Circadian Rhythm and Melatonin
Guest Editor
Prof. Ertugrul Kilic E-Mail
Head of Department of Physiology, Istanbul Medipol University, School of Medicine, Regenerative and Restorative Medical Research Center, Istanbul, Turkey
Research Keywords: Stroke, spinal cord injury, cell signaling, brain plasticity
About the Special lssue
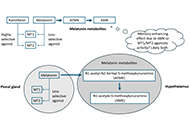
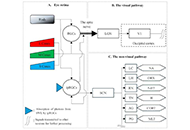
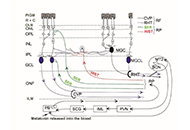
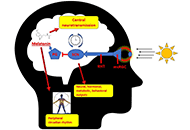
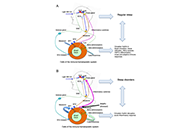
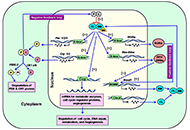
Circadian rhythm is driven by a master clock system within the suprachiasmatic nucleus of the hypothalamus, which regulates melatonin secretion and the circadian clock machinery. This circadian clock consists of self-sustained molecular clockwork which is regulated by the transcriptional activators Bmal1 and Circadian Locomotor Output Cycles Kaput Protein (Clock), and transcriptional repressors Cryptochrome Circadian Regulator 1 (Cry1), Cryptochrome Circadian Regulator 2 (Cry2), Period 1 (Per1), and Period 2 (Per2). Heterodimeric transcription factor Clock and Bmal1 activates enhancer box (E-Box), and both Per and Cry, which create a negative feedback loop of this circadian clock machinery in all cells in our body. Furthermore, other clock proteins such as Rev-Erb and Ror are also part of this cellular clock system. Discoveries of the molecular mechanisms of this system were also awarded with the Nobel Prize in 2017.
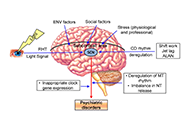
In the physiological conditions, melatonin and other circadian rhythm proteins regulate many functions, including sleep-wake cycle, behaviour, and many metabolic functions. However, in recent decades, the role of these molecules has been investigated in the disease conditions such as neurodegenerative disorders. It was shown that indolamine melatonin protects the brain in many neurodegenerative diseases with its direct antioxidant activity and indirectly via its effect on survival kinases. In addition, the role of circadian clock proteins in the function of the brain has been implicated both in the physiological and pathological conditions. An example for this, the absence of Bmal1 protein plays an essential role in the prognosis of Alzheimer's Disease and stroke.
In this special issue “Circadian Rhythm and Melatonin”, we expect to focus on the role of circadian rhythm and melatonin in the physiological brain function and pathophysiological events after neurodegenerative disorders.
Keywords: Bmal1, cell signaling, circadian rhythm, clock, free radicals, melatonin, Per1, pineal gland, Rev-Erb
Published Articles