-
29 results in Exploration of Endocrine and Metabolic DiseasesSort byMost Viewed
 The 2024 American Diabetes Association guidelines on Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes: key takeaways for laboratoryOpen AccessCommentaryThe escalating prevalence of diabetes poses a significant health concern. Uncontrolled diabetes leads to a multitude of complications. A comprehensive management plan and continual adaptation of gui [...] Read more.Dipti Tiwari, Tar Choon AwPublished: July 23, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:158–166
The 2024 American Diabetes Association guidelines on Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes: key takeaways for laboratoryOpen AccessCommentaryThe escalating prevalence of diabetes poses a significant health concern. Uncontrolled diabetes leads to a multitude of complications. A comprehensive management plan and continual adaptation of gui [...] Read more.Dipti Tiwari, Tar Choon AwPublished: July 23, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:158–166
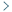
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eemd.2024.00013 Recent advances in artificial intelligence-assisted endocrinology and diabetesOpen AccessReviewArtificial intelligence (AI) has gained attention for various reasons in recent years, surrounded by speculation, concerns, and expectations. Despite being developed since 1960, its widespread appli [...] Read more.Ioannis T. Oikonomakos ... Stefan R. BornsteinPublished: April 01, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:16–26
Recent advances in artificial intelligence-assisted endocrinology and diabetesOpen AccessReviewArtificial intelligence (AI) has gained attention for various reasons in recent years, surrounded by speculation, concerns, and expectations. Despite being developed since 1960, its widespread appli [...] Read more.Ioannis T. Oikonomakos ... Stefan R. BornsteinPublished: April 01, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:16–26
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eemd.2023.00004 Glycemic trends, app engagement and achievement of gestational diabetes guideline targets using a diabetes app and Bluetooth® connected blood glucose metersOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Current diabetes guidelines recommend people with gestational diabetes mellitus (PwGDM) use primarily blood glucose meters (BGM) for diabetes management. We evaluated glycemic trends and gui [...] Read more.Mike Grady ... Elizabeth HoltPublished: July 24, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:167–176
Glycemic trends, app engagement and achievement of gestational diabetes guideline targets using a diabetes app and Bluetooth® connected blood glucose metersOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Current diabetes guidelines recommend people with gestational diabetes mellitus (PwGDM) use primarily blood glucose meters (BGM) for diabetes management. We evaluated glycemic trends and gui [...] Read more.Mike Grady ... Elizabeth HoltPublished: July 24, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:167–176
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eemd.2024.00014
This article belongs to the special issue The Impact of Digitalization To Improve Nutrition and Self-Management in Patients With Diabetes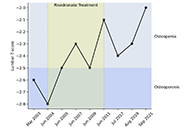 Beta thalassemia minor: a potential risk factor for osteopenia and osteoporosisOpen AccessCase ReportA 74-year-old male patient with beta thalassemia minor presented in 2022 for a follow-up of osteoporosis diagnosed prior to 2004. At the time of presentation, his medical history included: radiation [...] Read more.Felicia Woron ... Parvathy MadhavanPublished: October 31, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:213–217
Beta thalassemia minor: a potential risk factor for osteopenia and osteoporosisOpen AccessCase ReportA 74-year-old male patient with beta thalassemia minor presented in 2022 for a follow-up of osteoporosis diagnosed prior to 2004. At the time of presentation, his medical history included: radiation [...] Read more.Felicia Woron ... Parvathy MadhavanPublished: October 31, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:213–217
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eemd.2024.00017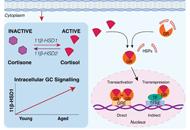 Endogenous glucocorticoids during skeletal ageingOpen AccessReviewStress hormones, namely glucocorticoids, have diverse actions throughout the body in regulating development, tissue metabolism, inflammation, circadian rhythms, and skeletal homeostasis. While endog [...] Read more.Eugenie Macfarlane ... Markus Joachim SeibelPublished: August 16, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:191–212
Endogenous glucocorticoids during skeletal ageingOpen AccessReviewStress hormones, namely glucocorticoids, have diverse actions throughout the body in regulating development, tissue metabolism, inflammation, circadian rhythms, and skeletal homeostasis. While endog [...] Read more.Eugenie Macfarlane ... Markus Joachim SeibelPublished: August 16, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:191–212
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eemd.2024.00016
