Current Views on Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Its Complications and Related Conditions
Guest Editor
Gulali Aktas E-Mail
Department of Internal Medicine, Abant Izzet Baysal University, Bolu, Turkey.
Research Keywords: type 2 diabetes mellitus; metabolic syndrome; obesity; nutrition; frailty; inflammation
About the Special lssue
Dear Colleagues,
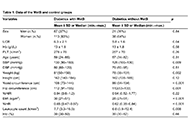
The most common metabolic disorder in the world is type 2 diabetes mellitus. Despite the establishment of diabetes prevention programs, its prevalence continues to rise at an alarming rate. Not only type 2 diabetes mellitus but also its complications have severe impacts on the diabetic population. Macrovascular complications include cardiovascular conditions such as coronary artery disease and stroke. Microvascular complications include diabetic kidney disease, peripheral symmetric neuropathy and retinopathy. Each complication increases the morbidity and mortality in this population. In addition, type 2 diabetes mellitus results in higher healthcare costs for patients, particularly in terms of health insurance. The evidence in the literature highlights that type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications impose a significant burden on healthcare systems Timely diagnosis and effective treatment are essential for preventing adverse outcomes associated with diabetes mellitus. This can be achieved through a deeper understanding of the disease’s pathogenesis and related complications.
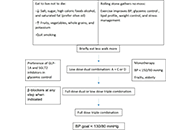
Research that focuses on the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus is of utmost importance. There is a strong need for studies that investigate effective treatment strategies, along with methods for preventing or detecting complications at an early stage. Treatments that offer maximum efficacy with minimal side effects are crucial for managing diabetes. Immediate implementation of lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise, is essential. However, many patients will need further interventions, including medical therapies like oral hypoglycemic agents, injectable glucagon-like peptide-1 analogs, or insulin. In recent years, surgical options such as sleeve gastrectomy have also been utilized for morbidly obese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Acute complications, such as hypoglycemia, can be prevented with early diagnosis, effective treatment, and heightened awareness among patients and caregivers. Additionally, chronic complications like diabetic nephropathy, neuropathy, retinopathy, foot ulcers, and macrovascular issues can be delayed or prevented with early diagnosis and proper disease management.
Type 2 diabetes is often seen not just as a standalone disease but frequently in association with other conditions. For example, metabolic syndrome is a condition present in many patients with type 2 diabetes and is known to increase cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease is another problem that frequently coexists with type 2 diabetes. Patients with type 2 diabetes are also expected to experience reduced vision, sensation, and other senses. Furthermore, the incidence of cancer is significantly higher in diabetic patients. Obesity is also associated with a high incidence of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Therefore, efforts to prevent, diagnose early, and effectively treat type 2 diabetes mellitus should align with efforts to prevent, detect early, and treat diseases associated with diabetes. In this special issue, we invite reviews and research aimed at advancing our understanding of the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus and related disorders, evaluating treatment options and their efficacy, and addressing the prevention, timely diagnosis, and management of diabetic complications and associated conditions. We eagerly await your valuable contributions to this special issue.
Diagnostic novel approaches, effective treatment strategies, and prevention and early detection methods of the diabetic complications are required for routine care of the diabetic population. Moreover, diabetes related conditions may also benefit from diabetes treatment. For example, SGLT2 inhibitors reduce liver steatosis and heart failure besides their glucose-lowering effects. Therefore, we also welcome review or research papers that aim to present better understanding of the pathogenesis, diagnosis and management of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease, obesity, metabolic syndrome, along with type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications in this special issue.
We eagerly await your valuable contributions.
Best regards
Prof. Gulali Aktas
Guest Editor
Keywords: type 2 diabetes mellitus; metabolic dysfunction associated fatty liver disease; obesity; metabolic syndrome; pathogenesis; diagnosis; treatment; diabetic kidney disease; diabetic retinopathy; diabetic neuropathy; diabetic foot ulcer; heart failure; cardiovascular diseases; hypoglycemia
Published Articles