Background:
The main objective of the study was to carry out a systematic literature review to investigate the beneficial role of antioxidants in obesity and diabetes and the association of antioxidants in neuro-gliopathies and gut microbiome on antioxidant production and enteric nervous system (ENS) protection.
Methods:
A literature search was done electronically on 8 June 2022 in the databases Google Scholar, and PubMed, reviewing all the articles published in English. There were no limitations for the study (region, or any time frame). The study included randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and observational studies on a human subject, primarily focusing on information such as a change in body weight, body mass index (BMI), waist-to-height ratio (WHtR), waist-to-hip ratio (WHR), fasting blood glucose level, glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c), and other parameters that connected with diabetes and obesity. The search was also conducted for neuro-gliopathies and gut microbiome.
Results:
The beginning database search picked out a total of 2,428 articles, 1,310 in PubMed, 876 in Google Scholar, and 242 records from other sources. A total of 2,040 (total duplicates 388) was found after removing the duplicated articles, and after reading the title and abstracts were further decreased to 139 full-text articles. These 139 studies went for full-text analysis, which resulted in the exclusion of 123 studies and generated a final 16 articles included for systemic analysis.
Discussion:
This literature search of present studies shows the interconnection between antioxidant intake among obese and diabetes neuro-gliopathies. The findings indicate both obese and diabetic patients have a minimum content of antioxidants, especially carotenoids, retinol, ascorbic acid, tocopherol, magnesium, and zinc. While few research illustrated that ingestion of the abovementioned antioxidants was lowered among diabetes and obese subjects in contrast with their normal-weight population, this was not endorsed by every study.
Background:
The main objective of the study was to carry out a systematic literature review to investigate the beneficial role of antioxidants in obesity and diabetes and the association of antioxidants in neuro-gliopathies and gut microbiome on antioxidant production and enteric nervous system (ENS) protection.
Methods:
A literature search was done electronically on 8 June 2022 in the databases Google Scholar, and PubMed, reviewing all the articles published in English. There were no limitations for the study (region, or any time frame). The study included randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and observational studies on a human subject, primarily focusing on information such as a change in body weight, body mass index (BMI), waist-to-height ratio (WHtR), waist-to-hip ratio (WHR), fasting blood glucose level, glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c), and other parameters that connected with diabetes and obesity. The search was also conducted for neuro-gliopathies and gut microbiome.
Results:
The beginning database search picked out a total of 2,428 articles, 1,310 in PubMed, 876 in Google Scholar, and 242 records from other sources. A total of 2,040 (total duplicates 388) was found after removing the duplicated articles, and after reading the title and abstracts were further decreased to 139 full-text articles. These 139 studies went for full-text analysis, which resulted in the exclusion of 123 studies and generated a final 16 articles included for systemic analysis.
Discussion:
This literature search of present studies shows the interconnection between antioxidant intake among obese and diabetes neuro-gliopathies. The findings indicate both obese and diabetic patients have a minimum content of antioxidants, especially carotenoids, retinol, ascorbic acid, tocopherol, magnesium, and zinc. While few research illustrated that ingestion of the abovementioned antioxidants was lowered among diabetes and obese subjects in contrast with their normal-weight population, this was not endorsed by every study.
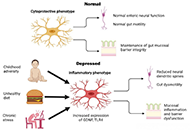 Do enteric glial cells play a role in the pathophysiology of major depression?Open AccessReviewMajor depressive disorder (MDD) is a common mental disorder associated with significant suffering and disability. Recent evidence has highlighted the role of the gut-brain axis in the pathogenesis o [...] Read more.Ravi Philip RajkumarPublished: April 28, 2024 Explor Neurosci. 2024;3:156–174
Do enteric glial cells play a role in the pathophysiology of major depression?Open AccessReviewMajor depressive disorder (MDD) is a common mental disorder associated with significant suffering and disability. Recent evidence has highlighted the role of the gut-brain axis in the pathogenesis o [...] Read more.Ravi Philip RajkumarPublished: April 28, 2024 Explor Neurosci. 2024;3:156–174 First outcomes of a therapeutic platform for drug resistant epilepsy based on transcutaneous electrical vagus nerve stimulationOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The aim of this paper is to discuss the main features and first outcomes of a therapeutic platform proposed to implement a public health therapeutic service for patients suffering refractory [...] Read more.Rene Ivan Gonzalez-Fernandez ... Jose Luis Hernandez-CaceresPublished: April 12, 2024 Explor Neurosci. 2024;3:144–155
First outcomes of a therapeutic platform for drug resistant epilepsy based on transcutaneous electrical vagus nerve stimulationOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The aim of this paper is to discuss the main features and first outcomes of a therapeutic platform proposed to implement a public health therapeutic service for patients suffering refractory [...] Read more.Rene Ivan Gonzalez-Fernandez ... Jose Luis Hernandez-CaceresPublished: April 12, 2024 Explor Neurosci. 2024;3:144–155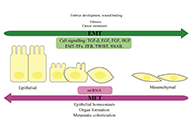 Brain metastasis from the perspective of molecular mechanisms and treatment, presenting a new approach for targeting ion channels by nano drugsOpen AccessReviewBrain metastasis is the most prevalent neurologic problem of systemic cancer and it can increase the mortality rate in patients with cancer. It occurs more in patients with lung cancer, breast cance [...] Read more.Zohreh Khosravi DehaghiPublished: April 10, 2024 Explor Neurosci. 2024;3:130–143
Brain metastasis from the perspective of molecular mechanisms and treatment, presenting a new approach for targeting ion channels by nano drugsOpen AccessReviewBrain metastasis is the most prevalent neurologic problem of systemic cancer and it can increase the mortality rate in patients with cancer. It occurs more in patients with lung cancer, breast cance [...] Read more.Zohreh Khosravi DehaghiPublished: April 10, 2024 Explor Neurosci. 2024;3:130–143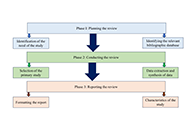 Role of antioxidants as immunity booster in obesity and diabetes: a systematic review on neuro-gliopathies perspectiveOpen AccessSystematic ReviewBackground: The main objective of the study was to carry out a systematic literature review to investigate the beneficial role of antioxidants in obesity and diabetes and the association of antio [...] Read more.Luxita Sharma, Dhananjay SharmaPublished: April 07, 2024 Explor Neurosci. 2024;3:103–129
Role of antioxidants as immunity booster in obesity and diabetes: a systematic review on neuro-gliopathies perspectiveOpen AccessSystematic ReviewBackground: The main objective of the study was to carry out a systematic literature review to investigate the beneficial role of antioxidants in obesity and diabetes and the association of antio [...] Read more.Luxita Sharma, Dhananjay SharmaPublished: April 07, 2024 Explor Neurosci. 2024;3:103–129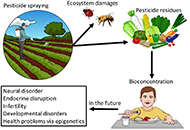 Crop and pesticide effects on gut microbiota and neurological functions: a reviewOpen AccessReviewPesticides are used to ensure the mass production and quality of foods, depending on the environment where they are grown. Trace amounts of pesticides are ingested through diet and high ratios of it [...] Read more.Tomomi Komura ... Yoshikazu NishikawaPublished: April 07, 2024 Explor Neurosci. 2024;3:80–102
Crop and pesticide effects on gut microbiota and neurological functions: a reviewOpen AccessReviewPesticides are used to ensure the mass production and quality of foods, depending on the environment where they are grown. Trace amounts of pesticides are ingested through diet and high ratios of it [...] Read more.Tomomi Komura ... Yoshikazu NishikawaPublished: April 07, 2024 Explor Neurosci. 2024;3:80–102