This article belongs to the special issue The Fountain of Youth: Decoding the Hormonal Regulation of Aging Adult-onset testosterone deficiency: the usefulness of hormone replacement in reducing mortality in men with this common age-related conditionOpen AccessReviewAdult-onset testosterone deficiency (TD) in men is diagnosed by the finding of low serum testosterone levels and recognised, associated symptoms. The condition has high prevalence in men over 50 yea [...] Read more.Amar Mann ... Sudarshan RamachandranPublished: June 28, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:83–100
Adult-onset testosterone deficiency: the usefulness of hormone replacement in reducing mortality in men with this common age-related conditionOpen AccessReviewAdult-onset testosterone deficiency (TD) in men is diagnosed by the finding of low serum testosterone levels and recognised, associated symptoms. The condition has high prevalence in men over 50 yea [...] Read more.Amar Mann ... Sudarshan RamachandranPublished: June 28, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:83–100
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eemd.2024.00010
This article belongs to the special issue The Fountain of Youth: Decoding the Hormonal Regulation of Aging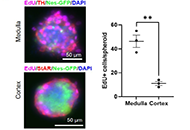 Development of adrenal 3-dimensional spheroid cultures: potential for the treatment of adrenal insufficiency and neurodegenerative diseasesOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Regenerative and curative strategies would be desirable for neurodegenerative and adrenal diseases, and multipotent adrenal stem cells are considered as promising biological tools for this p [...] Read more.Charlotte Steenblock ... Nicole BechmannPublished: April 01, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:27–38
Development of adrenal 3-dimensional spheroid cultures: potential for the treatment of adrenal insufficiency and neurodegenerative diseasesOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Regenerative and curative strategies would be desirable for neurodegenerative and adrenal diseases, and multipotent adrenal stem cells are considered as promising biological tools for this p [...] Read more.Charlotte Steenblock ... Nicole BechmannPublished: April 01, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:27–38
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eemd.2023.00005 Genome editing in the adrenal gland: a novel strategy for treating congenital adrenal hyperplasiaOpen AccessReviewCongenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency leads to high morbidity and mortality, despite the availability of life-saving corticosteroid replacement therapy. Gene therapy repres [...] Read more.Eva B. van Dijk ... Lara E. GravesPublished: July 09, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:101–121
Genome editing in the adrenal gland: a novel strategy for treating congenital adrenal hyperplasiaOpen AccessReviewCongenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency leads to high morbidity and mortality, despite the availability of life-saving corticosteroid replacement therapy. Gene therapy repres [...] Read more.Eva B. van Dijk ... Lara E. GravesPublished: July 09, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:101–121
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eemd.2024.00011
This article belongs to the special issue The HPA Axis in Health and Disease Application of chimeric antigen receptor-natural killer cells for the treatment of type 1 diabetesOpen AccessReviewFor the past 100 years, insulin supplementation has been the mainstay of treatment for type 1 diabetes (T1D), which is characterized by progressive autoimmune-mediated loss of insulin-producing β c [...] Read more.Charlotte Steenblock ... Stefan R. BornsteinPublished: April 01, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:4–11
Application of chimeric antigen receptor-natural killer cells for the treatment of type 1 diabetesOpen AccessReviewFor the past 100 years, insulin supplementation has been the mainstay of treatment for type 1 diabetes (T1D), which is characterized by progressive autoimmune-mediated loss of insulin-producing β c [...] Read more.Charlotte Steenblock ... Stefan R. BornsteinPublished: April 01, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:4–11
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eemd.2023.00002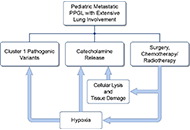 A case series of three patients with extensive lung metastatic pheochromocytoma/paraganglioma: evaluation, treatment challenges, and outcomesOpen AccessCase ReportPheochromocytomas (PCCs) and paragangliomas (PGLs; together PPGLs) are uncommon neuroendocrine tumors arising from adrenal medullary chromaffin cells and sympathetic/parasympathetic paraganglia. Tho [...] Read more.Kailah M. Charles ... Karel PacakPublished: November 15, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:218–233
