Anti-cancer γδ T lymphocytes: contradictory past and promising future
Recent anti-cancer strategies are based on the stimulation of anti-tumor immune reaction, exploiting distinct lymphocyte subsets. Among them, γδ T cells represent optimal anti-cancer candidates, especially in those tissues where
[...] Read more.
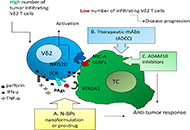
Recent anti-cancer strategies are based on the stimulation of anti-tumor immune reaction, exploiting distinct lymphocyte subsets. Among them, γδ T cells represent optimal anti-cancer candidates, especially in those tissues where they are highly localized, such as the respiratory or gastrointestinal tract. One important challenge has been the identification of stimulating drugs able to induce and maintain γδ T cell-mediated anti-cancer immune response. Amino-bisphosphonates (N-BPs) have been largely employed in anti-cancer clinical trials due to their ability to upregulate the accumulation of pyrophosphates that promote the activation of Vγ9Vδ2 T cells. This activation depends on the butyrophilin A family, which is crucial in contributing to Vγ9Vδ2 T cells stimulation but is not equally expressed in all cancer tissues. Thus, the clinical outcome of such treatments is still a challenge. In this viewpoint, a critical picture of γδ T cells as effective anti-cancer effectors is designed, with a specific focus on the best immune-stimulating therapeutic schemes involving this lymphocyte subset and the tools available to measure their efficacy and presence in tumor tissues. Some pre-clinical models, useful to measure γδ T cell anti-cancer potential and their response to stimulating drugs, therapeutic monoclonal antibodies, or bispecific antibodies are described. Computerized imaging and digital pathology are also proposed as a help in the identification of co-stimulatory molecules and localization of γδ T cell effectors. Finally, two types of novel drug preparation are proposed: nanoparticles loaded with N-BPs and pro-drug formulations that enhance the effectiveness of γδ T lymphocyte stimulation.
Alessandro Poggi, Maria Raffaella Zocchi
View:1707
Download:35
Times Cited: 0
Recent anti-cancer strategies are based on the stimulation of anti-tumor immune reaction, exploiting distinct lymphocyte subsets. Among them, γδ T cells represent optimal anti-cancer candidates, especially in those tissues where they are highly localized, such as the respiratory or gastrointestinal tract. One important challenge has been the identification of stimulating drugs able to induce and maintain γδ T cell-mediated anti-cancer immune response. Amino-bisphosphonates (N-BPs) have been largely employed in anti-cancer clinical trials due to their ability to upregulate the accumulation of pyrophosphates that promote the activation of Vγ9Vδ2 T cells. This activation depends on the butyrophilin A family, which is crucial in contributing to Vγ9Vδ2 T cells stimulation but is not equally expressed in all cancer tissues. Thus, the clinical outcome of such treatments is still a challenge. In this viewpoint, a critical picture of γδ T cells as effective anti-cancer effectors is designed, with a specific focus on the best immune-stimulating therapeutic schemes involving this lymphocyte subset and the tools available to measure their efficacy and presence in tumor tissues. Some pre-clinical models, useful to measure γδ T cell anti-cancer potential and their response to stimulating drugs, therapeutic monoclonal antibodies, or bispecific antibodies are described. Computerized imaging and digital pathology are also proposed as a help in the identification of co-stimulatory molecules and localization of γδ T cell effectors. Finally, two types of novel drug preparation are proposed: nanoparticles loaded with N-BPs and pro-drug formulations that enhance the effectiveness of γδ T lymphocyte stimulation.
