103 results in Exploration of Digestive Diseases
Latest
Sort by :
- Latest
- Most Viewed
- Most Downloaded
- Most Cited
Open Access
Case Report
Ixekizumab-associated severe Crohn’s in a patient without definitive immune-mediated inflammatory disease: case report and evidence-informed guidance for non-IBD clinicians
Taylor L. Spiewak ... Anish Patel
Published: December 01, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. 2025;4:1005103
Open Access
Editorial
Surveillance for cholangiocarcinoma in PSC: MRI, ERCP, both—or neither?
Vincenzo Giorgio Mirante
Published: November 26, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. 2025;4:1005102
This article belongs to the special issue Advances in Hepato-gastroenterology: Diagnosis, Prognostication, and Disease Stratification
Open Access
Review
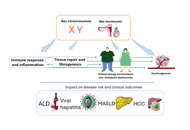
Sex differences in alcohol-related liver disease, viral hepatitis, metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease, and hepatocellular carcinoma
Amedeo Lonardo, Ayako Suzuki
Published: November 26, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. 2025;4:1005101
Open Access
Review
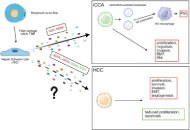
Neurotrophic signaling in liver cancers: mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets
Lorenzo Mainardi ... Chiara Raggi
Published: November 11, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. 2025;4:1005100
This article belongs to the special issue Fibrosis and Hepatobiliary Cancer
Open Access
Perspective
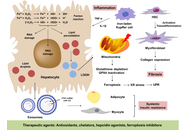
From spark to wildfire: how hyperferritinemia fans the flames of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease
Ralf Weiskirchen
Published: October 28, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. 2025;4:100599
This article belongs to the special issue Advances in Hepato-gastroenterology: Diagnosis, Prognostication, and Disease Stratification
Open Access
Review
Recent advances in Helicobacter pylori diagnosis, treatment, and management: a comprehensive review
Surbhi Dumra, Abhishek Ray
Published: October 21, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. 2025;4:100598
This article belongs to the special issue Helicobacter Pylori and Infection: Genomics, Diagnosis, Pathogenesis, Antibiotic Resistance, Microbiota, Cancer, Prevention and Therapeutics

Open Access
Review
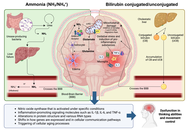
How the gut-liver axis shapes hepatic encephalopathy: mechanistic and therapeutic perspectives
Arnulfo E. Morales-Galicia ... Nahum Méndez-Sánchez
Published: October 14, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. 2025;4:100597
Open Access
Original Article
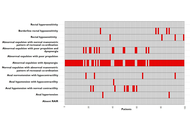
Multiple abnormalities of anorectal physiology co-exist with dyssynergia in patients with functional defecatory disorder—an observational study based on the London classification
Stephan Benny ... Noble Varghese Mathews
Published: October 11, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. 2025;4:100596
Open Access
Review
Precision prevention of liver cancer based on risk factors
Jian-Guo Chen
Published: September 29, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. 2025;4:100595
This article belongs to the special issue Prevention, Screening and Diagnosis for Primary Liver Cancer

Open Access
Original Article
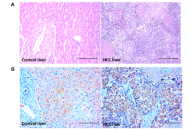
Elevated circulating pregnane X receptor as a novel diagnostic biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma
Balasubramaniyan Vairappan ... Biju Pottakkat
Published: September 25, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. 2025;4:100594
This article belongs to the special issue Prevention, Screening and Diagnosis for Primary Liver Cancer
Open Access
Review
Insights of hepatitis A virus disease burden in Indian subcontinent: why urbanized localities are vulnerable to disease outbreaks?
Zahid Hussain ... Vivek Patel
Published: September 24, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. 2025;4:100593
This article belongs to the special issue Viral Hepatitis