A case series of three patients with extensive lung metastatic pheochromocytoma/paraganglioma: evaluation, treatment challenges, and outcomesOpen AccessCase ReportPheochromocytomas (PCCs) and paragangliomas (PGLs; together PPGLs) are uncommon neuroendocrine tumors arising from adrenal medullary chromaffin cells and sympathetic/parasympathetic paraganglia. Tho [...] Read more.Kailah M. Charles ... Karel PacakPublished: November 15, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:218–233
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eemd.2024.00018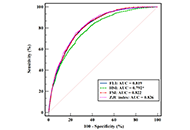 Four hepatic steatosis indices in predicting quantitative computed tomography-based metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver diseaseOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: To evaluate the prediction ability for quantitative computed tomography (QCT)-based metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) of four widely known hepatic steatosis algori [...] Read more.Bingwu Xu ... Yong ZhangPublished: May 23, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:62–76
Four hepatic steatosis indices in predicting quantitative computed tomography-based metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver diseaseOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: To evaluate the prediction ability for quantitative computed tomography (QCT)-based metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) of four widely known hepatic steatosis algori [...] Read more.Bingwu Xu ... Yong ZhangPublished: May 23, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:62–76
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eemd.2024.00008
This article belongs to the special issue Regulators of Glucose Homeostasis, Lipid Metabolism and Energy Balance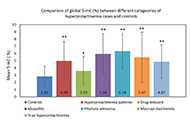 Epigenetics in etiopathology of hyperprolactinemiaOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Epigenetic alterations have been reported in patients with pituitary tumors and those on antipsychotic drugs, which are also responsible for hyperprolactinemia. This suggests a possible role [...] Read more.Amanpreet Kaur Kalsi ... Jai Bhagwan SharmaPublished: May 22, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:39–55
Epigenetics in etiopathology of hyperprolactinemiaOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Epigenetic alterations have been reported in patients with pituitary tumors and those on antipsychotic drugs, which are also responsible for hyperprolactinemia. This suggests a possible role [...] Read more.Amanpreet Kaur Kalsi ... Jai Bhagwan SharmaPublished: May 22, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:39–55
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eemd.2024.00006
This article belongs to the special issue The HPA Axis in Health and Disease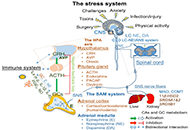 Hypothetical involvement of stress hormones-induced reprograming of adult stem/progenitor cells in tumorigenesisOpen AccessReviewStress is a state of threatened or perceived as threatened homeostasis that can be induced by various external and internal stimuli such as psychosocial factors, inflammatory or injurious conditions [...] Read more.Waldemar Kanczkowski ... George P. ChrousosPublished: July 15, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:122–157
Hypothetical involvement of stress hormones-induced reprograming of adult stem/progenitor cells in tumorigenesisOpen AccessReviewStress is a state of threatened or perceived as threatened homeostasis that can be induced by various external and internal stimuli such as psychosocial factors, inflammatory or injurious conditions [...] Read more.Waldemar Kanczkowski ... George P. ChrousosPublished: July 15, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:122–157
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eemd.2024.00012
This article belongs to the special issue The HPA Axis in Health and Disease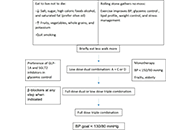 A brief approach to hypertension in type 2 diabetes mellitusOpen AccessReviewType 2 diabetes mellitus (DM) and hypertension (HT) are common major cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk factors. They share common pathophysiological mechanisms and are commonly co-existent. Prevalen [...] Read more.Yilmaz GunesPublished: February 04, 2025 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2025;2:101422
A brief approach to hypertension in type 2 diabetes mellitusOpen AccessReviewType 2 diabetes mellitus (DM) and hypertension (HT) are common major cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk factors. They share common pathophysiological mechanisms and are commonly co-existent. Prevalen [...] Read more.Yilmaz GunesPublished: February 04, 2025 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2025;2:101422
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eemd.2025.101422
This article belongs to the special issue Current Views on Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Its Complications and Related Conditions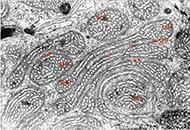 Unique original endocrine findings: the endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondrial unit in steroid producing cellsOpen AccessCommentaryStefan R. Bornstein ... Waldemar KanczkowskiPublished: April 01, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:12–15
