Viral Hepatitis
Guest Editors
Dr. Jinsheng Guo E-Mail
Chief Physician of Medicine, Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Zhong Shan Hospital, Department of Internal Medicine, Shanghai Medical College, Fudan University, Shanghai, China
Prof. Youhua Xie E-Mail
Professor, Key Laboratory of Medical Molecular Virology, Department of Microbiology and Parasitology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Fudan University, Shanghai, China
About the Special lssue
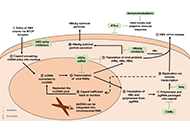
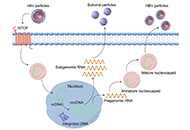
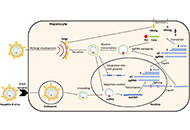
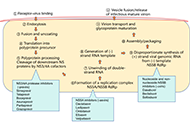
Hepatitis B and C viral infections represent a significant global health concern, imposing substantial economic burdens. These infections have various clinical implications, such as acute and chronic hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, hepatic failure, and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Among these, liver cirrhosis and HCC stand as the primary causes of mortality related to hepatitis virus-induced liver diseases. Consequently, identifying the risk factors for cirrhosis and HCC in patients with chronic HBV and HCV infection is of paramount importance.
While effective antiviral treatment can inhibit HBV replication and reduce serum viral load, potentially alleviating liver damage and diminishing the development of cirrhosis and liver cancer, achieving a complete cure for hepatitis B and eliminating the risk of HBV-related cancer remains a challenging task. Additionally, Hepatitis B reactivation significantly impacts the management of comorbidities. On the other hand, for hepatitis C, the progress in direct-acting antiviral agents has been remarkable in achieving a cure. However, one potential barrier to this approach is the occurrence of resistance-associated substitutions.
In this specific context of viral hepatitis, we aim to delve into the current progress and existing challenges surrounding the management of patients with viral hepatitis. Our ultimate goal is to work towards eradicating viral hepatitis, seeking more effective approaches to tackle these infections and improve patient outcomes.
Keywords: Hepatitis B virus, hepatitis C virus, chronic hepatitis, hepatic failure, liver cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma, hepatitis B reactivation, elimination of hepatitis virus
Published Articles