Bioactive Peptides discovery and development
Guest Editor
Prof. Xuechen Li E-Mail
Professor of Department of Chemistry, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China
Research Keywords: synthetic protein; antibiotics; glycoconjugates; drug conjugates
About the Special lssue
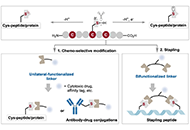
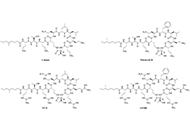
Peptides have emerged as an exciting therapeutic modality with middle-sized molecular weights and pharmacological properties in between traditional small molecule drugs and therapeutic proteins. Many peptide drugs have been clinically used for various diseases, including antimicrobial peptides, supplementary peptide hormones, peptide-drug conjugates and so on. In addition, peptides hold great promise for disrupting protein-protein interactions (PPIs) and drug delivery.
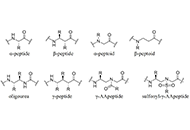
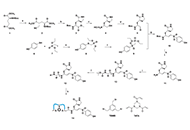
The past decades have witnesses great advances in bioactive peptides discovery and development. For instance, genome mining has led to many new ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides (RiPPs), various chemical methods have been developed to effectively cyclize peptides, peptide ligation allows for efficient synthesis of long peptides, super diverse peptide libraries provide powerful tools for high throughput screening and new knowledges have been gained for peptide intracellular delivery.
This special issue calls for the submission in all aspect in peptides, including, but not limited to, new bioactive peptide discovery, biosynthesis, peptide synthesis, peptide delivery, cyclic peptides, peptide-drug conjugates, medicinal chemistry, etc.
Keywords: bioactive peptide, peptide synthesis, ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides, peptide conjugates, peptide delivery, peptide high throughput screening
Published Articles