Affiliation:
College of Life Sciences, Shandong Agricultural University, Tai’an 271018, Shandong, China
†These authors contributed equally to this work.
Affiliation:
College of Life Sciences, Shandong Agricultural University, Tai’an 271018, Shandong, China
†These authors contributed equally to this work.
Affiliation:
College of Life Sciences, Shandong Agricultural University, Tai’an 271018, Shandong, China
†These authors contributed equally to this work.
Affiliation:
College of Life Sciences, Shandong Agricultural University, Tai’an 271018, Shandong, China
†These authors contributed equally to this work.
Affiliation:
College of Life Sciences, Shandong Agricultural University, Tai’an 271018, Shandong, China
†These authors contributed equally to this work.
Affiliation:
College of Life Sciences, Shandong Agricultural University, Tai’an 271018, Shandong, China
†These authors contributed equally to this work.
Email: haifangli@sdau.edu.cn
ORCID: https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2827-5925
Explor Dig Dis. 2025;4:100579 DOl: https://doi.org/10.37349/edd.2025.100579
Received: March 20, 2025 Accepted: June 04, 2025 Published: June 30, 2025
Academic Editor: Alfredo Caturano, Università degli Studi della Campania Luigi Vanvitelli, Italy
The article belongs to the special issue The Role of Gut Microbiota in the Pathogenesis and Management of Metabolic-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD)
As the most prevalent hepatic disorder worldwide, metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) afflicts over one-third of the global population, representing a significant public health challenge. The multifactorial pathogenesis of this condition is principally rooted in metabolic dysregulation. It is notable that emerging evidence highlights a critical role for gut microbiota (GM) in disease initiation and progression. This comprehensive review elaborates some representative GM species that influence hepatic lipid metabolism and elucidates the mechanisms through which GM dysbiosis exacerbates MASLD pathogenesis. Importantly, the positive or negative effects of intestinal bacterial communities on MASLD are largely dependent on their special metabolites, such as short chain fatty acids, ethanol, and trimethylamine N-oxide. Current therapeutic strategies targeting GM modulation, including prebiotics, probiotics, fecal microbiota transplantation, specific medicines, and bacteriphages, demonstrate promising efficacy that partially restores microbial equilibrium and mitigates hepatic steatosis. Although limitations still persist in achieving sustained clinical remission, the expanding frontier of microbiome research continues to refine our understanding of host-microbiota crosstalk in MASLD. Future investigations integrating multiple approaches and longitudinal clinical data hold potential to unravel complex microbial networks, paving the way for innovative therapeutic breakthroughs in metabolic liver disease management.
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) is a chronic liver disease closely related to metabolic syndrome, whose prevalence is increasing worldwide due to the pandemic of obesity [1]. The development and progression of MASLD is a dynamic process [2]. The incipient phase of MASLD arises predominantly from dysregulated lipid metabolism, culminating in pathologic triglyceride accumulation within hepatocytes, a precursor state to metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH). Concurrently, this metabolic perturbation triggers a bidirectional cascade of inflammatory activation and hepatocellular injury, wherein these mutually reinforcing mechanisms amplify disease progression [3]. Persistent hepatic inflammation and cellular damage further induce activation of quiescent hepatic stellate cells [4], initiating excessive extracellular matrix deposition and evolving into liver fibrosis [5]. The sustained fibrosis stage may subsequently progress into cirrhosis, a state marked by profound hepatic insufficiency and life-threatening complications including esophageal variceal hemorrhage [6], refractory ascites [7], and hepatic encephalopathy [8]. Notably, MASLD-induced cirrhosis constitutes a principal etiological driver of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), with tumorigenesis potentiated through paracrine signaling within the remodeled tumor microenvironment [9]. Notably, beyond hepatic pathology, MASLD exhibits systemic ramifications through its association with cardiovascular morbidity [10], chronic kidney disease (CKD) progression [11], type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) exacerbation [12], and neurocognitive impairment [13]. These extrahepatic manifestations substantially contribute to the elevated all-cause mortality observed in MASLD cohorts, underscoring its reconceptualization as a multisystem disorder with far-reaching clinical implications [14].
The pathogenesis of MASLD arises from a complex interplay of genetic predisposition, environmental factors, and lifestyle determinants [15]. Notably, individuals with MASLD frequently exhibit significant alterations in GM composition, characterized by reduced microbial diversity and a shift from dominant species to non-dominant microbial populations [16, 17]. Emerging evidence suggests that GM dysbiosis may directly contribute to MASLD progression through multiple mechanisms, including compromised intestinal barrier integrity, sustained inflammatory activation, exacerbated oxidative stress, and dysregulated bile acid metabolism [18]. In addition, GM-derived metabolites demonstrate dual roles in MASLD pathophysiology. Protective metabolites such as short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), predominantly consist of acetate, propionate, and butyrate, exhibit therapeutic potential by ameliorating hepatic steatosis and inflammation [19]. Conversely, deleterious metabolites including endogenous ethanol and trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) may accelerate disease progression by promoting metabolic dysfunction and hepatocellular injury [15]. These mechanistic insights highlight promising therapeutic strategies targeting the gut-liver axis. Clinical interventions such as prebiotics, probiotics, fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT), traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), and phage therapy are being actively explored for MASLD management [20]. Additionally, pharmacological modulation of gut microbiota (GM) metabolite production, either through inhibition of harmful metabolites or enhancement of beneficial compounds, represents a novel therapeutic frontier in MASLD treatment [21].
