials have received worldwide attention as promising biomaterials for tissue engineering and biomedical applications. So [...] Read more.Maria Elena Lombardo ... Diego MantovaniPublished: April 23, 2024 Explor BioMat-X. 2024;1:84–99
Effects of cold plasma treatment on the biological performances of decellularized bovine pericardium extracellular matrix-based films for biomedical applicationsOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Since decades, decellularized extracellular matrix (dECM)-derived materials have received worldwide attention as promising biomaterials for tissue engineering and biomedical applications. So [...] Read more.Maria Elena Lombardo ... Diego MantovaniPublished: April 23, 2024 Explor BioMat-X. 2024;1:84–99
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ebmx.2024.00007 Bio-materials for intramedullary pin application in canine femur: a comparative analysisOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: In this study, the finite elements analysis (FEA) was performed on an intramedullary (IM) pin to be used in the canine femur. The 03 different biomaterials [17-4-precipitated hardened (PH)-s [...] Read more.Minhaz Husain ... J. P. DavimPublished: June 27, 2024 Explor BioMat-X. 2024;1:178–189
Bio-materials for intramedullary pin application in canine femur: a comparative analysisOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: In this study, the finite elements analysis (FEA) was performed on an intramedullary (IM) pin to be used in the canine femur. The 03 different biomaterials [17-4-precipitated hardened (PH)-s [...] Read more.Minhaz Husain ... J. P. DavimPublished: June 27, 2024 Explor BioMat-X. 2024;1:178–189
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ebmx.2024.00013
This article belongs to the special issue Metal 3D Printing of Biometals for Prostheses and Implants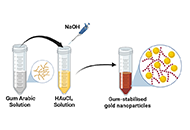 Gum Arabic-assisted green synthesis of gold nanoparticles as fluorescence modulator for potential analytical applicationsOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: To demonstrate a simple, eco-friendly, and cost-effective green method to synthesize gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) using the aqueous extract of gum Arabic (GA) as a reducing and stabilizing age [...] Read more.Ahmed T. Algahiny ... Fryad Z. HenariPublished: July 28, 2024 Explor BioMat-X. 2024;1:190–201
Gum Arabic-assisted green synthesis of gold nanoparticles as fluorescence modulator for potential analytical applicationsOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: To demonstrate a simple, eco-friendly, and cost-effective green method to synthesize gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) using the aqueous extract of gum Arabic (GA) as a reducing and stabilizing age [...] Read more.Ahmed T. Algahiny ... Fryad Z. HenariPublished: July 28, 2024 Explor BioMat-X. 2024;1:190–201
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ebmx.2024.00014
This article belongs to the special issue Green Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications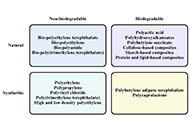 A review of biopolymer innovations in oculoplastic surgery: reconstruction of eyelid, lacrimal, and orbital structuresOpen AccessReviewThe fusion of biomaterial science with clinical practice in oculoplastic and orbital surgery, particularly in the reconstruction of the posterior lamella of the eyelid, the lacrimal system, orbital [...] Read more.Merve Kulbay ... Patrick DaiglePublished: November 28, 2024 Explor BioMat-X. 2024;1:300–330
A review of biopolymer innovations in oculoplastic surgery: reconstruction of eyelid, lacrimal, and orbital structuresOpen AccessReviewThe fusion of biomaterial science with clinical practice in oculoplastic and orbital surgery, particularly in the reconstruction of the posterior lamella of the eyelid, the lacrimal system, orbital [...] Read more.Merve Kulbay ... Patrick DaiglePublished: November 28, 2024 Explor BioMat-X. 2024;1:300–330
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ebmx.2024.00022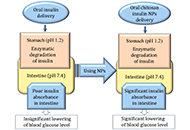 Nanomaterials in the treatment of degenerative intellectual and developmental disabilitiesOpen AccessReviewNanoparticles (NPs) are at the forefront as they are providing unprecedented solutions to obstacles and issues in treating neurodegenerative diseases. Due to their size, surface characteristics, and [...] Read more.Humaira Aslam ... Misbah Ullah KhanPublished: December 13, 2024 Explor BioMat-X. 2024;1:353–365
Nanomaterials in the treatment of degenerative intellectual and developmental disabilitiesOpen AccessReviewNanoparticles (NPs) are at the forefront as they are providing unprecedented solutions to obstacles and issues in treating neurodegenerative diseases. Due to their size, surface characteristics, and [...] Read more.Humaira Aslam ... Misbah Ullah KhanPublished: December 13, 2024 Explor BioMat-X. 2024;1:353–365
