




Aim:
The aim of this study is to investigate the polyphenol composition and distribution in the core, flesh, and peel of 20 apple varieties from China and its relation with browning characteristics of apple slices in the drying process.
Methods:
In this paper, the prominent phenolic compounds, which was determined by photo diode array-high-performance liquid chromatography (PDA-HPLC), and the chromatic value [coherent infrared energy (CIE) L*, a*, b*] were correlation analysised.
Results:
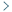
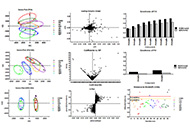
The results showed that apple core, flesh, and peel were characterized by phloridzin, chlorogenic acid, quercetin, and related derivatives respectively. The 20 apple varieties showed a significant difference (* P < 0.05) in browning variation in the drying process. The browning at the initial stage was mainly L* declined, which was induced by polyphenols enzymatic oxidation. While the browning was characterized by b* and a* value increment at the end of the drying process, where the Maillard reaction was the dominant factor.
Conclusions:
The correlation distance between the main phenolic compounds in apple core, flesh, and peel with the average chromatic L*, a*, and b* values varied at different stages of the drying process.
Aim:
The aim of this study is to investigate the polyphenol composition and distribution in the core, flesh, and peel of 20 apple varieties from China and its relation with browning characteristics of apple slices in the drying process.
Methods:
In this paper, the prominent phenolic compounds, which was determined by photo diode array-high-performance liquid chromatography (PDA-HPLC), and the chromatic value [coherent infrared energy (CIE) L*, a*, b*] were correlation analysised.
Results:
The results showed that apple core, flesh, and peel were characterized by phloridzin, chlorogenic acid, quercetin, and related derivatives respectively. The 20 apple varieties showed a significant difference (* P < 0.05) in browning variation in the drying process. The browning at the initial stage was mainly L* declined, which was induced by polyphenols enzymatic oxidation. While the browning was characterized by b* and a* value increment at the end of the drying process, where the Maillard reaction was the dominant factor.
Conclusions:
The correlation distance between the main phenolic compounds in apple core, flesh, and peel with the average chromatic L*, a*, and b* values varied at different stages of the drying process.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2023.00006

Aim:
The aim of this study is to comprehensively investigate the distribution of amine and phenol compounds in different flavors of Baijiu.
Methods:
12C-/13C-dansyl chloride labeling was applied for untargeted and quantitative analyses of amine and phenol compounds in Baijiu.
Results:
A total of 267 amine/phenol compounds were detected, and 30 of them were confirmed by the standards. 4 of 30 confirmed compounds were newly identified in Baijiu, and 16 ones were related with flavor or biological activity. After statistical analysis, 34 amine/phenol compounds were defined as potential markers for indicating sauce flavor, strong flavor, and light flavor Baijiu. 30 compounds in Baijiu were quantified with high precision, high accuracy, and high sensitivity. Results of the untargeted and quantitative analyses indicated that the number and contents of amine and phenol compounds were generally richest in sauce flavor Baijiu, while lowest in light flavor Baijiu.
Conclusions:
The results obtained in the research are beneficial for comprehensively understanding the amine and phenol compounds in Baijiu and further provide the basis for the flavor blending of Baijiu.
Aim:
The aim of this study is to comprehensively investigate the distribution of amine and phenol compounds in different flavors of Baijiu.
Methods:
12C-/13C-dansyl chloride labeling was applied for untargeted and quantitative analyses of amine and phenol compounds in Baijiu.
Results:
A total of 267 amine/phenol compounds were detected, and 30 of them were confirmed by the standards. 4 of 30 confirmed compounds were newly identified in Baijiu, and 16 ones were related with flavor or biological activity. After statistical analysis, 34 amine/phenol compounds were defined as potential markers for indicating sauce flavor, strong flavor, and light flavor Baijiu. 30 compounds in Baijiu were quantified with high precision, high accuracy, and high sensitivity. Results of the untargeted and quantitative analyses indicated that the number and contents of amine and phenol compounds were generally richest in sauce flavor Baijiu, while lowest in light flavor Baijiu.
Conclusions:
The results obtained in the research are beneficial for comprehensively understanding the amine and phenol compounds in Baijiu and further provide the basis for the flavor blending of Baijiu.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2023.00007

Aim:
This study aims to develop sensitive and reliable analytical technologies to enable the distinction between wild-caught and farmed fish through appropriate molecular markers to protect consumers from fraudulent fish labelling. Gilthead sea bream, Sparus aurata L. (S. aurata L.), is a very common fish used as foodstuff worldwide and globally produced in aquaculture in the Mediterranean basin. Wild-caught and farmed species are very different in feed and lifestyle and the quality and safety of these products strongly depend on fish growth, processing history, and storage conditions.
Methods:
Hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography (HILIC) coupled with electrospray ionization (ESI) and Fourier-transform mass spectrometry (FTMS; HILIC-ESI-FTMS) was employed to discriminate the phospholipidome profiles of fillets extracts of wild-caught from farmed gilthead sea breams.
Results:
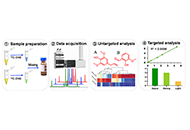
The untargeted approach led to the annotation of a total of 216 phospholipids (PLs), namely 65 phosphatidylethanolamines (PEs), 27 lyso-PEs (LPEs), 61 phosphatidylcholines (PCs), 34 lyso-PCs (LPCs), and 29 sphingomyelins (SMs). Untargeted lipidomics data were investigated by principal component analysis (PCA) and K-means clustering. Lyso-PLs (LPLs) of PEs and PCs including ether-linked side chains were found as discriminating markers between the two types of fish samples. The PLs that were most responsible for distinguishing between the lipid extracts of farmed and wild S. aurata fillets were successfully characterized by tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS). The analysis revealed that wild fillet lipid extracts contained some PE exhibiting ether bonds (PE P-), viz. 16:0, 18:0, 18:1, and 18:2 and polyunsaturated fatty acyl chains (i.e., 22:6 and 22:5). In farmed species, the estimated abundance ratios of fatty acyl chains 20:4/18:2 and 22:6/20:5 were 0.9 and 0.05, respectively. However, in wild-caught fish, these ratios were found to be two-fold higher and four-fold higher, respectively.
Conclusions:
This work demonstrates that the combination of HILIC-ESI-FTMS and chemometrics can serve as a valuable tool for evaluating fish authenticity and assessing quality concerns by monitoring specific lipid ratios.
Aim:
This study aims to develop sensitive and reliable analytical technologies to enable the distinction between wild-caught and farmed fish through appropriate molecular markers to protect consumers from fraudulent fish labelling. Gilthead sea bream, Sparus aurata L. (S. aurata L.), is a very common fish used as foodstuff worldwide and globally produced in aquaculture in the Mediterranean basin. Wild-caught and farmed species are very different in feed and lifestyle and the quality and safety of these products strongly depend on fish growth, processing history, and storage conditions.
Methods:
Hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography (HILIC) coupled with electrospray ionization (ESI) and Fourier-transform mass spectrometry (FTMS; HILIC-ESI-FTMS) was employed to discriminate the phospholipidome profiles of fillets extracts of wild-caught from farmed gilthead sea breams.
Results:
The untargeted approach led to the annotation of a total of 216 phospholipids (PLs), namely 65 phosphatidylethanolamines (PEs), 27 lyso-PEs (LPEs), 61 phosphatidylcholines (PCs), 34 lyso-PCs (LPCs), and 29 sphingomyelins (SMs). Untargeted lipidomics data were investigated by principal component analysis (PCA) and K-means clustering. Lyso-PLs (LPLs) of PEs and PCs including ether-linked side chains were found as discriminating markers between the two types of fish samples. The PLs that were most responsible for distinguishing between the lipid extracts of farmed and wild S. aurata fillets were successfully characterized by tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS). The analysis revealed that wild fillet lipid extracts contained some PE exhibiting ether bonds (PE P-), viz. 16:0, 18:0, 18:1, and 18:2 and polyunsaturated fatty acyl chains (i.e., 22:6 and 22:5). In farmed species, the estimated abundance ratios of fatty acyl chains 20:4/18:2 and 22:6/20:5 were 0.9 and 0.05, respectively. However, in wild-caught fish, these ratios were found to be two-fold higher and four-fold higher, respectively.
Conclusions:
This work demonstrates that the combination of HILIC-ESI-FTMS and chemometrics can serve as a valuable tool for evaluating fish authenticity and assessing quality concerns by monitoring specific lipid ratios.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2023.00008