In the present review, we primarily searched the PubMed and ScienceDirect databases, retrieving and collecting publications relevant to the above topics, including original research articles and review papers. Based on these resources, we systematically examined the GM species influencing hepatic lipid metabolism, elucidated their mechanistic pathways, and evaluated the therapeutic potential of GM modulation in MASLD management. By synthesizing current evidence on these specific mechanisms, this analysis not only advances our understanding of the involvement of GM in MASLD pathogenesis, but also establishes a conceptual framework to guide future translational research and therapeutic innovation.
Specific GM species are strongly associated with hepatic lipid metabolism markers, suggesting their regulatory role in MASLD. A meta-analysis shows that MASLD patients have less diverse GM than healthy people, with more Bacteroidetes and fewer Prevotella [22]. Another study shows that the abundance of Escherichia coli, Prevotella, Streptococcus, Coprococcus, Faecalibacterium, and Ruminococcus is a common gut bacterial feature in MASLD [23]. Effenberger et al. [24] revealed that the abundance of Enterobacteriaceae, Prevotellaceae, and Lactobacillaceae is associated with increased serum fatty apolipoproteins. In contrast, Ruminococcaceae, which helps maintain gut microenvironment homeostasis, gradually decreases in MASLD patients as the disease worsens and fibrosis becomes more severe. This section synthesizes current evidence on key gut microbial communities implicated in MASLD progression, focusing on their mechanistic roles and clinical relevance (Figure 1 and Table 1).
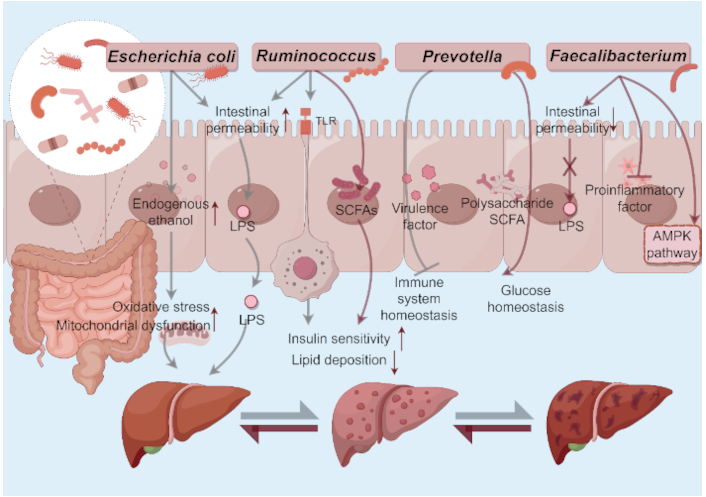
Roles of some gut microbial communities in MASLD initiation and progression. a) Escherichia coli: 1) Produce endogenous ethanol→Induce liver inflammation and mitochondrial dysfunction; 2) Boost gut permeability→Enhance LPS translocation→Activate inflammasomes. b) Ruminococcus: 1) Boost gut permeability→Enhance LPS translocation→Activate inflammasomes; 2) Activate the TLR4 pathway→Worsen insulin resistance and fat deposition; 3) Produce SCFAs→Improve insulin sensitivity and inhibit liver fat production. c) Prevotella: 1) SCFA metabolism→Maintain the glucose homeostasis; 2) Produce virulence factors→Disrupt immune homeostasis. d) Faecalibacterium: 1) Produce butyrate→Inhibit translocation of endotoxins; 2) Activate AMPK pathway→Improve insulin sensitivity→Decrease hepatic lipid deposition. MASLD: metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease; LPS: lipopolysaccharide; SCFA: short-chain fatty acid; AMPK: AMP-activated protein kinase. By Figdraw (ID: WOWIA4e047)
The effects of microbial intervention on MASLD
| Gut microbiota species | Mechanism | Clinical status | Limitations | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Escherichia coli |
|
| Further studies are needed to investigate the various effects of different E. coli strains on the liver. | [16, 26–29] |
| Ruminococcus |
|
| Current evidence remains primarily correlative, though preliminary experimental data suggest potential causal mechanisms. | [34–38] |
| Prevotella |
|
| The therapeutic protocol demonstrates relatively low correlation with lifestyle interventions and conventional medications. | [39, 40, 44–46] |
| Faecalibacterium |
|
| Further research is required to determine the optimal dosage regimen, administration route, and mechanism of action. | [47–50, 53, 54] |
MASLD: metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease; SCFAs: short-chain fatty acids
E. coli is a main pathogenic bacterium causing high lipopolysaccharide (LPS) content in patients with fatty liver [25]. The overgrowth of E. coli may boost gut permeability and LPS levels in the portal vein, thus activating inflammasomes and causing liver damage [16]. Some E. coli strains can ferment carbohydrates to produce ethanol and raise the blood ethanol levels [26]. Endogenous ethanol could induce oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in liver cells, worsening fatty liver [27]. Shen et al. [28] demonstrated an increased abundance of intestinal Enterobacteriaceae in MASLD patients with severe fat deposition and fibrosis. Importantly, translocation of E. coli exacerbated hepatic steatosis, inflammation, and fibrosis in MASLD mice [28]. E. coli has a bidirectional causal relationship with MASLD. The metabolic disorders accompanying MASLD, such as obesity and insulin resistance, may alter GM composition and cause E. coli proliferation, creating a vicious cycle. Given the strain heterogeneity of E. coli (commensal vs pathogenic), its diverse effects on the liver need further strain-specific research [29]. Iannone et al. [30] found that aldafermin-expressing E. coli Nissle 1917 combined with dietary changes could improve epididymal visceral adipose tissue (eVAT) histology, and alleviate liver steatosis and other MASLD-related pathological conditions by improving liver metabolism through eVAT-liver interactions. Thus, therapeutic intervention targeting E. coli may be a promising candidate for MASLD therapy.
