Cross Talk Among Skin Cells and Immune Cells
Guest Editor
Dr. Masutaka Furue E-Mail
Professor and Chair, Department of Dermatology; Director, Research and Clinical Center for Yusho and Dioxin, Graduate School of Medical Sciences, Kyushu University, Fukuoka, Japan
Research Keywords: Atopic dermatitis, aryl hydrocarbon receptor, antioxidant, melanoma, skin disease, dioxin
About the Special lssue
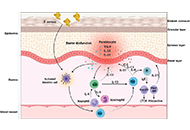
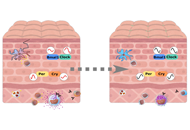
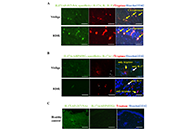
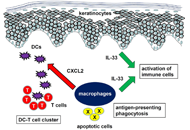
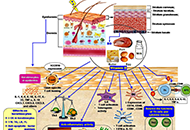
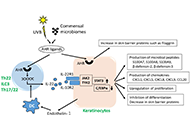
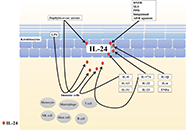
As the skin is an interface organ between the body and the external harsh environment, it is equipped with barrier-forming skin cells and highly sophisticated immune cells that provide innate and acquired immunity. Recent therapeutic advances, such as biologics, underpin the notion that selective crosstalk among skin cells and specific immune cells develops a variety of skin diseases. For instance, psoriasis is driven by the IL-23/IL-17A axis in concert with the TNF-α axis. The IL-13/IL-4-induced JAK/STAT6 & STAT3 activation is the major pathogenic pathway for the development of atopic dermatitis. Th1-driven melanocyte damage is suspected in vitiligo. Stem cell transplantation is highlighted in the treatment of patients with severe systemic sclerosis. Immune checkpoint inhibitors are now an indispensable treatment option for melanoma and other malignant neoplasms. These therapeutic evidences point to the idea that the characterization and evaluation of the crosstalk among skin and immune cells may provide a clue to develop new targeted drugs for immune-related cutaneous diseases.
In this Special Issue, we will publish cutting-edge information including keratinocytes, fibroblasts, dendritic cells, Th1/Th2/Th17/Treg cells, innate lymphoid cells, NK cells, and cyto-chemokines. We warmly welcome your submissions including original papers and reviews.
Keywords: Keratinocytes, fibroblasts, dendritic cells, Th1/Th2/Th17/Treg cells, innate lymphoid cells, NK cells, and cyto-chemokines
Published Articles