Aim:
The aim of this study is to apply untargeted proton nuclear magnetic resonance (1H NMR) and chemometric analysis to obtain the cacao pod husk (CPH) fingerprint and evaluate the effect of dehydration in the CPH metabolome.
Methods:
Phosphate buffer extracts (pH 6.5) were obtained and measured using a one-dimension (1D) 1H NMR spectrometry. The 1D 1H NMR spectra were recorded without spinning and using the presaturation (PRESAT) pulse sequence to suppress the residual H2O signal. The 3-(trimethylsilyl) propionic-2,2,3,3-d4 acid sodium salt (TSP) was used as an internal reference. Analysis of processed data, applying an orthogonal projection on latent structure-discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA) model was used to highlight significant differences between the three dehydration treatments. Signal assignment of CPH metabolites was carried out based on the coupling constant, software simulation prediction, published data comparison, and metabolomics databases.
Results:
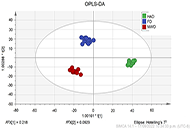
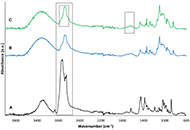
A total of 25 compounds were detected by 1H NMR, methylxanthines, sugars, some amino acids, fatty acids, and organic acids were found among the identified compounds. The fingerprint spectra of the three dehydration methods were clustered separately discriminating the metabolome profile of each of the dehydration treatments, finding that metabolome remarkably differed in theanine, myristic acid, fumaric acid, and aspartic acid composition.
Conclusions:
An untargeted metabolomics to obtain the fingerprint of CPH was successfully established. A 1H NMR spectra with a detailed signal assignment aided to identify 25 metabolites present in CPH fresh and dried by different methods. The results complement the information about CPH composition and how it is affected by the temperature used during the dehydration process. The multivariate analysis points out that freeze drying (FD) preserves the metabolites better than microwave drying (MWD) or hot air drying (HAD). FD and MWD are similar in composition maintaining most of the compounds after drying.
Aim:
The aim of this study is to apply untargeted proton nuclear magnetic resonance (1H NMR) and chemometric analysis to obtain the cacao pod husk (CPH) fingerprint and evaluate the effect of dehydration in the CPH metabolome.
Methods:
Phosphate buffer extracts (pH 6.5) were obtained and measured using a one-dimension (1D) 1H NMR spectrometry. The 1D 1H NMR spectra were recorded without spinning and using the presaturation (PRESAT) pulse sequence to suppress the residual H2O signal. The 3-(trimethylsilyl) propionic-2,2,3,3-d4 acid sodium salt (TSP) was used as an internal reference. Analysis of processed data, applying an orthogonal projection on latent structure-discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA) model was used to highlight significant differences between the three dehydration treatments. Signal assignment of CPH metabolites was carried out based on the coupling constant, software simulation prediction, published data comparison, and metabolomics databases.
Results:
A total of 25 compounds were detected by 1H NMR, methylxanthines, sugars, some amino acids, fatty acids, and organic acids were found among the identified compounds. The fingerprint spectra of the three dehydration methods were clustered separately discriminating the metabolome profile of each of the dehydration treatments, finding that metabolome remarkably differed in theanine, myristic acid, fumaric acid, and aspartic acid composition.
Conclusions:
An untargeted metabolomics to obtain the fingerprint of CPH was successfully established. A 1H NMR spectra with a detailed signal assignment aided to identify 25 metabolites present in CPH fresh and dried by different methods. The results complement the information about CPH composition and how it is affected by the temperature used during the dehydration process. The multivariate analysis points out that freeze drying (FD) preserves the metabolites better than microwave drying (MWD) or hot air drying (HAD). FD and MWD are similar in composition maintaining most of the compounds after drying.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2023.00009