Some Ruminococcus species, such as R. gnavus [31], R. bromii [32], and R. albus [33], could break down gut mucus, damage the mucous layer, and increase the risk of leaky gut, which promote the translocation of endotoxins like LPS and further lead to liver inflammation [34]. Moreover, certain Ruminococcus-derived metabolites may activate the TLR4 pathway, worsening insulin resistance and hepatic fat deposition [35]. On the other hand, species like R. bromii could ferment dietary fibers to produce SCFAs, thereby improving insulin sensitivity and inhibiting liver fat production [36]. The role of Ruminococcus and related molecules in MASLD is largely correlative, yet some experiments hint at potential causal mechanisms. It has been shown that transplanting GM enriched in Ruminococcus from MASLD patients into germ-free mice would induce liver steatosis and inflammation [37]. Also, clinical studies indicate a positive correlation between Ruminococcus abundance and liver fibrosis severity in MASLD patients [38].
Prevotella, a prominent genus within the Bacteroidetes phylum, exhibits context-dependent roles in human health. While recognized as a commensal bacterium contributing to polysaccharide degradation and SCFA metabolism that is critical for maintaining glucose homeostasis, certain strains display pathogenic potential linked to chronic inflammatory disorders [39]. This transition from commensal to pathobiont is driven by dysbiosis-induced upregulation of virulence factors, which disrupts immune tolerance and shifts host-microbe equilibrium [40]. Prevotella also showed inconsistent results in the progression of MASLD. Yuan et al. [39] have demonstrated that Prevotella plays a unique role in carbohydrate metabolism. It can also produce higher levels of LPS, which stimulate inflammation and promote the development of MASLD [41, 42]. Clinical studies indicate that Prevotella copri is significantly enriched in MASLD patients and positively correlates with liver fat and plasma/serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) [16]. Animal experiments show that transferring GM from mice with inflammasome defects (Asc or IL-18 knockout) to wild-type mice aggravates NASH induced by a methionine-choline-deficient diet. This is seen as increased liver steatosis, inflammation, and elevated liver enzymes when Prevotella-rich microbiota is present [43]. Thus, Prevotella has a pro-disease association with MASLD. However, some research reveals a protective role in high dietary fiber intake individuals, wherein Prevotella is more abundant and liver fat is lower, which may result from its propionate production improving metabolism [44]. Michail et al. [45] found that children with MASLD have more Prevotella, whereas opposite results were obtained in adult studies. These discrepancies suggest that Prevotella’s impact on MASLD is modulated by age, metabolic context, and strain-specific functional differences. Regarding Prevotella-targeted therapies, potential strategies include antibiotics that directly combat Prevotella and prebiotics/probiotics (e.g., dietary fiber supplements) to modulate GM. Additionally, lifestyle changes and traditional medications are mentioned, though their relevance is relatively low [46].
Faecalibacterium, a member of the Firmicutes phylum, is a strictly anaerobic, oxygen-sensitive, gram-positive bacterium. As a major butyrate producer, it strengthens the intestinal barrier by inhibiting translocation of endotoxins to the liver, thereby reducing systemic inflammation and hepatic injury [47]. Additionally, it enhances insulin sensitivity via AMPK pathway activation, decreases hepatic lipid accumulation [48], and suppresses pro-inflammatory mediators such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) [49]. Wang et al. [50] showed that oral administration of either live F. prausnitzii or its extracellular vesicles significantly reduced the severity of fibrosis induced by repeated administration of DSS in mice. Butyrate-producing bacteria such as F. prausnitzii could reduce bacterial translocation and stimulate mucin secretion, thus maintaining intestinal integrity [51]. MASLD patients frequently exhibit reduced GM diversity and diminished Faecalibacterium abundance, positioning this bacterium or its derivatives as promising therapeutic agents for MASLD-associated intestinal pathologies [52]. FMT from healthy donors is often used to introduce beneficial bacteria like Faecalibacterium into MASLD patients’ gut [53]. Also, postbiotics derived from Faecalibacterium species, such as cell wall components, exopolysaccharides and SCFAs, exert anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, immunomodulatory, and gut barrier enhancing effects, thus indirectly improving MASLD [54]. However, further research is required to establish optimal dosing regimens, administration routes, and mechanistic pathways to maximize its therapeutic potential.
Emerging evidence highlights that GM is a pivotal modulator in the pathogenesis and advancement of MASLD [55]. This microbial consortium exerts direct regulatory effects on host physiology through multiple interconnected mechanisms: (1) compromising intestinal epithelial integrity through tight junction disruption [56]; (2) triggering systemic inflammation via pathogen-associated molecular pattern translocation [57]; (3) intensifying redox imbalance through reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation [58]; and (4) modifying bile acid enterohepatic circulation [59].
GM modulates intestinal permeability through regulation of tight junction complexes (particularly occludins and claudins) in epithelial cells, thereby promoting bacterial and metabolite translocation to the liver, a process mechanistically linked to MASLD development [60]. Nakajima et al. [61] revealed that Porphyromonas gingivalis administration suppresses Tjp-1 and Occludin gene expression, exacerbates GM dysbiosis and barrier impairment, which subsequently triggers hepatic inflammatory responses with concomitant lipid metabolic dysregulation.