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ebmx.2024.00024 Nanoparticle-functionalized acrylic bone cement for local therapeutic delivery to spine metastasesOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Polymethylmethacrylate bone cement is often used to reconstruct critical-sized defects generated by the surgical resection of spinal metastases. Residual tumor cells after a resection can dr [...] Read more.Ateeque Siddique ... Derek H. RosenzweigPublished: April 28, 2024 Explor BioMat-X. 2024;1:135–157
Nanoparticle-functionalized acrylic bone cement for local therapeutic delivery to spine metastasesOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Polymethylmethacrylate bone cement is often used to reconstruct critical-sized defects generated by the surgical resection of spinal metastases. Residual tumor cells after a resection can dr [...] Read more.Ateeque Siddique ... Derek H. RosenzweigPublished: April 28, 2024 Explor BioMat-X. 2024;1:135–157
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ebmx.2024.00010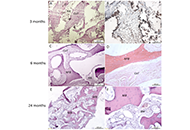 Tissue engineering approach to the creation of grafting material for rhinoplasty: clinical case reportsOpen AccessCase ReportThe use of autologous cartilage and bone grafts remains the gold standard in augmentation rhinoplasty performed to reconstruct of the nasal dorsum. Meanwhile, limited number of available sources, do [...] Read more.Vladimir Karpiuk ... Olga PonkinaPublished: June 03, 2024 Explor BioMat-X. 2024;1:158–173
Tissue engineering approach to the creation of grafting material for rhinoplasty: clinical case reportsOpen AccessCase ReportThe use of autologous cartilage and bone grafts remains the gold standard in augmentation rhinoplasty performed to reconstruct of the nasal dorsum. Meanwhile, limited number of available sources, do [...] Read more.Vladimir Karpiuk ... Olga PonkinaPublished: June 03, 2024 Explor BioMat-X. 2024;1:158–173
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ebmx.2024.00011
This article belongs to the special issue Bioinspired Material for Regenerative Medicine Biomaterials in dentistry: the analogue/digital transitionOpen AccessEditorialLuca FiorilloPublished: June 04, 2024 Explor BioMat-X. 2024;1:174–177
Biomaterials in dentistry: the analogue/digital transitionOpen AccessEditorialLuca FiorilloPublished: June 04, 2024 Explor BioMat-X. 2024;1:174–177
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ebmx.2024.00012
This article belongs to the special issue Innovations in Biomaterials for Dentistry and Oral Surgery Interaction of Pseudomonas aeruginosa with surface-modified silica studied by ultra-high frequency acoustic wave biosensorOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: This study aimed to examine the amount of surface non-specific adsorption, or fouling, observed by Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa) on a quartz crystal based acoustic wave biosensor un [...] Read more.Brian De La Franier, Michael ThompsonPublished: January 01, 2024 Explor BioMat-X. 2024;1:5–13
Interaction of Pseudomonas aeruginosa with surface-modified silica studied by ultra-high frequency acoustic wave biosensorOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: This study aimed to examine the amount of surface non-specific adsorption, or fouling, observed by Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa) on a quartz crystal based acoustic wave biosensor un [...] Read more.Brian De La Franier, Michael ThompsonPublished: January 01, 2024 Explor BioMat-X. 2024;1:5–13
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ebmx.2023.00002 Fabrication of anthracite-derived multicolor graphene quantum dots for their potential application in nanomedicineOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: This study aims to discover an alternative precursor with abundant source and low cost for multicolor graphene quantum dots (GQDs) preparation and application. Methods: In the current [...] Read more.Hongyu Pan ... Kai YuPublished: January 01, 2024 Explor BioMat-X. 2024;1:14–22
Fabrication of anthracite-derived multicolor graphene quantum dots for their potential application in nanomedicineOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: This study aims to discover an alternative precursor with abundant source and low cost for multicolor graphene quantum dots (GQDs) preparation and application. Methods: In the current [...] Read more.Hongyu Pan ... Kai YuPublished: January 01, 2024 Explor BioMat-X. 2024;1:14–22
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ebmx.2023.00003 Journey of medical device development from the bench to the bedside—four real-life examples of commercial biomaterials developmentOpen AccessReviewTranslating biomaterials research into clinical products is a multidisciplinary yet rewarding journey. It should primarily aim to improve patient treatment and clinical outcomes by addressing unmet [...] Read more.Yves Bayon ... Didier LetourneurPublished: January 16, 2024 Explor BioMat-X. 2024;1:23–33
