Drug-induced Liver Injury: From Bench to Clinical Application
Guest Editors
Prof. Jose C Fernandez-Checa E-Mail
Spanish National Research Council at the Institute of Biomedical Research of Barcelona (IIBB-CSIC); Institute of Biomedical Research August Pi i Sunyer (IDIBAPS); CIBEREHD
Research Keywords: Mitochondria, ASH, NASH, liver cancer, cholesterol
Prof. Wen-Xing Ding E-Mail
University of Kansas Medical Center, Kansas City, KS, USA
Research Keywords: Autophagy, mitochondria, alcohol associated liver disease, alcohol-associated pancreatitis, drug-induced liver injury (DILI), lipid metabolism
About the Special lssue
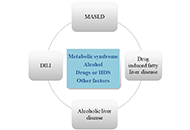
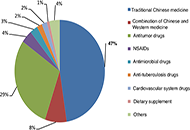
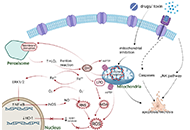
Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is a major cause of acute liver failure (ALF) and a leading reason for drug withdrawal from the market. Unlike intrinsic DILI, which is predictable, reproducible, and dose-dependent, idiosyncratic DILI is unpredictable, not strictly dose-dependent, and although rare it accounts for 10% to 15% of ALF cases in Western societies. Given the wide use of both prescribed and over the counter drugs, DILI has become a major health issue for which there is a pressing need to find novel and effective therapies. Although significant progress has been made in understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying DILI, our incomplete knowledge of its pathogenesis and inability to predict DILI is largely due to both discordance between human and animal DILI in preclinical drug development and a lack of models that faithfully recapitulate complex pathophysiological features of human DILI. This is exemplified by the hepatotoxicity of acetaminophen (APAP) overdose, a major cause of ALF because of its extensive worldwide use as an analgesic. Despite recent progress with current animal and in vitro models, the mechanisms involved in the hepatotoxicity of APAP are still not fully understood.
In this Special Issue, we invite experts in the field to cover a wide range of topics of interest in enhancing our current understanding of DILI, from novel technological and in vitro approaches to metabolomics profile and computational modelling as well as clinical implications and registry. Our hope is to collect a state-of-the-art collection of articles that may stimulate mutidisciplinary research in this critical field of basic and clinical liver research.
Keywords: Acetaminophen hepatotoxicity, iPSC, metabolomics, computational modelling, microbiota, idiosyncratic DILI
Published Articles