Aim:
This study aimed to isolate, characterize, and encapsulate a lupeol-rich fraction obtained from the hexanic extract of Coccoloba uvifera L. leaves to evaluate its potential use in nutraceutical or pharmaceutical applications.
Methods:
The C. uvifera leaf extract was fractionated by column chromatography and the presence of lupeol was assessed by thin layer chromatography, attenuated total reflection-Fourier transform infrared (ATR-FTIR) spectroscopy, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS). Additionally, the lupeol-rich fraction was characterized according to its antioxidant capacity and cytotoxicity. Finally, this fraction was encapsulated into electrospun nanofibers made of high degree of polymerization agave fructans (HDPAF) combined with polyethylene oxide (PEO). The obtained nanofibers were characterized in terms of morphology, chemical composition, and in vitro permeability using the Caco-2 cell line.
Results:
Fraction 6 showed a 77% of lupeol, quantified by chromatography, and presented a 7.3% inhibition of 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH). 100 µg/mL of fraction 6 showed a decrease in Caco-2 cell viability. Finally, fraction 6 was encapsulated into electrospun nanofibers, which showed an increase in the apparent permeability of the lupeol present in fraction 6 in Caco-2 cells in comparison to neat fraction 6.
Conclusions:
It was possible to isolate and encapsulate a lupeol-rich fraction from C. uvifera into electrospun nanofibers, which allows the increasing the apparent permeability of lupeol, and consequently, they could be used for nutraceutical or pharmaceutical applications.
Aim:
This study aimed to isolate, characterize, and encapsulate a lupeol-rich fraction obtained from the hexanic extract of Coccoloba uvifera L. leaves to evaluate its potential use in nutraceutical or pharmaceutical applications.
Methods:
The C. uvifera leaf extract was fractionated by column chromatography and the presence of lupeol was assessed by thin layer chromatography, attenuated total reflection-Fourier transform infrared (ATR-FTIR) spectroscopy, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS). Additionally, the lupeol-rich fraction was characterized according to its antioxidant capacity and cytotoxicity. Finally, this fraction was encapsulated into electrospun nanofibers made of high degree of polymerization agave fructans (HDPAF) combined with polyethylene oxide (PEO). The obtained nanofibers were characterized in terms of morphology, chemical composition, and in vitro permeability using the Caco-2 cell line.
Results:
Fraction 6 showed a 77% of lupeol, quantified by chromatography, and presented a 7.3% inhibition of 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH). 100 µg/mL of fraction 6 showed a decrease in Caco-2 cell viability. Finally, fraction 6 was encapsulated into electrospun nanofibers, which showed an increase in the apparent permeability of the lupeol present in fraction 6 in Caco-2 cells in comparison to neat fraction 6.
Conclusions:
It was possible to isolate and encapsulate a lupeol-rich fraction from C. uvifera into electrospun nanofibers, which allows the increasing the apparent permeability of lupeol, and consequently, they could be used for nutraceutical or pharmaceutical applications.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2023.00010
This article belongs to the special issue Natural Products in Health and Disease

Aim:
As far as is known, the pharmaceutical effects of neem on human B-lymphoblastoid (TK6) cells have not been studied until now. Hence, the present study aimed to obtain neem phenolic extracts for inhibits the proliferation of TK6 cells and explore some possible underlying mechanisms involved in these effects.
Methods:
Hexane extract (HE) was obtained in the first step. After that, the residual hexane was removed from the neem. The dried neem sample was used in a new extraction for obtaining the ethyl acetate extract (EAE). Total phenolic compounds (TPC) and total flavonoid contents (TFC) were determined by spectrophotometric methods. Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) tests were used to evaluate the cytotoxicity in TK6 cells. The stop at G0/G1 cell cycle and inducing apoptosis in the TK6 cells were analyzed by flow cytometry. For deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) damage evaluation, the alkaline comet test was used.
Results:
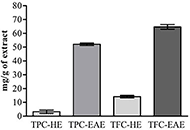
The higher TFC (65.50 mg/g of extract ± 1.17 mg/g of extract) and TPC (52.08 mg of extract ± 0.88 mg of extract) were obtained in EAE compared to HE that was obtained TFC of 14.61 mg/g of extract ± 0.60 mg/g of extract and TPC of 3.20 mg/g of extract ± 1.20 mg/g of extract. EAE was more significantly cytotoxic to TK6 cells than HE. The apoptosis induction was higher after exposure to 15.0 µg/mL of EAE (11.29%) in comparison to 15.0 µg/mL of HE (2.52%). The G0/G1 phase increased from 72% negative control (NC) to 83% after treatment with neem extracts (15 µg/mL). Neem extracts were also able to cause DNA strand breaks in TK6 cells.
Conclusions:
The extraction residue from neem leaf after hexane extraction is a source important of cytotoxic and genotoxic molecules against TK6 cells, the results also can suggest that the toxic effects in TK6 cells can be provided most likely due to the presence of high content of TPC from neem extracts.
Aim:
As far as is known, the pharmaceutical effects of neem on human B-lymphoblastoid (TK6) cells have not been studied until now. Hence, the present study aimed to obtain neem phenolic extracts for inhibits the proliferation of TK6 cells and explore some possible underlying mechanisms involved in these effects.
Methods:
Hexane extract (HE) was obtained in the first step. After that, the residual hexane was removed from the neem. The dried neem sample was used in a new extraction for obtaining the ethyl acetate extract (EAE). Total phenolic compounds (TPC) and total flavonoid contents (TFC) were determined by spectrophotometric methods. Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) tests were used to evaluate the cytotoxicity in TK6 cells. The stop at G0/G1 cell cycle and inducing apoptosis in the TK6 cells were analyzed by flow cytometry. For deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) damage evaluation, the alkaline comet test was used.
Results:
The higher TFC (65.50 mg/g of extract ± 1.17 mg/g of extract) and TPC (52.08 mg of extract ± 0.88 mg of extract) were obtained in EAE compared to HE that was obtained TFC of 14.61 mg/g of extract ± 0.60 mg/g of extract and TPC of 3.20 mg/g of extract ± 1.20 mg/g of extract. EAE was more significantly cytotoxic to TK6 cells than HE. The apoptosis induction was higher after exposure to 15.0 µg/mL of EAE (11.29%) in comparison to 15.0 µg/mL of HE (2.52%). The G0/G1 phase increased from 72% negative control (NC) to 83% after treatment with neem extracts (15 µg/mL). Neem extracts were also able to cause DNA strand breaks in TK6 cells.
Conclusions:
The extraction residue from neem leaf after hexane extraction is a source important of cytotoxic and genotoxic molecules against TK6 cells, the results also can suggest that the toxic effects in TK6 cells can be provided most likely due to the presence of high content of TPC from neem extracts.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2023.00011