Microbiota-driven immune dysregulation manifests as transcriptional reprogramming of cytokine networks, characterized by IL-10 suppression [62] and TNF-α/IL-1β dominance [63], which orchestrates intrahepatic inflammasome activation to potentiate MASLD pathobiology. Nakamoto et al. [64] demonstrated Klebsiella pneumoniae as a primary driver of PSC-associated dysbiosis, with humanized microbiota transfer inducing compartmentalized hepatic Th17 polarization and parenchymal injury markers correlating with IL-17A titers. Concurrently, Muñoz et al. [65] established in chemically-induced cirrhosis models that microbiota-immune crosstalk disruption directly mediates fibrogenic niche formation through STAT3/NF-κB co-activation pathways. Prevotella promotes periodontitis by inducing neutrophil recruitment via the Th17 immune response [66]. These findings highlight how alterations in GM abundance (including specific bacterial strains) may trigger inflammatory dise. Mechanistic studies revealed GM-TLR4 synergy in non-hematopoietic hepatic stromal cells as a non-redundant checkpoint for hepatocarcinogenesis, with MyD88-dependent signaling constituting > 60% of tumorigenic potential in chronic injury milieus [67].
GM-derived oxidative stress exacerbation constitutes a non-canonical pathway in MASLD pathogenesis through endotoxin-mediated MASLD oxidase hyperactivation in hepatic macrophages (Kupffer cells), and subsequent ROS overproduction exceeding antioxidant defense capacity [68]. Ahmad et al. [69] mechanistically demonstrated that dysbiosis-induced microbial translocation elevates circulatory LPS levels, triggering TLR4-dependent ROS generation, a key contributor to hepatic lipid peroxidation and subsequent TLR-4/NFκB-mediated inflammatory liver injury. Complementary evidence from study [70] revealed that rifaximin administration in dietary hepatotoxicity models restores redox homeostasis via upregulation of tight junction proteins (TJPs) that reversing microbial translocation, and suppression of NOX2-mediated superoxide production, ultimately attenuating F4/80+ macrophage infiltration.
Beyond classical pathways, GM orchestrates bidirectional regulation of MASLD progression through bile acid enterohepatic reprogramming. Dysbiosis-induced bile acid metabolism perturbation manifests as cytotoxic bile acid accumulation triggering hepatocyte apoptosis via JNK1/caspase-3 activation, and suppression of nuclear receptor FXR axis (7α-hydroxylase) that disrupts bile acid homeostasis, forming a pathogenic feedback loop [71]. Crucially, bile acid signaling converges on dual metabolic regulators, nuclear FXR and membrane-bound TGR5, whose coordinated activation maintains hepatic lipidostasis. MASLD-associated dysbiosis shifts bile acid pool composition toward FXR/TGR5 antagonistic species, thereby impairing β-oxidation capacity and amplifying ROS-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction. Further therapeutic validation demonstrates that 3-sucCA-mediated expansion of Akkermansia muciniphila induces FGF15/19 hepatic signaling to achieve 58% MASLD amelioration through bile acid-FXR-TGR5 axis restoration [72].
Besides the direct regulation of GM on the gut-liver axis, several GM metabolites have been identified as key mediators of microbial influence on hepatic metabolism and function. While beneficial compounds like SCFAs alleviate the symptom of MASLD via sustaining lipid metabolism homeostasis and strengthening the gut barrier, harmful byproducts, such as endogenous ethanol and TAMO, promote MASLD progression through stimulating oxidative stress and inflammatory reactions (Figure 2).
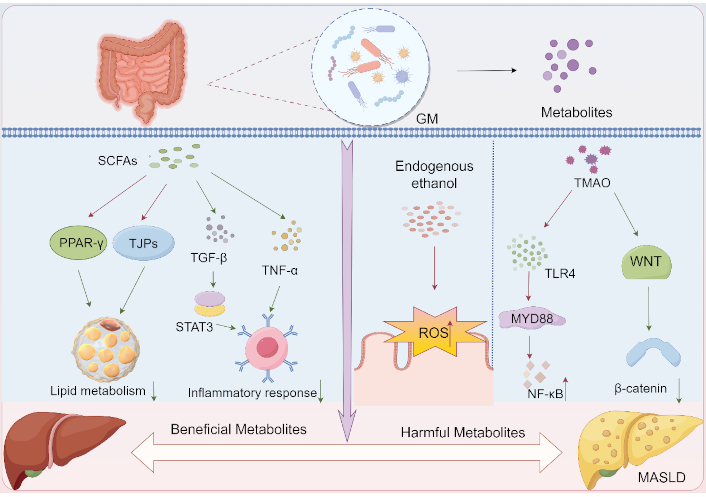
Roles of GM metabolites in MASLD initiation and progression. a) Protective metabolites: 1) SCFAs: Activate PPAR-γ→Enhance lipid metabolism homeostasis; 2) SCFAs: Upregulate TJPs→Strengthen gut barrier→Suppress systemic inflammation; b) Detrimental metabolites: 1) Ethanol: Induces ROS overproduction→Oxidative stress→Metabolic dysregulation; 2) TMAO: Activates TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB inflammatory axis→Metabolic dysregulation. SCFAs: short-chain fatty acids; GM: gut microbiota; PPAR-γ: peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ; TJPs: tight junction proteins; TGF-β: transforming growth factor-beta; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor-alpha; STAT3: signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; ROS: reactive oxygen species; TLR4: toll-like receptor 4; TMAO: trimethylamine N-oxide; WNT: wingless / integrated; MASLD: metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. By Figdraw (ID: TTOYWbbb4b)
SCFAs are the primary metabolites derived from GM-mediated fermentation of carbohydrates or amino acids, which mostly exhibit protective functions for MASLD [73]. SCFAs alleviate metabolic syndrome by activating PPARγ-dependent lipid utilization over synthesis, reversing diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance through tissue-specific PPARγ modulation in adipose (regulating energy expenditure) and liver (reducing steatosis), positioning SCFAs as potential therapeutic PPARγ-targeted agents [74]. Clinical investigations by Xiong et al. [75] revealed an inverse correlation between plasma SCFA levels and TNF-α concentrations in patients with MASLD, suggesting that SCFA dynamics may serve as biomarkers for disease progression. Mechanistically, Yang et al. [76] demonstrated that sodium butyrate dose-dependently restored intestinal TJP integrity in 16-week-old db/db mice and ameliorated high glucose-induced barrier dysfunction in Caco-2 cell monolayers. Study [77] has shown that consumption of lactucin improves CCl4-induced hepatic fibrosis in mice via enhancing the levels of acetate and butyrate, further decreasing inflammatory responses, and acting on the TGF-β1/STAT3 signaling pathway. Additionally, SCFAs, butyrate in particular, play a pivotal role in regulating GM homeostasis. Butyrate improves the pH of the gut and feces, which inhibits the growth of potential pathogens and promotes the growth and colonization of beneficial bacteria [78].
