Biosimilars: State of the Art in the Treatment of Rheumatic Diseases
Guest Editor
Prof. Valderilio Feijó Azevedo E-Mail
Federal University of Paraná, Brazil
Research Keywords: Spondyloarthritis, gout, biopharmaceuticals, biosimilars, gut microbioma, psoriatic arthritis, pharmacoeconomics
About the Special lssue
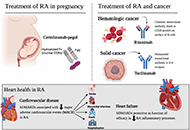
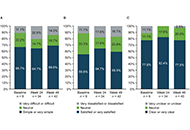
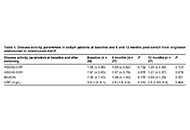
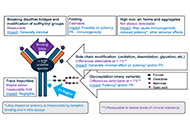
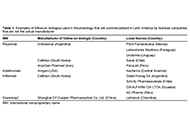
Widespread use of biological medicines has transformed outcomes for many patients with inflammatory conditions such as autoimmune rheumatic disorders (ARDs). These therapies come at a price, however, and as their patents expire, a new class of products, very regulated copies named biosimilars are entering the market. Biosimilars are more affordable for healthcare organisations and enable greater patient access to treatment. Biosimilars are subject to a robust regulatory framework to gain approval worldwide. These products have shown biosimilarity in terms of structure, biological activity and therapeutic equivalence in efficacy, safety, and immunogenicity profile. Since the approval of the first Mab Biosimilar used to treat Rheumatic diseases in 2013, many other biosimilars are available as safe and cost reduced options to treat ARDs. A number of real-world scenarios, of a medical and non-medical nature, may lead to cross-switching between biosimilars of the same reference product. This special issue intends to discuss and point out new challenges for biosimilars in rheumatology.
Keywords: Biosimilars, biologic medicines, biopharmaceuticals, reference products, rheumatic diseases
Published Articles