Unique original endocrine findings: the endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondrial unit in steroid producing cellsOpen AccessCommentaryStefan R. Bornstein ... Waldemar KanczkowskiPublished: April 01, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:12–15
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eemd.2023.00003
This article belongs to the special issue The HPA Axis in Health and Disease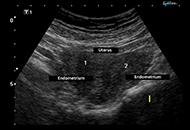 Hypoparathyroidism, deafness and renal dysplasia syndrome with bilateral cataract and bicornuate uterus caused by a de novo GATA3 mutationOpen AccessCase ReportHypoparathyroidism, deafness and renal dysplasia (HDR) syndrome is a rare genetic disorder caused by haploinsufficiency of the GATA3 gene. A very limited number of cases have been reported in the li [...] Read more.Rajesh Chetiwal ... Priyank RastogiPublished: May 27, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:77–82
Hypoparathyroidism, deafness and renal dysplasia syndrome with bilateral cataract and bicornuate uterus caused by a de novo GATA3 mutationOpen AccessCase ReportHypoparathyroidism, deafness and renal dysplasia (HDR) syndrome is a rare genetic disorder caused by haploinsufficiency of the GATA3 gene. A very limited number of cases have been reported in the li [...] Read more.Rajesh Chetiwal ... Priyank RastogiPublished: May 27, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:77–82
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eemd.2024.00009 Message of welcome from the editor-in-chiefOpen AccessEditorialStefan R. BornsteinPublished: April 01, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:1–3
Message of welcome from the editor-in-chiefOpen AccessEditorialStefan R. BornsteinPublished: April 01, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:1–3
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eemd.2023.00001 Diabetes and cancer: two epidemic diseases requiring an opposite therapeutic approach to target cellsOpen AccessPerspectiveDiabetes and cancer are two chronic metabolic diseases with ever-increasing incidence rates worldwide. These disorders can often occur together, as diabetes presents an important risk factor for can [...] Read more.Katrin SakPublished: May 23, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:56–61
Diabetes and cancer: two epidemic diseases requiring an opposite therapeutic approach to target cellsOpen AccessPerspectiveDiabetes and cancer are two chronic metabolic diseases with ever-increasing incidence rates worldwide. These disorders can often occur together, as diabetes presents an important risk factor for can [...] Read more.Katrin SakPublished: May 23, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:56–61
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eemd.2024.00007 Testosterone undecanoate is associated with improved ageing male symptoms score in men with type 2 diabetes and adult-onset testosterone deficiency: re-analyzed results from a randomised controlled trialOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: To evaluate changes in quality of life via the ageing male symptom scale (AMSS) and somatic, psychological, and sexual sub-scales following testosterone undecanoate (TU) or placebo (P) treat [...] Read more.Pravinath Ramachandran ... Geoffrey HackettPublished: August 13, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:177–190
Testosterone undecanoate is associated with improved ageing male symptoms score in men with type 2 diabetes and adult-onset testosterone deficiency: re-analyzed results from a randomised controlled trialOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: To evaluate changes in quality of life via the ageing male symptom scale (AMSS) and somatic, psychological, and sexual sub-scales following testosterone undecanoate (TU) or placebo (P) treat [...] Read more.Pravinath Ramachandran ... Geoffrey HackettPublished: August 13, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:177–190
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eemd.2024.00015
This article belongs to the special issue The Fountain of Youth: Decoding the Hormonal Regulation of Aging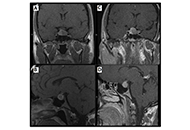 Patient diagnosed with acromegaly and pituitary apoplexy after breast carcinoma treatment: challenges in diagnosis and managementOpen AccessCase ReportThe clinical case presented describes a 44-year-old woman with a history of mucinous carcinoma in the right breast, who is diagnosed with a pituitary adenoma. Physical examination revealed signs of [...] Read more.Ignacio Jiménez Hernando, Laura González FernándezPublished: November 26, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:234–243
Patient diagnosed with acromegaly and pituitary apoplexy after breast carcinoma treatment: challenges in diagnosis and managementOpen AccessCase ReportThe clinical case presented describes a 44-year-old woman with a history of mucinous carcinoma in the right breast, who is diagnosed with a pituitary adenoma. Physical examination revealed signs of [...] Read more.Ignacio Jiménez Hernando, Laura González FernándezPublished: November 26, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:234–243
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eemd.2024.00019 -