Emerging evidence highlights the critical role of GM-derived ethanol in the pathogenesis of MASLD. Intestinal bacterial fermentation of carbohydrates generates endogenous ethanol, which has been mechanistically linked to hepatic injury through pro-inflammatory signaling activation [79]. Clinical studies demonstrate that pediatric MASLD patients exhibit substantially elevated circulating ethanol levels compared to healthy controls, suggesting gut-originated ethanol may exacerbate liver pathology by modulating inflammatory cascades [27]. Further investigation indicated that MASLD patients displayed marked increases in microbiome-derived ethanol within the hepatic portal circulation, and experimental models utilizing high-fat diet (HFD)-induced mice revealed that such ethanol exposure potentiates oxidative stress through ROS overproduction, thereby compromising intestinal epithelial integrity and facilitating endotoxin translocation [80]. The cumulative evidence establishes a microbiota-ethanol-liver axis wherein microbial metabolic activity disrupts both intestinal barrier function and hepatic homeostasis through intertwined inflammatory and oxidative pathways.
TMAO, a prototypical GM-derived metabolite, contributes to MASLD pathogenesis through dual mechanisms involving systemic inflammation and intestinal barrier compromise [81]. Notably, this microbial metabolite paradoxically suppresses the cytoprotective WNT/β-catenin pathway, exacerbating mucosal vulnerability and disrupting enterocyte homeostasis [82]. It has been revealed that TMAO induces structural/functional deterioration of the colonic epithelial barrier while activating pro-inflammatory cascades via the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB axis [83]. These findings establish TMAO as a critical molecular mediator linking microbial metabolism to multi-organ dysfunction in MASLD.
Dietary intervention remains the cornerstone therapy for MASLD, necessitating research into gut-liver axis optimization through microbial modulation. Current evidence highlights prebiotics and probiotics as key targets, demonstrating their therapeutic potential in reshaping GM and mitigating MASLD progression [84] (Figure 3a).
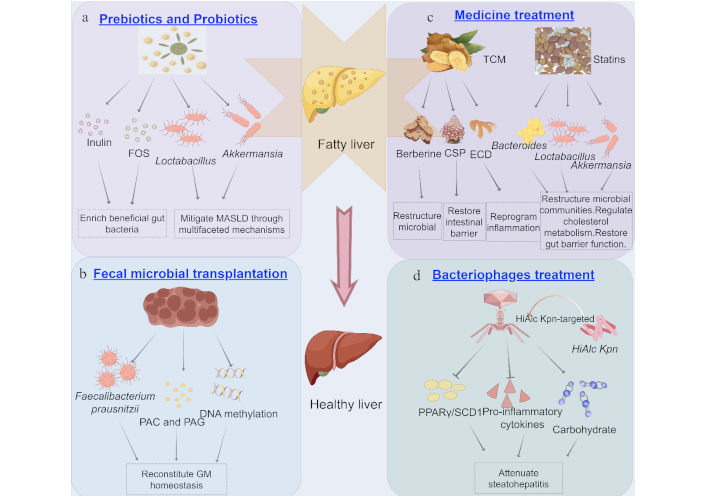
Treatment of MASLD from the perspective of GM. a) Effects of prebiotics (inulin and FOS) and probiotics (Lactobacillus and Akkermansia) on MASLD treatment; b) Fecal microbial transplantation improves MASLD by correcting GM dysbiosis; c) Effects of medicines on MASLD treatment; d) HiAlcKpn-targeted bacteriophages attenuate steatohepatitis via multi-omics remodeling. MASLD: metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease; GM: gut microbiota; FOS: fructooligofructose; TCM: traditional Chinese medicine; CSP: chaihu shugan powder; ECD: erchen decoction; PAC: phenylacetylcarnitine; PAG: phenylacetylglutamine; PPARγ: peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ; SCD1: stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1. By Figdraw (ID: AARIWbb556)
Prebiotics, defined as “selectively utilized substrates that confer health benefits through host microbiota modulation”, represent indigestible food components that bypass human digestion. While humans lack enzymatic capacity to process polysaccharides/oligosaccharides, GM metabolize these compounds, thereby regulating microbial composition and functionality [85]. Prebiotics are pharmacologically classified into three bioactive categories: non-digestible carbohydrates [fructooligofructose (FOS), inulin, galactooligosaccharides, xylooligosaccharides], phenolic compounds (catechins, proanthocyanidins), and functional derivatives (resistant starch, lactulose) [86, 87]. Current research prioritizes inulin and FOS due to their demonstrated bifidogenic effects.