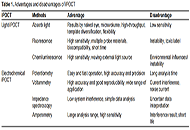
The on-site, rapid, and intelligence detection methods are the wave in food safety. Recently, intelligent point-of-care test (iPOCT) methods serve as a promising alternative for advanced monitoring in food safety. By integrating smartphones with various detection methods, iPOCT methods demonstrate unique merits. Compared with lab-dependent instruments, iPOCT strategies have a short turnaround time (several minutes), high accuracy (μm level or less), and portability (smartphones). This work discussed principles of optical and electrical iPOCT methods, including absorbing light, fluorescence, chemiluminescence, potentiometry, voltammetry, impedance spectroscopy, and amperometry. The review emphasizes the practical applications for testing chemical and biological hazards in complex food matrices. The commercialization, challenges, and future trends of iPOCT are discussed as well.
The on-site, rapid, and intelligence detection methods are the wave in food safety. Recently, intelligent point-of-care test (iPOCT) methods serve as a promising alternative for advanced monitoring in food safety. By integrating smartphones with various detection methods, iPOCT methods demonstrate unique merits. Compared with lab-dependent instruments, iPOCT strategies have a short turnaround time (several minutes), high accuracy (μm level or less), and portability (smartphones). This work discussed principles of optical and electrical iPOCT methods, including absorbing light, fluorescence, chemiluminescence, potentiometry, voltammetry, impedance spectroscopy, and amperometry. The review emphasizes the practical applications for testing chemical and biological hazards in complex food matrices. The commercialization, challenges, and future trends of iPOCT are discussed as well.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2023.00012

Aim:
In this study, Polyphenol and chemical profiles in core, pulp, and peel of 7 apple varieties [Fuji (FS), Qinguan (QG), Qingping (QP), Jinshuai (JS), Gala (GL), Changmiou (CMO), and Huahong (HH)] were comparatively studied to distinguish the different metabolism biomarkers in the three parts of apple fruit.
Methods:
This study investigated the distribution of 15 polyphenolic compounds using a combination of multivariate analysis and ultra-performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS).
Results:
chlorogenic acid, catechin, epicatechin, phloretin were the most abundant components. While phloretin was the dominant component in core, chlorogenic acid was the main phenolic compound in pulp, and quercetin was mainly found in apple peel. The multivariate analysis showed that the chemical profile of peel was significantly distinct from that of apple pulp and core, whereas apple pulp and core overlapped with each other. The difference attributed to the compounds that were predicted from ultra-high performance liquid chromatography combined with quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS), which were remarkably different (P < 0.05) and belong to polyphenol.
Conclusions:
It indicates that the potential superior biomarker of polyphenols is to differentiate the products from apple core, pulp, and peel respectively. This research provided an insight on the polyphenolic profile of core, pulp, and peel of apple fruits.
Aim:
In this study, Polyphenol and chemical profiles in core, pulp, and peel of 7 apple varieties [Fuji (FS), Qinguan (QG), Qingping (QP), Jinshuai (JS), Gala (GL), Changmiou (CMO), and Huahong (HH)] were comparatively studied to distinguish the different metabolism biomarkers in the three parts of apple fruit.
Methods:
This study investigated the distribution of 15 polyphenolic compounds using a combination of multivariate analysis and ultra-performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS).
Results:
chlorogenic acid, catechin, epicatechin, phloretin were the most abundant components. While phloretin was the dominant component in core, chlorogenic acid was the main phenolic compound in pulp, and quercetin was mainly found in apple peel. The multivariate analysis showed that the chemical profile of peel was significantly distinct from that of apple pulp and core, whereas apple pulp and core overlapped with each other. The difference attributed to the compounds that were predicted from ultra-high performance liquid chromatography combined with quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS), which were remarkably different (P < 0.05) and belong to polyphenol.
Conclusions:
It indicates that the potential superior biomarker of polyphenols is to differentiate the products from apple core, pulp, and peel respectively. This research provided an insight on the polyphenolic profile of core, pulp, and peel of apple fruits.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2023.00013

DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2022.00001

Aim:
The scope of the present study was to investigate the phytochemical profile of Psidium guajava and Carica papaya leaves aqueous extracts, from plants cultivated on Crete island in Greece.
Methods:
Total phenolic content (TPC) in the aqueous extracts was determined spectrometrically using the Folin-Ciocalteu (F-C) assay. The identification and quantification of different phenolic compounds in the aqueous extracts were conducted using reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC) analysis. Different metals were also determined (K, Fe, Zn, Ca, Mg, Pb, and Cd) to investigate the potential health claims or hazards in the water extractable infusion using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) method.
Results:
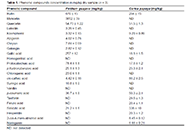
TPC in the aqueous extracts was found to be 28.0 g gallic acid equivalent (GAE)/kg dry leaves for Psidium guajava leaves aqueous extract and 15.0 g GAE/kg dry leaves for Carica papaya leaves aqueous extract. The dominant phenolic compounds in Psidium guajava leaves aqueous extract were myricetin (3,852 mg/kg dry sample) and rutin (670 mg/kg dry sample) while the dominant phenolic compounds in Carica papaya leaves aqueous extract were salicylic acid (338 mg/kg dry sample) and rutin (264 mg/kg dry sample). Different metals were also determined (K, Fe, Zn, Ca, Mg, Pb, and Cd) to investigate the potential health claims or hazards in the water extractable infusion, and it was found that no toxic metals were extracted whereas some nutritional benefits were achieved.
Conclusions:
Results proved that Psidium guajava and Carica papaya can be provided a strong antioxidant activity and can be used as medicinal plants.
Aim:
The scope of the present study was to investigate the phytochemical profile of Psidium guajava and Carica papaya leaves aqueous extracts, from plants cultivated on Crete island in Greece.
Methods:
Total phenolic content (TPC) in the aqueous extracts was determined spectrometrically using the Folin-Ciocalteu (F-C) assay. The identification and quantification of different phenolic compounds in the aqueous extracts were conducted using reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC) analysis. Different metals were also determined (K, Fe, Zn, Ca, Mg, Pb, and Cd) to investigate the potential health claims or hazards in the water extractable infusion using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) method.
Results:
TPC in the aqueous extracts was found to be 28.0 g gallic acid equivalent (GAE)/kg dry leaves for Psidium guajava leaves aqueous extract and 15.0 g GAE/kg dry leaves for Carica papaya leaves aqueous extract. The dominant phenolic compounds in Psidium guajava leaves aqueous extract were myricetin (3,852 mg/kg dry sample) and rutin (670 mg/kg dry sample) while the dominant phenolic compounds in Carica papaya leaves aqueous extract were salicylic acid (338 mg/kg dry sample) and rutin (264 mg/kg dry sample). Different metals were also determined (K, Fe, Zn, Ca, Mg, Pb, and Cd) to investigate the potential health claims or hazards in the water extractable infusion, and it was found that no toxic metals were extracted whereas some nutritional benefits were achieved.
Conclusions:
Results proved that Psidium guajava and Carica papaya can be provided a strong antioxidant activity and can be used as medicinal plants.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2023.00002

