Advances in pharmacogenomics: optimizing antiepileptic drug therapy for drug-resistant epilepsy
Epilepsy, a complex neurological disorder, is influenced by intricate interactions within cortical, hippocampal, or thalamocortical neuronal networks, presenting a genetically complex condition with
[...] Read more.
Epilepsy, a complex neurological disorder, is influenced by intricate interactions within cortical, hippocampal, or thalamocortical neuronal networks, presenting a genetically complex condition with non-Mendelian inheritance patterns. This complexity is underscored by the involvement of numerous “susceptibilities” or “modifier” genes, complicating the assessment of risk and therapy outcomes. A critical inquiry in epilepsy treatment involves understanding how genetic diversity impacts treatment strategies and efficacy. Pharmacogenomic advancements have elaborated the connection between genetic variants and antiseizure medication (ASM) safety and response, marking a shift towards precision medicine in epilepsy care. Notably, genetic screening for variants such as HLA-B*1502 and HLA-A*3101 has demonstrated significant efficacy in preventing severe hypersensitivity reactions, including toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) and Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), particularly among specific ethnic populations. However, putting pharmacogenomic discoveries into clinical practice faces numerous challenges, including educational, legal, and economic barriers, emphasizing the need for broader acceptance and integration of pharmacogenomic data. This review synthesizes recent studies on pharmacogenomics in epilepsy, highlighting the current advances and prospects for personalizing epilepsy treatment through genetic insights, aiming to enhance ASM safety, reduce adverse effects, and improve treatment outcomes. Through a comprehensive examination of the genetic basis of epilepsy and its influence on pharmacotherapy, this review endeavors to contribute to the evolving landscape of precision medicine in epilepsy care, advocating for a more individualized and effective treatment approach.
Amna Shahid ... Sameen Abbas
View:1315
Download:32
Times Cited: 0
Epilepsy, a complex neurological disorder, is influenced by intricate interactions within cortical, hippocampal, or thalamocortical neuronal networks, presenting a genetically complex condition with non-Mendelian inheritance patterns. This complexity is underscored by the involvement of numerous “susceptibilities” or “modifier” genes, complicating the assessment of risk and therapy outcomes. A critical inquiry in epilepsy treatment involves understanding how genetic diversity impacts treatment strategies and efficacy. Pharmacogenomic advancements have elaborated the connection between genetic variants and antiseizure medication (ASM) safety and response, marking a shift towards precision medicine in epilepsy care. Notably, genetic screening for variants such as HLA-B*1502 and HLA-A*3101 has demonstrated significant efficacy in preventing severe hypersensitivity reactions, including toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) and Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), particularly among specific ethnic populations. However, putting pharmacogenomic discoveries into clinical practice faces numerous challenges, including educational, legal, and economic barriers, emphasizing the need for broader acceptance and integration of pharmacogenomic data. This review synthesizes recent studies on pharmacogenomics in epilepsy, highlighting the current advances and prospects for personalizing epilepsy treatment through genetic insights, aiming to enhance ASM safety, reduce adverse effects, and improve treatment outcomes. Through a comprehensive examination of the genetic basis of epilepsy and its influence on pharmacotherapy, this review endeavors to contribute to the evolving landscape of precision medicine in epilepsy care, advocating for a more individualized and effective treatment approach.
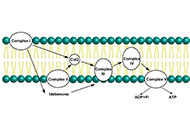 The potential positive effects of coenzyme Q10 on the regeneration of peripheral nerve injuryOpen AccessReviewPeripheral nerve injuries (PNIs) constitute a significant concern as they predominantly affect young and productive age groups of the population, causing social and economic pressure on patients. PN [...] Read more.Ahmed Mead ... Süleyman KaplanPublished: June 21, 2024 Explor Neuroprot Ther. 2024;4:288–299
The potential positive effects of coenzyme Q10 on the regeneration of peripheral nerve injuryOpen AccessReviewPeripheral nerve injuries (PNIs) constitute a significant concern as they predominantly affect young and productive age groups of the population, causing social and economic pressure on patients. PN [...] Read more.Ahmed Mead ... Süleyman KaplanPublished: June 21, 2024 Explor Neuroprot Ther. 2024;4:288–299 Cognitive-motor interference in multiple sclerosis and healthy controls: results from single, dual, and triple task posturographyOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: This article is based on our previous research, which was presented as a poster at the ECTRIMS Congress 2018 and published as a conference abstract (https://www.professionalabstracts.com/ect [...] Read more.Patrik Althoff ... Tanja Schmitz-HübschPublished: June 12, 2024 Explor Neuroprot Ther. 2024;4:273–287
Cognitive-motor interference in multiple sclerosis and healthy controls: results from single, dual, and triple task posturographyOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: This article is based on our previous research, which was presented as a poster at the ECTRIMS Congress 2018 and published as a conference abstract (https://www.professionalabstracts.com/ect [...] Read more.Patrik Althoff ... Tanja Schmitz-HübschPublished: June 12, 2024 Explor Neuroprot Ther. 2024;4:273–287 Effect of gardening physical activity on neuroplasticity and cognitive functionOpen AccessSystematic ReviewBackground: The beneficial effects of gardening as a form of physical activity have garnered growing interest in recent years. This research aimed to evaluate the effect of gardening as a physica [...] Read more.Antonio G. LentoorPublished: June 05, 2024 Explor Neuroprot Ther. 2024;4:251–272
Effect of gardening physical activity on neuroplasticity and cognitive functionOpen AccessSystematic ReviewBackground: The beneficial effects of gardening as a form of physical activity have garnered growing interest in recent years. This research aimed to evaluate the effect of gardening as a physica [...] Read more.Antonio G. LentoorPublished: June 05, 2024 Explor Neuroprot Ther. 2024;4:251–272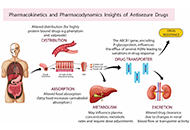 Advances in pharmacogenomics: optimizing antiepileptic drug therapy for drug-resistant epilepsyOpen AccessReviewEpilepsy, a complex neurological disorder, is influenced by intricate interactions within cortical, hippocampal, or thalamocortical neuronal networks, presenting a genetically complex condition with [...] Read more.Amna Shahid ... Sameen AbbasPublished: May 28, 2024 Explor Neuroprot Ther. 2024;4:240–250
Advances in pharmacogenomics: optimizing antiepileptic drug therapy for drug-resistant epilepsyOpen AccessReviewEpilepsy, a complex neurological disorder, is influenced by intricate interactions within cortical, hippocampal, or thalamocortical neuronal networks, presenting a genetically complex condition with [...] Read more.Amna Shahid ... Sameen AbbasPublished: May 28, 2024 Explor Neuroprot Ther. 2024;4:240–250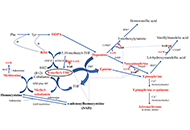 Diverse avenues of research support the transmethylation theory of psychosis: implications for neuroprotectionOpen AccessReviewTransmethylation in the context of psychiatry has historically referred to the enzymatic transfer of a methyl group from one biochemical to another, whose resulting function can change so dramatical [...] Read more.Christine L. MillerPublished: May 15, 2024 Explor Neuroprot Ther. 2024;4:198–239
Diverse avenues of research support the transmethylation theory of psychosis: implications for neuroprotectionOpen AccessReviewTransmethylation in the context of psychiatry has historically referred to the enzymatic transfer of a methyl group from one biochemical to another, whose resulting function can change so dramatical [...] Read more.Christine L. MillerPublished: May 15, 2024 Explor Neuroprot Ther. 2024;4:198–239