Inulin demonstrates preventive and therapeutic effects against MASLD primarily through intestinal flora modulation, which enriches beneficial gut bacteria (e.g., Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus) and enhances SCFAs production [88]. These SCFAs reduce intestinal pH to suppress harmful bacteria, energize gut cells, and regulate systemic metabolism [89]. Mechanistically, inulin lowers hepatic triglycerides and improves lipid metabolism, while boosting SCFA-mediated glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) activation to enhance insulin sensitivity, thereby alleviating glucose dysregulation and hepatic lipid accumulation [90, 91]. Its anti-inflammatory properties involve reducing TNF-α/IL-6 levels via AMPK signaling and modulating macrophage polarization (M1 inhibition/M2 promotion) through SCFAs, collectively mitigating liver inflammation [92, 93]. These integrated mechanisms highlight inulin’s potential for MASLD management (Table 2).
The mechanisms and clinical status of microbical intervention for MASLD
| Microbial interventions | Mechanism | Clinical status | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inulin |
| Inulin reduces hepatic triglycerides, enhances lipid metabolism, and demonstrates therapeutic potential. | [88–93] |
| Fructooligofructose (FOS) |
| FOS serve as prebiotic supplements in food, nutraceuticals, and pharmaceuticals. | [94–97] |
| Lactobacillus |
| Lactobacillus demonstrates clinical significance as a probiotic and therapeutic potential for MASLD management. | [103–107] |
| Akkermansia |
| Akkermansia emerges as a next-generation probiotic candidate with therapeutic potential for MASLD and associated metabolic syndromes. | [108–112] |
| Fecal microbial transplantation (FMT) |
| FMT induces significant microbial composition alterations; long-term consequences remain understudied, necessitating longitudinal risk-benefit evaluation. | [115–120] |
| Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) |
| TCM’s “multi-component, multi-target” mechanisms exhibit high complexity; advanced omics technologies are required for mechanistic insights. | [121–125] |
| Statins |
| Statins exhibit multi-modal therapeutic effects. | [126–131] |
| Bacteriophages |
| Bacteriophage’s therapy (microbiome-targeted intervention): insufficient long-term safety validation. | [130–134] |
MASLD: metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease; SCFAs: short-chain fatty acids; GLP-1: glucagon-like peptide-1
Due to its physiological benefits and safety profile, FOS are widely utilized in food, nutraceuticals, and pharmaceuticals as prebiotic supplements. The health-promoting effects of FOS primarily arise from GM modulation, including enriching beneficial bacteria (e.g., Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus) while suppressing harmful species (e.g., Bacteroidetes and Clostridium) [94, 95]. In MASLD mice fed a HFD, FOS alleviates liver inflammation by decreasing intestinal endotoxin production, and reducing hepatic expression of IL-6/IL-1β [96]. Additionally, FOS strengthens intestinal barrier function by upregulating TJPs (e.g., Claudin-2/Claudin-4), limiting leakage of harmful substances and subsequent inflammatory responses [97]. Through the dual microbial restructuring and barrier reinforcement mechanisms, FOS effectively mitigates metabolic disorders by reducing inflammatory damage and optimizing gut-liver crosstalk (Table 2).
In addition to inulin and FOS, plant polyphenols such as catechins and proanthocyanidins exhibit multi-target mechanisms in mitigating MASLD. These compounds scavenge free radicals and suppress NADPH oxidase activity, reducing hepatic ROS accumulation, disrupting the oxidative stress-lipid peroxidation cycle, and preserving mitochondrial function while inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation [98]. A study demonstrated that grape seed proanthocyanidin extract (GSPE) modulates hepatic lipid metabolism circadian rhythms by activating BMAL1/CLOCK core clock genes, upregulating the fatty acid β-oxidation enzyme CPT1A and suppressing SREBP-1c-mediated lipogenesis [99]. Additionally, catechins regulate GM composition, enhance intestinal barrier function, and reduce portal vein LPS levels, thereby inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB pathway-driven hepatic inflammation [100]. Their synergistic activation of the Nrf2/ARE and PPARα pathways provides molecular targets for precision dietary interventions in MASLD.
Probiotics, defined as “live microorganisms that confer health benefits when administered in adequate amounts,” require two operational criteria: viability at consumption and dosage sufficiency. Probiotics encompass phylogenetically distinct microbial taxa, primarily classified into: lactic acid bacteria (Bifidobacterium, Lactobacillus), Saccharomycetic fungi (Saccharomyces boulardii, Saccharomyces cerevisiae), Streptococcus (Streptococcus thermophilus), Bacillus (Bacillus licheniformis, Bacillus subtilis), and Enterococcus (Enterococcus faecalis). Emerging genera including Akkermansia and Lactobacillus demonstrate intestinal microbiota modulation capacity [101, 102]. Current evidence supports Lactobacillus and Akkermansia as predominant genera with clinically validated host-beneficial effects.
L. acidophilus, a clinically significant probiotic, mitigates MASLD through multifaceted mechanisms, including lipid modulation, anti-inflammatory action, gut barrier enhancement, and HCC prevention [103]. Strain YL01 and its extracellular polysaccharide activate AMPK/ACC signaling to suppress hepatic fat synthesis, while strain ATCC4356 downregulates NPC1L1 to inhibit cholesterol uptake and steatosis progression [104, 105]. L. acidophilus reduces serum IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-α levels via Th17/Treg cell balance regulation, thereby alleviating liver inflammation [106]. L. acidophilus secretes valerate acid and strengthens intestinal integrity, curbing endotoxemia linked to MASLD pathogenesis [107]. Additionally, it blocks MASLD-to-HCC progression through valerate-GPR41/43 receptor interactions [108]. These synergistic effects underscore L. acidophilus’ therapeutic potential for MASLD management (Table 2).