Among the species of the rich algological flora of the North Atlantic, some can be used for direct consumption in human food, although few are currently cultivated on a large scale and/or marketed for this purpose. The European tradition regarding this custom is practically nil and the expression of current eating habits is little different from the past. In Europe, only in times of hunger (for example, during the Great World Wars) was seaweed consumed by the populations closest to the coastline. In addition to the multiple applications described, which expanded enormously in the 1970s, based on phycocolloids (agar, carrageenans, and alginates)—used as thickeners in the food industry, in soups, meat preserves, dairy products, and pastries—there is currently a trend of increasing consumption, both in North America and Europe.
Among the species of the rich algological flora of the North Atlantic, some can be used for direct consumption in human food, although few are currently cultivated on a large scale and/or marketed for this purpose. The European tradition regarding this custom is practically nil and the expression of current eating habits is little different from the past. In Europe, only in times of hunger (for example, during the Great World Wars) was seaweed consumed by the populations closest to the coastline. In addition to the multiple applications described, which expanded enormously in the 1970s, based on phycocolloids (agar, carrageenans, and alginates)—used as thickeners in the food industry, in soups, meat preserves, dairy products, and pastries—there is currently a trend of increasing consumption, both in North America and Europe.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2023.00003
This article belongs to the special issue The food (r)evolution towards food quality/security and human nutrition

Aim:
In this work, the development for the first time of a green and efficient method to obtain bioactive extracts from Mentha x rotundifolia leaves has been investigated.
Methods:
The efficiency of three techniques [microwave-assisted extraction (MAE), subcritical water extraction (SWE), and ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE)] was compared in terms of total phenolic content (TPC) and antioxidant activity [1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) and 2,2’-azino-bis (3-ethylbenzthioazoline-6-sulfonic acid) (ABTS) assays].
Results:
Under similar operating conditions, SWE outperformed MAE and UAE for providing M. rotundifolia extracts with improved antioxidant activity. Further in-depth optimization of the SWE method by means of a Box-Behnken experimental design showed 120°C, 5 min, 0.08 g dry sample: 1 mL water and 2 extraction cycles as optimal experimental parameters to provide the maximum yield of phenolics and the highest bioactivity. The application of the developed SWE method to M. rotundifolia leaves collected in different annuities (2014–2017) showed, in general, no significant differences regarding both composition and antioxidant capacity, as expected from plant samples grown in field under drip irrigation conditions.
Conclusions:
The SWE method here optimized is shown as a sustainable and efficient alternative for providing bioactive M. rotundifolia extracts with application as functional ingredients, natural preservatives, etc. in the food industry, among others.
Aim:
In this work, the development for the first time of a green and efficient method to obtain bioactive extracts from Mentha x rotundifolia leaves has been investigated.
Methods:
The efficiency of three techniques [microwave-assisted extraction (MAE), subcritical water extraction (SWE), and ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE)] was compared in terms of total phenolic content (TPC) and antioxidant activity [1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) and 2,2’-azino-bis (3-ethylbenzthioazoline-6-sulfonic acid) (ABTS) assays].
Results:
Under similar operating conditions, SWE outperformed MAE and UAE for providing M. rotundifolia extracts with improved antioxidant activity. Further in-depth optimization of the SWE method by means of a Box-Behnken experimental design showed 120°C, 5 min, 0.08 g dry sample: 1 mL water and 2 extraction cycles as optimal experimental parameters to provide the maximum yield of phenolics and the highest bioactivity. The application of the developed SWE method to M. rotundifolia leaves collected in different annuities (2014–2017) showed, in general, no significant differences regarding both composition and antioxidant capacity, as expected from plant samples grown in field under drip irrigation conditions.
Conclusions:
The SWE method here optimized is shown as a sustainable and efficient alternative for providing bioactive M. rotundifolia extracts with application as functional ingredients, natural preservatives, etc. in the food industry, among others.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2023.00004

Nanoscience and nanotechnology have experienced a dizzying development in recent years, which undoubtedly contributes to various fields of human activity such as biotechnology, engineering, medical sciences, food security, etc. This impact has taken place in the food field too, especially in the role played by nanomaterials (NMs) for producing quality nano-based products, food shelf life, and target-specific bioactive delivery, since traditionally the presence of these materials was not at the nano-scale. Anyway, switching these materials to their nano-forms carries benefits as well as risks that must be assessed. Thus, the evaluation of the presence and quantity of these NMs must be achieved based on reliable physic-chemical-analytical information; hence the impact that analytical chemistry should have in the nanoscience to develop validated methodologies for its control. Currently, this fact represents a significant challenge due to the difficulties of measuring entities at the nanoscale in complex samples such as those of food. This review critically explores these analytical challenges, their difficulties, and their trends within the general framework of NMs’ analytical monitoring in food.
Nanoscience and nanotechnology have experienced a dizzying development in recent years, which undoubtedly contributes to various fields of human activity such as biotechnology, engineering, medical sciences, food security, etc. This impact has taken place in the food field too, especially in the role played by nanomaterials (NMs) for producing quality nano-based products, food shelf life, and target-specific bioactive delivery, since traditionally the presence of these materials was not at the nano-scale. Anyway, switching these materials to their nano-forms carries benefits as well as risks that must be assessed. Thus, the evaluation of the presence and quantity of these NMs must be achieved based on reliable physic-chemical-analytical information; hence the impact that analytical chemistry should have in the nanoscience to develop validated methodologies for its control. Currently, this fact represents a significant challenge due to the difficulties of measuring entities at the nanoscale in complex samples such as those of food. This review critically explores these analytical challenges, their difficulties, and their trends within the general framework of NMs’ analytical monitoring in food.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2023.00005

