Pharmacological and Non-Pharmacological Management of Gout
Guest Editor
Prof. George Nuki E-Mail
University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, UK
About the Special lssue
Although safe, effective, inexpensive, and potentially ‘curative’ urate-lowering drugs have been available for more than 50 years, there has been a global increase in the incidence of gout, and gout is now the most prevalent type of chronic inflammatory arthritis in Europe and North America. While there are numerous reasons why this eminently treatable disease has grown in incidence, prevalence and severity, it is clear that both the pharmacological and non-pharmacological management of gout remain suboptimal, despite the availability of national and international evidence-based treatment guidelines.
This special issue aims to bring together current research and some novel approaches to both the pharmacological and non- pharmacological management and prevention of gout flares, tophi, chronic gouty arthritis, and its renal, metabolic and cardiovascular co-morbidities.
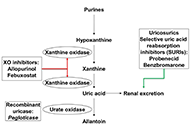
Keywords: Gout, management, urate lowering therapy, uricosurics, xanthine oxidase inhibitors, uricase, nlrp3 inflammasome inhibitors, interleukin-1 antagonists, colchicine
Published Articles