Editor's Picks
Articles
Latest
Most Viewed
Most Downloaded
Most Cited
Open Access
Case Report
Double heterozygous pathogenic variants in BRCA2 and CHEK2 in a girl with adrenocortical carcinoma
Victoria E. Fincke ... Michaela Kuhlen
Published: April 17, 2025 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2025;2:101429
Open Access
Commentary
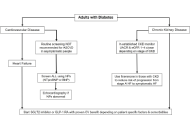
Updates from the 2025 American Diabetes Association guidelines on standards of medical care in diabetes
Dipti Tiwari ... Tar Choon Aw
Published: April 15, 2025 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2025;2:101428
Open Access
Review
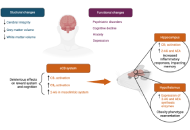
Circulating endocannabinoids and brain anatomy: unraveling the weight loss connection through lifestyle and surgery approaches
Gabrielle St-Arnaud ... Vincenzo Di Marzo
Published: April 07, 2025 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2025;2:101427
This article belongs to the special issue Regulators of Glucose Homeostasis, Lipid Metabolism and Energy Balance
Open Access
Review
Glucocorticoid receptor alpha: origins and functions of the master regulator of homeostatic corrections in health and critical illness
Gianfranco Umberto Meduri
Published: March 28, 2025 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2025;2:101426

Open Access
Review
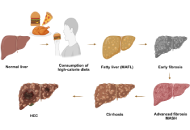
Significance of FXR agonists in MASLD treatment: a deep dive into lipid alteration by analytical techniques
Pirangi Srikanth ... Sukhendu Nandi
Published: March 25, 2025 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2025;2:101425
This article belongs to the special issue Regulators of Glucose Homeostasis, Lipid Metabolism and Energy Balance
Open Access
Review
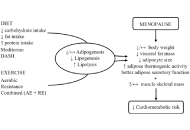
Healthy adipose tissue after menopause: contribution of balanced diet and physical exercise
Bruno Vecchiatto ... Fabiana S. Evangelista
Published: March 13, 2025 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2025;2:101424
This article belongs to the special issue Metabolic Syndrome in Menopause
Open Access
Commentary
The 2024 American Diabetes Association guidelines on Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes: key takeaways for laboratory
Dipti Tiwari, Tar Choon Aw
Published: July 23, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:158–166

Open Access
Review
Recent advances in artificial intelligence-assisted endocrinology and diabetes
Ioannis T. Oikonomakos ... Stefan R. Bornstein
Published: April 01, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:16–26
Open Access
Original Article
Glycemic trends, app engagement and achievement of gestational diabetes guideline targets using a diabetes app and Bluetooth® connected blood glucose meters
Mike Grady ... Elizabeth Holt
Published: July 24, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:167–176
This article belongs to the special issue The Impact of Digitalization To Improve Nutrition and Self-Management in Patients With Diabetes

Open Access
Review
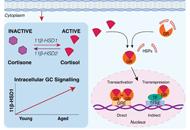
Endogenous glucocorticoids during skeletal ageing
Eugenie Macfarlane ... Markus Joachim Seibel
Published: August 16, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:191–212
This article belongs to the special issue The Fountain of Youth: Decoding the Hormonal Regulation of Aging
Open Access
Case Report
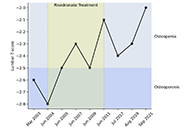
Beta thalassemia minor: a potential risk factor for osteopenia and osteoporosis
Felicia Woron ... Parvathy Madhavan
Published: October 31, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:213–217
Open Access
Review
Adult-onset testosterone deficiency: the usefulness of hormone replacement in reducing mortality in men with this common age-related condition
Amar Mann ... Sudarshan Ramachandran
Published: June 28, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:83–100
This article belongs to the special issue The Fountain of Youth: Decoding the Hormonal Regulation of Aging
Open Access
Review
Recent advances in artificial intelligence-assisted endocrinology and diabetes
Ioannis T. Oikonomakos ... Stefan R. Bornstein
Published: April 01, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:16–26

Open Access
Review
Endogenous glucocorticoids during skeletal ageing
Eugenie Macfarlane ... Markus Joachim Seibel
Published: August 16, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:191–212
This article belongs to the special issue The Fountain of Youth: Decoding the Hormonal Regulation of Aging