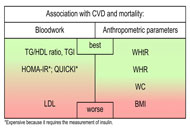
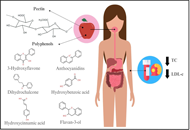
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) stands as the leading global cause of mortality, underscoring the critical need for practical tools to assess CVD risk at an early stage. An accessible approach involves the evaluation of bloodwork alongside simple anthropometric measurements. This narrative review seeks to establish the appropriateness of common parameters used in the outpatient setting in assessing the risk of developing CVD. These parameters encompass bloodwork values employed to characterize insulin resistance (IR) and dyslipidemia, as well as anthropometric measurements used to describe issues related to overweight and fat distribution. A particular emphasis is placed on understanding how Mediterranean and ketogenic diets influence these parameters. In the realm of bloodwork, findings indicate that the triglycerides (TG) to high-density lipoproteins (HDL) ratio serves as a valuable tool for assessing both IR and dyslipidemia. Less emphasis should be placed on total cholesterol and low-density lipoproteins (LDL) because the existing literature lacks consistency and fails to establish a clear, direct correlation between cholesterol levels, CVD, and mortality. On the other hand, numerous studies consistently demonstrate a direct correlation between CVD, mortality, and the levels of small-dense LDL (sdLDL), which represent the oxidized form of LDL. Regarding anthropometric parameters, the body mass index (BMI) falls short in value as it neglects to consider fat distribution and lean mass. More informative are anthropometric parameters that account for a single measure of fat mass and another for lean mass, such as the waist-height ratio (WHtR) or the waist-hip ratio (WHR). Both Mediterranean and ketogenic diets demonstrate improvements across major parameters used to evaluate CVD and mortality risk. The ketogenic diet, in particular, yields superior results in most aspects, except cholesterol levels. Further studies are recommended to refine dyslipidemia characterization and its connection to health outcomes.
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) stands as the leading global cause of mortality, underscoring the critical need for practical tools to assess CVD risk at an early stage. An accessible approach involves the evaluation of bloodwork alongside simple anthropometric measurements. This narrative review seeks to establish the appropriateness of common parameters used in the outpatient setting in assessing the risk of developing CVD. These parameters encompass bloodwork values employed to characterize insulin resistance (IR) and dyslipidemia, as well as anthropometric measurements used to describe issues related to overweight and fat distribution. A particular emphasis is placed on understanding how Mediterranean and ketogenic diets influence these parameters. In the realm of bloodwork, findings indicate that the triglycerides (TG) to high-density lipoproteins (HDL) ratio serves as a valuable tool for assessing both IR and dyslipidemia. Less emphasis should be placed on total cholesterol and low-density lipoproteins (LDL) because the existing literature lacks consistency and fails to establish a clear, direct correlation between cholesterol levels, CVD, and mortality. On the other hand, numerous studies consistently demonstrate a direct correlation between CVD, mortality, and the levels of small-dense LDL (sdLDL), which represent the oxidized form of LDL. Regarding anthropometric parameters, the body mass index (BMI) falls short in value as it neglects to consider fat distribution and lean mass. More informative are anthropometric parameters that account for a single measure of fat mass and another for lean mass, such as the waist-height ratio (WHtR) or the waist-hip ratio (WHR). Both Mediterranean and ketogenic diets demonstrate improvements across major parameters used to evaluate CVD and mortality risk. The ketogenic diet, in particular, yields superior results in most aspects, except cholesterol levels. Further studies are recommended to refine dyslipidemia characterization and its connection to health outcomes.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2023.00019
This article belongs to the special issue Ketogenic Diet as Medical Nutrition Therapy

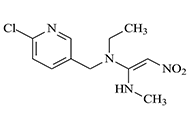
Nitenpyram (NIT) and dinotefuran (DNF) are neonicotinoid pesticides commonly used in the production and storage of agricultural products, as well as in forests and gardens, for the purpose of protection from insect pests. Although they are safer for mammals, their toxic effects on pollinators, such as bees, and their long-term accumulation in water and soil, are important problems. Therefore, it is crucial to ensure that their usage remains within certain specific limits and that their residues are quickly, precisely, and reliably monitored in various samples. In this review, electrochemical methods, which are voltammetry, amperometry, and potentiometry, for the determination of NIT and DNF in pure solutions, agricultural, and environmental samples by using various modified electrodes were reviewed. The results obtained from studies published since 2011 were compared, and the effectiveness of the selected methods was demonstrated. It was observed that the electrochemical methods, particularly voltammetry, used in the studies conducted for NIT and DNF yielded selective and sensitive results at detection limits at nmol L–1 levels. These methods also exhibited high precision and accuracy without being affected by the matrix of the studied samples, such as soil, water, or agricultural products.
Nitenpyram (NIT) and dinotefuran (DNF) are neonicotinoid pesticides commonly used in the production and storage of agricultural products, as well as in forests and gardens, for the purpose of protection from insect pests. Although they are safer for mammals, their toxic effects on pollinators, such as bees, and their long-term accumulation in water and soil, are important problems. Therefore, it is crucial to ensure that their usage remains within certain specific limits and that their residues are quickly, precisely, and reliably monitored in various samples. In this review, electrochemical methods, which are voltammetry, amperometry, and potentiometry, for the determination of NIT and DNF in pure solutions, agricultural, and environmental samples by using various modified electrodes were reviewed. The results obtained from studies published since 2011 were compared, and the effectiveness of the selected methods was demonstrated. It was observed that the electrochemical methods, particularly voltammetry, used in the studies conducted for NIT and DNF yielded selective and sensitive results at detection limits at nmol L–1 levels. These methods also exhibited high precision and accuracy without being affected by the matrix of the studied samples, such as soil, water, or agricultural products.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2023.00020
This article belongs to the special issue New Generation Analytical Technologies in Food Analysis

Aim:
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) are among the main causes of death worldwide and dyslipidemias account for one of the risk factors for these diseases. Habitual apple consumption appears to be inversely associated with reduced cardiovascular risk. Then, this systematic review aims to investigate the effect of chronic apple consumption on the lipid profile of adults with dyslipidemia.
Methods:
A systematic search was performed in electronic databases, including PubMed, Embase, Web of Science and Scopus, without restriction of year of publication. Inclusion criteria were randomized clinical trials in humans that investigated the effect of chronic consumption of whole fresh or dried apple, for a period longer than two weeks of intervention on the lipid profile.
Results:
Based on the methodology used and following the pre-established search strategies, 4,468 articles were found. After applying the inclusion and exclusion criteria, five articles were selected for qualitative evaluation, covering 522 adult participants of both sexes. Three randomized controlled trials included in this review demonstrated that there was a decrease in plasma total cholesterol (TC), triglyceride and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-c) concentrations, in addition to an increase in high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-c) concentration. Two other studies found different results. Low risk of bias was identified in three studies.
Conclusions:
The analysis of the studies indicates that the consumption of fresh and/or dried apples with the peel has a beneficial effect on the lipid profile of adults, with a decrease in TC and LDL-c. These effects may be related to polyphenols and soluble fibers, among other functional compounds present in this fruit.
Aim:
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) are among the main causes of death worldwide and dyslipidemias account for one of the risk factors for these diseases. Habitual apple consumption appears to be inversely associated with reduced cardiovascular risk. Then, this systematic review aims to investigate the effect of chronic apple consumption on the lipid profile of adults with dyslipidemia.
Methods:
A systematic search was performed in electronic databases, including PubMed, Embase, Web of Science and Scopus, without restriction of year of publication. Inclusion criteria were randomized clinical trials in humans that investigated the effect of chronic consumption of whole fresh or dried apple, for a period longer than two weeks of intervention on the lipid profile.
Results:
Based on the methodology used and following the pre-established search strategies, 4,468 articles were found. After applying the inclusion and exclusion criteria, five articles were selected for qualitative evaluation, covering 522 adult participants of both sexes. Three randomized controlled trials included in this review demonstrated that there was a decrease in plasma total cholesterol (TC), triglyceride and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-c) concentrations, in addition to an increase in high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-c) concentration. Two other studies found different results. Low risk of bias was identified in three studies.
Conclusions:
The analysis of the studies indicates that the consumption of fresh and/or dried apples with the peel has a beneficial effect on the lipid profile of adults, with a decrease in TC and LDL-c. These effects may be related to polyphenols and soluble fibers, among other functional compounds present in this fruit.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2023.00022