A. muciniphila emerges as a therapeutic ally against metabolic disorders like MASLD, via mechanisms such as metabolite secretion, immune modulation, and metabolic reprogramming [108]. A. muciniphila produces SCFAs that bind GPR41/43 receptors to suppress systemic inflammation and barrier disruption, and secretes GLP-1 to enhance glucose homeostasis and mitigate hepatic steatosis [109, 110]. The phospholipid components in the bacterium activate TLR2/4 and TLR2/1 heterodimeric pathways to maintain mucosal immune balance, while the threonine-tRNA synthase targets macrophage polarization to resolve inflammation [111]. A. muciniphila could restore gut epithelial function and microbial structure in obesity/T2D, with its abundance inversely correlating to metabolic disease severity [112]. These tripartite actions position A. muciniphila as a next-generation probiotic candidate for MASLD and associated metabolic syndromes (Table 2).
Although preliminary findings demonstrate therapeutic potential, multicenter randomized controlled trials are warranted to validate long-term safety profiles and optimal therapeutic parameters (including strain specificity and dosage protocols) of probiotic interventions in MASLD management. Concurrently, mechanistic investigations are required to elucidate synergistic therapeutic mechanisms between probiotics and lifestyle modifications, particularly nutritional metabolic regulation and exercise-induced insulin sensitization [113, 114].
FMT is a therapeutic approach that involves transplanting fecal microbial communities from healthy donors into a patient’s intestinal tract to reconstruct gut microbial ecology, thereby restoring gut dysbiosis and alleviating associated disorders [115]. FMT represents a cutting-edge therapeutic modality for MASLD [116], involving the transfer of processed donor microbiota to reconstitute GM homeostasis. Mechanistically grounded in the gut-liver axis theory, this approach targets the dysregulated interplay between intestinal microbiota and hepatic metabolic pathways. Preclinical studies demonstrate that FMT significantly ameliorates MASLD pathology, primarily mediated through correction of gut dysbiosis [117] (Figure 3b). Zhou et al. [118] reported reduced hepatic lipid accumulation and inflammatory markers in MASLD model mice following FMT. A multi-omics investigation further elucidated FMT’s multi-target mechanisms, revealing its capacity to reshape GM profiles (e.g., increased Faecalibacterium prausnitzii and Blautia wexlerae abundance), modulate plasma metabolites including PAC and PAG, and normalize hepatic DNA methylation patterns [119]. Clinically, a systematic review and meta-analysis confirmed FMT’s safety and efficacy, showing significant improvement in NAFLD-associated metabolic parameters without severe adverse events [117]. However, given the multifactorial pathogenesis of MASLD involving the interplay of metabolic pathways and GM, FMT may induce profound alterations in microbial composition, yet its long-term consequences remain poorly characterized, necessitating longitudinal studies to comprehensively evaluate its risk-benefit profile [120] (Table 2).
TCM, a holistic medical system rooted in syndrome differentiation and natural herbal formulations, modulates host physiology through multi-target and multi-pathway mechanisms. It emphasizes systemic regulation and syndrome differentiation-guided therapeutics, formulating individualized treatment protocols based on patients’ clinical manifestations and constitutional characteristics [121]. In the context of MASLD, TCM primarily targets the remodeling of GM via tripartite regimens, such as microbial restructuring and metabolic improvement, intestinal barrier restoration and hepatoprotection, and anti-inflammatory reprogramming (Figure 3c and Table 2). For example, berberine restores the Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio, enriches Bifidobacterium, and ameliorates serum transaminases (ALT/AST) and lipid profiles (reduced TG, LDL-C) in HFD mice [122]. Chaihu Shugan powder (CSP) upregulates FXR/PPARγ expression, reduces intestinal permeability and LPS translocation, thereby alleviating hepatic steatosis, inflammation, and fibrosis in NAFLD rats [123, 124]. TCM formulations suppress TLR4/NF-κB signaling, downregulate TNF-α, IL-1β, and LPS levels, thereby attenuating hepatic inflammation [125]. TCM’s synergistic multi-target effects via the gut-liver axis significantly improve MASLD-related metabolic dysregulation and inflammation, with components like Berberine validated by randomized controlled trials [122]. However, the complexity of TCM’s “multi-component, multi-target” mechanisms necessitates advanced omics technologies (e.g., metabolomics, metagenomics) for deeper mechanistic insights, while standardization of herbal formulations remains critical to ensure efficacy consistency and clinical reproducibility.
Notably, statins also demonstrate pleiotropic therapeutic effects in MASLD through GM modulation. As HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, their mechanisms include: (1) Microbial restructuring and lipid homeostasis: Statins enhance colonization of SCFA-producing genera (Faecalibacterium and Bacteroides), which regulate hepatic lipid metabolism via GPCRs, reducing lipotoxicity. Concurrently, suppression of Clostridium reduces secondary bile acid synthesis, mitigating bile acid-induced hepatocyte injury and cholestatic stress in MASLD [126, 127]. (2) Cholesterol metabolism regulation: By enriching Lactobacillus, statins promote intestinal cholesterol excretion and alleviate microbiota-mediated inhibition of the FXR/PXR pathway on CYP7A1. This restores cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase activity, accelerating cholesterol-to-bile acid conversion and reducing hepatic cholesterol accumulation, a key driver of MASLD progression [128, 129]. (3) Gut barrier restoration: Statins upregulate mucin-degrading Akkermansia, which enhances TJP expression (e.g., Occludin, Zonula occludens-1) and reduces LPS translocation. This alleviates hepatic inflammation by suppressing TLR4/NF-κB signaling, a critical pathway in MASLD-related hepatocyte injury [130] (Figure 3C and Table 2). These mechanisms collectively target MASLD hallmarks, lipotoxicity, inflammation, and gut barrier dysfunction, highlighting statins’ multi-modal therapeutic potential.