Open Access
Mini Review
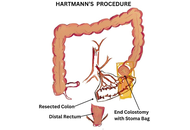
Surgical interventions: new approaches in diverticulitis treatment
Kaushal Yadav, Sagir Ahamed
Published: September 18, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. 2025;4:100592
This article belongs to the special issue Diverticulitis: Pathomechanism, Diagnosis and Treatment
Open Access
Original Article
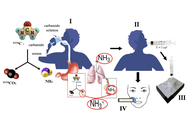
Novel research in the field of non-invasive diagnostics of Helicobacter pylori utilizing a library of chemical piezoelectric sensors and portable devices
Tatyana Anatolievna Kuchmenko ... Arina Kopaeva
Published: September 14, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. 2025;4:100591
This article belongs to the special issue Helicobacter Pylori and Infection: Genomics, Diagnosis, Pathogenesis, Antibiotic Resistance, Microbiota, Cancer, Prevention and Therapeutics
Open Access
Review
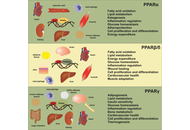
PPARs in molecular pathogenesis and drug treatment of type 2 diabetes-related MASLD
Amedeo Lonardo, Ralf Weiskirchen
Published: September 02, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. 2025;4:100590
This article belongs to the special issue Nuclear Receptors and the Digestive Tract: from Molecular Physiology to Clinics via Pharmacology
Open Access
Review
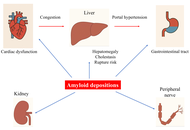
Amyloidosis and liver. Review.
Paul Carrier ... Véronique Loustaud-Ratti
Published: August 28, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. 2025;4:100589
Open Access
Review
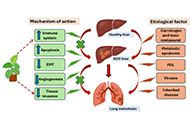
The role of medicinal plants in the management of hepatocellular carcinoma and its metastasis
Manoj Kumar Nagar ... Balasubramaniyan Vairappan
Published: August 24, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. 2025;4:100588
Open Access
Review
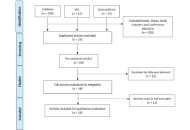
Pediatric liver transplantation in Brazil over two decades: a scoping review
Julia Ribeiro Kormann ... Camila Aparecida Moraes Marques
Published: August 19, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. 2025;4:100587
Open Access
Review
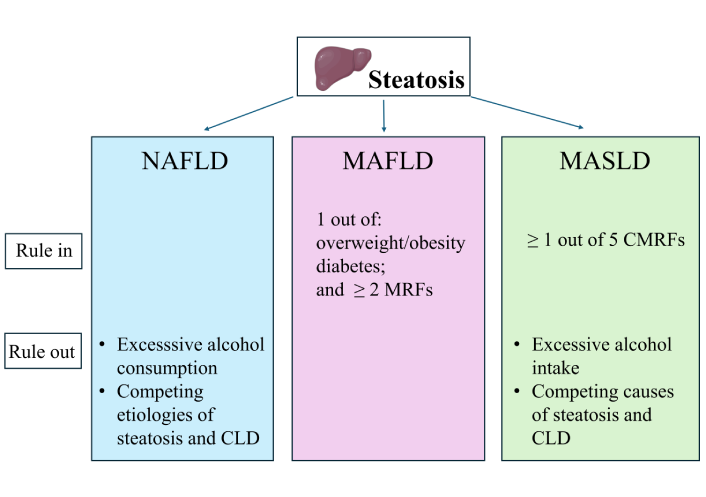
MASLD vs. MAFLD. A narrative review
Amedeo Lonardo ... Mohammed Eslam
Published: August 14, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. 2025;4:100586
Open Access
Review
Microbiota and iron metabolism
Natalia Baryshnikova ... Valeria Novikova
Published: August 08, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. 2025;4:100585
This article belongs to the special issue Gut Microbiota towards Personalized Medicine in Metabolic Disease

Open Access
Review
Towards personalized microbial therapies for metabolic alterations in celiac disease
Alejandro Borrego-Ruiz, Juan J. Borrego
Published: August 07, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. 2025;4:100584
This article belongs to the special issue Gut Microbiota towards Personalized Medicine in Metabolic Disease