Aim:
This study aims to evaluate the sensory profile of corn-based extrudates fortified with phytosterol and pea protein isolates (PPI) using the fuzzy logic technique to assess similarity values and rank the quality attributes.
Methods:
Using a mix of yellow PPI (ranging from 0 to 20%) and corn flour (ranging from 80% to 100%), extrudates were developed, ensuring a consistent addition of phytosterol-containing oil at 5%. For this experiment, the Box-Behnken (BB) design was used, comprising 17 runs, factoring in parameters like the percentage of PPI (0–20%), screw speed (300–500 rpm), and temperature (130°–150°C). The optimal conditions were found to be 2.78% PPI, a screw speed of 451 rpm, and a temperature of 150°C, resulting in a desirability value of 0.725. For sensory evaluation, the fuzzy logic technique was used to compare the functional extrudates (S1) with commercial variants (S2, S3, and S4). This helped to gauge acceptance/rejection, similarity values, rankings, and overall consumer acceptability of the extrudates.
Results:
Commercial sample S4 achieved the highest ranking on the sensory scale as “very good”. When considering the quality attributes of extrudates, taste and mouthfeel were the most favored, followed by color and flavor. This study underscored the value of using fuzzy logic for sensory evaluation in determining the acceptance of new food products. It also proved effective in assessing food products’ quality attributes, especially after evaluating the phytosterol content post-extrusion.
Conclusions:
The fuzzy logic technique in sensory evaluation has effectively identified the optimal extrudates and their quality attributes during the development of new functional food.
Aim:
This study aims to evaluate the sensory profile of corn-based extrudates fortified with phytosterol and pea protein isolates (PPI) using the fuzzy logic technique to assess similarity values and rank the quality attributes.
Methods:
Using a mix of yellow PPI (ranging from 0 to 20%) and corn flour (ranging from 80% to 100%), extrudates were developed, ensuring a consistent addition of phytosterol-containing oil at 5%. For this experiment, the Box-Behnken (BB) design was used, comprising 17 runs, factoring in parameters like the percentage of PPI (0–20%), screw speed (300–500 rpm), and temperature (130°–150°C). The optimal conditions were found to be 2.78% PPI, a screw speed of 451 rpm, and a temperature of 150°C, resulting in a desirability value of 0.725. For sensory evaluation, the fuzzy logic technique was used to compare the functional extrudates (S1) with commercial variants (S2, S3, and S4). This helped to gauge acceptance/rejection, similarity values, rankings, and overall consumer acceptability of the extrudates.
Results:
Commercial sample S4 achieved the highest ranking on the sensory scale as “very good”. When considering the quality attributes of extrudates, taste and mouthfeel were the most favored, followed by color and flavor. This study underscored the value of using fuzzy logic for sensory evaluation in determining the acceptance of new food products. It also proved effective in assessing food products’ quality attributes, especially after evaluating the phytosterol content post-extrusion.
Conclusions:
The fuzzy logic technique in sensory evaluation has effectively identified the optimal extrudates and their quality attributes during the development of new functional food.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2023.00021

Aim:
Cynometra cauliflora (namnam) belongs to the family Fabaceae and is native to eastern Peninsular Malaysia. It grows well with an annual rainfall of 1,500–2,000 mm. Even though a considerable amount of research has been carried out with C. caulifora, there is a dearth of information about biomolecules that may pave the way for drug discoveries and food supplements, which is a gap addressed in this study.
Methods:
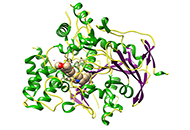
The study presented in this paper has identified several antimicrobial, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory substances, and an in silico approach was used to understand the behaviors of kaempferol-3-O-rhamnoside (K-3-Rh) and β-sitosterol acetate against Alzheimer’s disease (AD). The molecular dynamics (MD) simulations were performed with the selected protein ligand complex of two natural molecules and the synthetic ligand to analyze the dynamic behaviors and binding free energy throughout the 100 ns simulation time. Further, both natural molecules that were investigated comply with Lipinski’s drug-likeness rules.
Results:
The docking scores of both K-3-Rh and sitosterol were found to be compatible with the synthetic AD drug molecules [donepezil analogue (H0L)] used as a reference in the study. Hence, the phytochemicals of Cynometra caulifora showed comparatively similar potency against acetylcholinesterase (AChE).
Conclusions:
Overall, the potential binding affinity from molecular docking and static thermodynamics features from MD simulation suggest that K-3-Rh and β-sitosterol acetate could be considered as a potential therapeutic lead to inhibit AChE leading for AD treatment.
Aim:
Cynometra cauliflora (namnam) belongs to the family Fabaceae and is native to eastern Peninsular Malaysia. It grows well with an annual rainfall of 1,500–2,000 mm. Even though a considerable amount of research has been carried out with C. caulifora, there is a dearth of information about biomolecules that may pave the way for drug discoveries and food supplements, which is a gap addressed in this study.
Methods:
The study presented in this paper has identified several antimicrobial, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory substances, and an in silico approach was used to understand the behaviors of kaempferol-3-O-rhamnoside (K-3-Rh) and β-sitosterol acetate against Alzheimer’s disease (AD). The molecular dynamics (MD) simulations were performed with the selected protein ligand complex of two natural molecules and the synthetic ligand to analyze the dynamic behaviors and binding free energy throughout the 100 ns simulation time. Further, both natural molecules that were investigated comply with Lipinski’s drug-likeness rules.
Results:
The docking scores of both K-3-Rh and sitosterol were found to be compatible with the synthetic AD drug molecules [donepezil analogue (H0L)] used as a reference in the study. Hence, the phytochemicals of Cynometra caulifora showed comparatively similar potency against acetylcholinesterase (AChE).
Conclusions:
Overall, the potential binding affinity from molecular docking and static thermodynamics features from MD simulation suggest that K-3-Rh and β-sitosterol acetate could be considered as a potential therapeutic lead to inhibit AChE leading for AD treatment.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2024.00023
This article belongs to the special issue Natural Products in Health and Disease