MASLD pathogenesis is mechanistically linked to gut dysbiosis, with alcohol-hyperproducing Klebsiella pneumoniae (HiAlcKpn) identified as a key microbial driver through its portal vein-mediated ethanol delivery that directly induces hepatocyte steatosis and lipid dysregulation [131]. Bacteriophage therapy emerges as a precision antimicrobial strategy, leveraging taxon-specific lysis to selectively eradicate pathobionts like HiAlcKpn while preserving commensal microbiota integrity [132]. Preclinical validation demonstrates that HiAlcKpn-targeted bacteriophages attenuate steatohepatitis via multi-omics remodeling, such as normalizing hepatic transcriptomic profiles (downregulating lipogenic PPARγ/SCD1), reducing pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-6, TNF-α), and restoring lipid/carbohydrate metabolic flux [131] (Figure 3d). Human-relevant efficacy is further supported by FMT studies where Enterococcus faecalis-specific phages significantly reduced serum ALT levels and hepatic steatosis in humanized mice [133]. Bacteriophages therapy, as a novel microbiome-targeted intervention, remains insufficiently validated for long-term safety. The precision elimination of specific bacterial taxa by phages may induce gut microbial dysbiosis, potentially disrupting host-microbiota metabolic crosstalk and exerting multifaceted impacts on MASLD progression. This necessitates longitudinal studies to delineate its clinical risk-benefit equilibrium [134] (Table 2).
Emerging evidence establishes GM dysbiosis may be fundamental to drive both the initiation and progression of MASLD [18, 55]. Not only do specific microbial taxa directly interact with host systems, but their metabolic derivatives also demonstrate pleiotropic effects [14–17]. This dual regulatory capacity underscores the imperative to investigate microbial species-specific functions at varying quantitative thresholds and combinatorial ratios, positioning GM modulation as a promising therapeutic paradigm for MASLD management.
Alterations in microbial diversity exert bidirectional effects on hepatic homeostasis. Beneficial modifications may enhance immune competence and suppress pro-inflammatory cascades, whereas dysbiosis-induced impairment of intestinal barrier integrity and subsequent gut-liver axis hyperpermeability could exacerbate hepatic injury. Based on these insights, probiotics and prebiotics could promote the proliferation of beneficial bacteria, thereby optimizing GM composition and effectively mitigating MASLD progression [85–89]. Notably, microbial metabolites, including SCFAs, ethanol, and TMAO, modulate disease pathogenesis through metabolic pathway interference [80, 83, 84], establishing a critical role for metabolite-targeted interventions.
Moreover, it is worth noting that there are close associations and synonyms effects of GM in cardiovascular disorders (CVD) as well, which is integrally also related to MASLD and inflammation/endothelial dysfunction. Meanwhile, there is a close interaction between inflammation and endothelial dysfunction. Inflammation is an important cause of endothelial dysfunction, while endothelial dysfunction further exacerbates the inflammatory response, creating a vicious cycle. Bartlett et al. [135] indicate that oxidative stress in MASLD occurs independently of obesity, and patients with MASLD may have an elevated future risk of CVD. Study [136] has shown a specific association between GM metabolites and the left ventricular mass index (a marker reflecting CVD), demonstrating that GM and its metabolites not only influence MASLD occurrence but are also closely related to cardiovascular disease development. Kipp et al. [137] found that the bilirubin reductase bacterial enzyme and its expressing bacterial strains elevate plasma bilirubin levels while inhibiting production of the GM-derived secondary metabolite urobilin, thereby effectively preventing MASLD and CVD occurrence.
Despite these advances, significant challenges persist. For instance, notable differences have been observed in the composition of GM between pediatric and elderly MASLD patients, accompanied by variations in the rates of steatosis and fibrosis progression. Similarly, in populations with distinct metabolic backgrounds, the progression speed and pathological patterns of MASLD are not entirely consistent. These discrepancies indicate that probiotic and prebiotic therapies might not comprehensively address the needs of all patient subgroups. Moreover, innovative strategies such as FMT and phage therapy currently remain largely confined to preclinical stages in animal models, with unresolved issues concerning differences in drug metabolism and the complex interplay of multiple factors when translating to human applications. In clinical practice, rigorous control over donor-recipient matching, routes of administration, and treatment duration is imperative. Therefore, further exploration into the standardized application and personalized intervention of these therapies should be emphasized as a critical focus for the future clinical translation and nursing practice of MASLD treatments.
ALT: alanine aminotransferase
AMPK: AMP-activated protein kinase
eVAT: epididymal visceral adipose tissue
FMT: fecal microbiota transplantation
FOS: fructooligofructose
GLP-1: glucagon-like peptide-1
GM: gut microbiota
HCC: hepatocellular carcinoma
HFD: high-fat diet
LPS: lipopolysaccharides
MASLD: metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease
ROS: reactive oxygen species
SCFAs: short-chain fatty acids
TCM: traditional Chinese medicine
TJPs: tight junction proteins
TMAO: trimethylamine N-oxide
TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor-alpha
The figures in this paper were created using Figdraw software and are published with the permission granted by the software’s license.
WQ, LH, CF, and TZ: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing—original draft, Writing—review & editing. HW: Investigation, Writing—review & editing. HL: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing—review & editing, Supervision.
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Not applicable.
Not applicable.
Not applicable.
Not applicable.
This work was supported by the grant from the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province, China (No. [ZR2023MC085]). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
© The Author(s) 2025.
Open Exploration maintains a neutral stance on jurisdictional claims in published institutional affiliations and maps. All opinions expressed in this article are the personal views of the author(s) and do not represent the stance of the editorial team or the publisher.
Copyright: © The Author(s) 2025. This is an Open Access article licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, for any purpose, even commercially, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
Luis A. Rodríguez-Rojas ... Roxana U. Miranda-Labra