 Anti-cancer γδ T lymphocytes: contradictory past and promising futureOpen AccessPerspectiveRecent anti-cancer strategies are based on the stimulation of anti-tumor immune reaction, exploiting distinct lymphocyte subsets. Among them, γδ T cells represent optimal anti-cancer candidates, especially in those tissues where [...] Read more.Alessandro Poggi, Maria Raffaella ZocchiPublished: April 28, 2022 Explor Immunol. 2022;2:220–228
Anti-cancer γδ T lymphocytes: contradictory past and promising futureOpen AccessPerspectiveRecent anti-cancer strategies are based on the stimulation of anti-tumor immune reaction, exploiting distinct lymphocyte subsets. Among them, γδ T cells represent optimal anti-cancer candidates, especially in those tissues where [...] Read more.Alessandro Poggi, Maria Raffaella ZocchiPublished: April 28, 2022 Explor Immunol. 2022;2:220–228 A proposed new paradigm for an anti-AIDS tolerogenic vaccineOpen AccessReviewUntil now, despite 30 years of intensive work, the RV144 human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) vaccine trial initiated in 2003 remains so far the most protective vaccine prototype of all those tested ( [...] Read more.Christine JacometPublished: April 24, 2022 Explor Immunol. 2022;2:211–219
A proposed new paradigm for an anti-AIDS tolerogenic vaccineOpen AccessReviewUntil now, despite 30 years of intensive work, the RV144 human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) vaccine trial initiated in 2003 remains so far the most protective vaccine prototype of all those tested ( [...] Read more.Christine JacometPublished: April 24, 2022 Explor Immunol. 2022;2:211–219 Thymosin alpha 1 therapy alleviates organ dysfunction of sepsis patients: a retrospective cohort studyOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Thymosin alpha 1 (Tα1) is a promising treatment for the improvement of sepsis patients. Until now, its function in reducing acute organ damage of sepsis patients is still unclear. The aim of this study was to determine wheth [...] Read more.Fei Pei ... on behalf of the China Critical Care Immunotherapy Research GroupPublished: April 22, 2022 Explor Immunol. 2022;2:200–210
Thymosin alpha 1 therapy alleviates organ dysfunction of sepsis patients: a retrospective cohort studyOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Thymosin alpha 1 (Tα1) is a promising treatment for the improvement of sepsis patients. Until now, its function in reducing acute organ damage of sepsis patients is still unclear. The aim of this study was to determine wheth [...] Read more.Fei Pei ... on behalf of the China Critical Care Immunotherapy Research GroupPublished: April 22, 2022 Explor Immunol. 2022;2:200–210 Single-cell differentiation trajectories define early stages of a human cutaneous T-cell lymphomaOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The aim of this article is to characterize in detail the γδ T lymphocytes from an adult patient with primary cutaneous T-cell lymphoma of γδ s [...] Read more.Juan-Pablo Cerapio ... Jean-Jacques FourniePublished: April 15, 2022 Explor Immunol. 2022;2:185–199
Single-cell differentiation trajectories define early stages of a human cutaneous T-cell lymphomaOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The aim of this article is to characterize in detail the γδ T lymphocytes from an adult patient with primary cutaneous T-cell lymphoma of γδ s [...] Read more.Juan-Pablo Cerapio ... Jean-Jacques FourniePublished: April 15, 2022 Explor Immunol. 2022;2:185–199 Paradigms in HIV vaccine researchOpen AccessReviewAlthough a large number of preventative human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) vaccine trials have been carried out during the last 30 years, it is remarkable that an effective HIV vaccine has not yet b [...] Read more.Marc H.V. Van RegenmortelPublished: March 17, 2022 Explor Immunol. 2022;2:180–184
Paradigms in HIV vaccine researchOpen AccessReviewAlthough a large number of preventative human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) vaccine trials have been carried out during the last 30 years, it is remarkable that an effective HIV vaccine has not yet b [...] Read more.Marc H.V. Van RegenmortelPublished: March 17, 2022 Explor Immunol. 2022;2:180–184 Augmenting human gamma delta lymphocytes for cancer therapy with chimeric antigen receptorsOpen AccessReviewGamma delta lymphocytes (γδ T) sit at the interface between innate and adaptive immunity. They have the capacity to recognize cancer cells by interaction of their surface receptors with an array of cancer cell surface target ant [...] Read more.Gabrielle M. Ferry, John AndersonPublished: March 17, 2022 Explor Immunol. 2022;2:168–179
Augmenting human gamma delta lymphocytes for cancer therapy with chimeric antigen receptorsOpen AccessReviewGamma delta lymphocytes (γδ T) sit at the interface between innate and adaptive immunity. They have the capacity to recognize cancer cells by interaction of their surface receptors with an array of cancer cell surface target ant [...] Read more.Gabrielle M. Ferry, John AndersonPublished: March 17, 2022 Explor Immunol. 2022;2:168–179 The role of γδ T cells in the context of allogeneic stem cell transplantationOpen AccessReviewAllogeneic stem cell transplantation is currently the only curative approach for a variety of malignant and non-malignant diseases. In the early transplant era, the intent of this treatment was to a [...] Read more.Rupert Handgretinger ... Manon QueudevillePublished: March 16, 2022 Explor Immunol. 2022;2:157–167
The role of γδ T cells in the context of allogeneic stem cell transplantationOpen AccessReviewAllogeneic stem cell transplantation is currently the only curative approach for a variety of malignant and non-malignant diseases. In the early transplant era, the intent of this treatment was to a [...] Read more.Rupert Handgretinger ... Manon QueudevillePublished: March 16, 2022 Explor Immunol. 2022;2:157–167 High avidity of vaccine-induced immunoglobulin G against SARS-CoV-2: potential relevance for protective humoral immunityOpen AccessReviewAvidity of immunoglobulin G (IgG) is defined as its binding strength to its target antigen. As a consequence of affinity maturation of the IgG response, avidity is maturing as well. Therefore, acute [...] Read more.Georg BauerPublished: March 16, 2022 Explor Immunol. 2022;2:133–156
High avidity of vaccine-induced immunoglobulin G against SARS-CoV-2: potential relevance for protective humoral immunityOpen AccessReviewAvidity of immunoglobulin G (IgG) is defined as its binding strength to its target antigen. As a consequence of affinity maturation of the IgG response, avidity is maturing as well. Therefore, acute [...] Read more.Georg BauerPublished: March 16, 2022 Explor Immunol. 2022;2:133–156