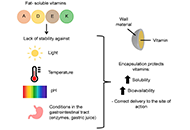
Vitamins are essential micronutrients for the functioning of the human body. Vitamins can be classified as water-soluble and fat-soluble, and are obtained through diet or supplementation. Fat-soluble vitamins include vitamin A, vitamin D, vitamin E, and vitamin K. These compounds are very sensitive to external factors, including light, oxygen, pH, and temperature. Lack of compound stability, poor solubility, and low permeability can compromise the bioavailability and usefulness of fat-soluble vitamins. The methodology of encapsulation of vitamins is currently being widely studied in order to improve their transportation and usage. Proteins (including protein isolates and concentrates) and carbohydrates derived from legumes are very interesting materials to coat compounds, considering their functional properties, and the fact that they are beneficial for the environment and human health. This review describes in detail the current knowledge about the use of legume protein and carbohydrates as materials for the encapsulation of fat-soluble vitamins. The functionality, health, and environmental advantages of legume fractions (particularly soy and pea fractions) as wall materials are also discussed. Future use of legume wastewater (soaking and cooking water derived from the treatment of legumes) as wall materials is evaluated as well. The study of encapsulation of fat-soluble vitamins by leguminous fractions is mainly focused on soy and pea protein isolates and concentrates and can still be expanded, considering the numerous benefits of encapsulation they provide. Research on encapsulation using legume carbohydrates is scarce and may be interesting due to their high encapsulation efficiency and easy digestibility. Saponins, proteins, and carbohydrates present in legume wastewaters could offer useful properties to encapsulation processes, while benefiting the environment.
Vitamins are essential micronutrients for the functioning of the human body. Vitamins can be classified as water-soluble and fat-soluble, and are obtained through diet or supplementation. Fat-soluble vitamins include vitamin A, vitamin D, vitamin E, and vitamin K. These compounds are very sensitive to external factors, including light, oxygen, pH, and temperature. Lack of compound stability, poor solubility, and low permeability can compromise the bioavailability and usefulness of fat-soluble vitamins. The methodology of encapsulation of vitamins is currently being widely studied in order to improve their transportation and usage. Proteins (including protein isolates and concentrates) and carbohydrates derived from legumes are very interesting materials to coat compounds, considering their functional properties, and the fact that they are beneficial for the environment and human health. This review describes in detail the current knowledge about the use of legume protein and carbohydrates as materials for the encapsulation of fat-soluble vitamins. The functionality, health, and environmental advantages of legume fractions (particularly soy and pea fractions) as wall materials are also discussed. Future use of legume wastewater (soaking and cooking water derived from the treatment of legumes) as wall materials is evaluated as well. The study of encapsulation of fat-soluble vitamins by leguminous fractions is mainly focused on soy and pea protein isolates and concentrates and can still be expanded, considering the numerous benefits of encapsulation they provide. Research on encapsulation using legume carbohydrates is scarce and may be interesting due to their high encapsulation efficiency and easy digestibility. Saponins, proteins, and carbohydrates present in legume wastewaters could offer useful properties to encapsulation processes, while benefiting the environment.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2024.00024
This article belongs to the special issue Delivery of Hydrophobic Compounds in Food Systems

Aim:
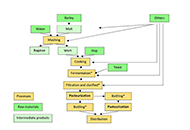
This study delves into the pasteurization process for craft beer, exploring its impact on containers and closures. Focusing on small breweries, it have been assess various treatments and find that batch immersion pasteurization post-bottling is optimal. Commercial crowns withstand pasteurization without altering the inner plastic material, crucial for extending the shelf life of craft beers, especially non-alcoholic variants.
Methods:
Artisanal pasteurization of craft beer batches was performed after evaluating available methods. Given the lack of literature on craft beer pasteurization, this study offers essential insights for the artisanal beer sector. Analyses of crown corks pre- and post-pasteurization were conducted using differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). Organoleptic analysis of pasteurized beers was also conducted.
Results:
DSC results indicate the film’s glass transition temperature (Tg) is around 62°C, while pasteurization at 66°C for 30 min did not degrade the polymer. Pressure retention and FTIR spectra show no clear differences between reference, pasteurized, and unpasteurized samples. Immersion pasteurization at 66°C with the analysed crowns is suitable for bottling craft beers without affecting polyvinyl chloride (PVC).
Conclusions:
The study concludes that the chosen pasteurization process does not impact crown PVC, ensuring its suitability for craft beer bottling. Severe pasteurization can alter beer qualities, but at 66°C, no such effects were observed in the organoleptic analysis.
Aim:
This study delves into the pasteurization process for craft beer, exploring its impact on containers and closures. Focusing on small breweries, it have been assess various treatments and find that batch immersion pasteurization post-bottling is optimal. Commercial crowns withstand pasteurization without altering the inner plastic material, crucial for extending the shelf life of craft beers, especially non-alcoholic variants.
Methods:
Artisanal pasteurization of craft beer batches was performed after evaluating available methods. Given the lack of literature on craft beer pasteurization, this study offers essential insights for the artisanal beer sector. Analyses of crown corks pre- and post-pasteurization were conducted using differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). Organoleptic analysis of pasteurized beers was also conducted.
Results:
DSC results indicate the film’s glass transition temperature (Tg) is around 62°C, while pasteurization at 66°C for 30 min did not degrade the polymer. Pressure retention and FTIR spectra show no clear differences between reference, pasteurized, and unpasteurized samples. Immersion pasteurization at 66°C with the analysed crowns is suitable for bottling craft beers without affecting polyvinyl chloride (PVC).
Conclusions:
The study concludes that the chosen pasteurization process does not impact crown PVC, ensuring its suitability for craft beer bottling. Severe pasteurization can alter beer qualities, but at 66°C, no such effects were observed in the organoleptic analysis.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2024.00025
This article belongs to the special issue The food (r)evolution towards food quality/security and human nutrition