Open Access
Case Report
Beta thalassemia minor: a potential risk factor for osteopenia and osteoporosis
Felicia Woron ... Parvathy Madhavan
Published: October 31, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:213–217

Open Access
Case Report
A case series of three patients with extensive lung metastatic pheochromocytoma/paraganglioma: evaluation, treatment challenges, and outcomes
Kailah M. Charles ... Karel Pacak
Published: November 15, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:218–233
Open Access
Commentary
The 2024 American Diabetes Association guidelines on Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes: key takeaways for laboratory
Dipti Tiwari, Tar Choon Aw
Published: July 23, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:158–166

Open Access
Original Article
Glycemic trends, app engagement and achievement of gestational diabetes guideline targets using a diabetes app and Bluetooth® connected blood glucose meters
Mike Grady ... Elizabeth Holt
Published: July 24, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:167–176
This article belongs to the special issue The Impact of Digitalization To Improve Nutrition and Self-Management in Patients With Diabetes

Open Access
Original Article
Waist-to-height ratio as a novel marker of metabolic syndrome in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Elif Basaran, Gulali Aktas
Published: January 10, 2025 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2025;2:101421
This article belongs to the special issue Current Views on Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Its Complications and Related Conditions
Open Access
Commentary
The 2024 American Diabetes Association guidelines on Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes: key takeaways for laboratory
Dipti Tiwari, Tar Choon Aw
Published: July 23, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:158–166

Open Access
Review
Recent advances in artificial intelligence-assisted endocrinology and diabetes
Ioannis T. Oikonomakos ... Stefan R. Bornstein
Published: April 01, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:16–26

Open Access
Review
Adult-onset testosterone deficiency: the usefulness of hormone replacement in reducing mortality in men with this common age-related condition
Amar Mann ... Sudarshan Ramachandran
Published: June 28, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:83–100
This article belongs to the special issue The Fountain of Youth: Decoding the Hormonal Regulation of Aging

Open Access
Review
Glucocorticoid receptor alpha: origins and functions of the master regulator of homeostatic corrections in health and critical illness
Gianfranco Umberto Meduri
Published: March 28, 2025 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2025;2:101426

Open Access
Original Article
Development of adrenal 3-dimensional spheroid cultures: potential for the treatment of adrenal insufficiency and neurodegenerative diseases
Charlotte Steenblock ... Nicole Bechmann
Published: April 01, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:27–38
Special Issues
Ongoing Special lssues
Completed Special lssues
Innovative Strategies for Diabetes and Metabolic Disorders: Current and Future Directions
Dawood Khan Victor Gault
September 20, 2025
Published Articles: 0

Current Views on Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Its Complications and Related Conditions
Gulali Aktas
July 01, 2025
Published Articles: 2
Role of Dysregulated Cytokine Signaling Pathways in Metabolic Disease
Alister C. Ward
July 30, 2025
Published Articles: 0
Oxidative Stress and Diabetes – Remedies through Functional Food
Viduranga Y. Waisundara
July 07, 2025
Published Articles: 0

Metabolic Syndrome in Menopause
Tzong-Shyuan Lee
July 06, 2025
Published Articles: 1
The Impact of Digitalization To Improve Nutrition and Self-Management in Patients With Diabetes
Peter Schwarz
July 05, 2025
Published Articles: 1

The Fountain of Youth: Decoding the Hormonal Regulation of Aging
Marijn Speeckaert
July 04, 2025
Published Articles: 3

Regulators of Glucose Homeostasis, Lipid Metabolism and Energy Balance
Nikolaos Perakakis
July 03, 2025
Published Articles: 3

The HPA Axis in Health and Disease
Charlotte Steenblock
July 02, 2025
Published Articles: 4

Journal Information
Journal Indexing
Journal Metrics
Article Usage (total)
Views: 59,683
Downloads: 1,974








 Title: Unravelling the interplaybetween #Harmattan wind andbaroreflex functions: implicationon environmental health andcardiovascular #pathophys
Title: Unravelling the interplaybetween #Harmattan wind andbaroreflex functions: implicationon environmental health andcardiovascular #pathophys