Journey of medical device development from the bench to the bedside—four real-life examples of commercial biomaterials developmentOpen AccessReviewTranslating biomaterials research into clinical products is a multidisciplinary yet rewarding journey. It should primarily aim to improve patient treatment and clinical outcomes by addressing unmet [...] Read more.Yves Bayon ... Didier LetourneurPublished: January 16, 2024 Explor BioMat-X. 2024;1:23–33
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ebmx.2024.00004 Advances in bone tissue engineering using biomaterial based scaffolds, purine crosslinking and Wnt signalingOpen AccessReviewThe design of effective treatments for critical size bone defects, which result from various conditions such as trauma, infection, injury, or tumor resection, presents a significant challenge in cli [...] Read more.Celine J. Agnes ... Maryam TabrizianPublished: February 14, 2025 Explor BioMat-X. 2025;2:101327
Advances in bone tissue engineering using biomaterial based scaffolds, purine crosslinking and Wnt signalingOpen AccessReviewThe design of effective treatments for critical size bone defects, which result from various conditions such as trauma, infection, injury, or tumor resection, presents a significant challenge in cli [...] Read more.Celine J. Agnes ... Maryam TabrizianPublished: February 14, 2025 Explor BioMat-X. 2025;2:101327
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ebmx.2025.101327 Silver nanoparticles biosynthesized from Stenocereus queretaroensis with antiproliferative activityOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: This work aimed to evaluate the antiproliferative activity of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) biosynthesized with aqueous extract of Stenocereus queretaroensis peel (SAgNPs) in pancreatic ducta [...] Read more.Ariadna Abigail Villarreal-Amézquita ... Eduardo Padilla-CamberosPublished: February 16, 2025 Explor BioMat-X. 2025;2:101328
Silver nanoparticles biosynthesized from Stenocereus queretaroensis with antiproliferative activityOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: This work aimed to evaluate the antiproliferative activity of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) biosynthesized with aqueous extract of Stenocereus queretaroensis peel (SAgNPs) in pancreatic ducta [...] Read more.Ariadna Abigail Villarreal-Amézquita ... Eduardo Padilla-CamberosPublished: February 16, 2025 Explor BioMat-X. 2025;2:101328
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ebmx.2025.101328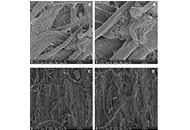 Antifungal effect against wilting disease factor Verticillium dahliae Kleb. by green synthesized silver nanoparticlesOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: This study aimed to synthesize, characterize, and evaluate the antifungal efficacy of green-synthesized silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) against Verticillium dahliae Kleb., a soil-borne fungal p [...] Read more.Alp Cokislerel ... Lale Yildiz AktasPublished: February 18, 2025 Explor BioMat-X. 2025;2:101329
Antifungal effect against wilting disease factor Verticillium dahliae Kleb. by green synthesized silver nanoparticlesOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: This study aimed to synthesize, characterize, and evaluate the antifungal efficacy of green-synthesized silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) against Verticillium dahliae Kleb., a soil-borne fungal p [...] Read more.Alp Cokislerel ... Lale Yildiz AktasPublished: February 18, 2025 Explor BioMat-X. 2025;2:101329
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ebmx.2025.101329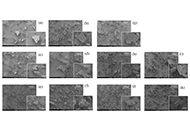 Preparation and characterization of stearyl glycyrrhetinate/cyclodextrin complex using co-grindingOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: In this study, the physicochemical properties of stearyl glycyrrhetinate/β-cyclodextrin (SG/βCD) and SG/γCD complexes were characterized, and the complexes were prepared using the co-milling [...] Read more.Momoko Ebisawa ... Yutaka InouePublished: February 26, 2025 Explor BioMat-X. 2025;2:101330
Preparation and characterization of stearyl glycyrrhetinate/cyclodextrin complex using co-grindingOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: In this study, the physicochemical properties of stearyl glycyrrhetinate/β-cyclodextrin (SG/βCD) and SG/γCD complexes were characterized, and the complexes were prepared using the co-milling [...] Read more.Momoko Ebisawa ... Yutaka InouePublished: February 26, 2025 Explor BioMat-X. 2025;2:101330
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ebmx.2025.101330
This article belongs to the special issue Nature-Based Biomaterials for Biomedical Applications -