Natural Products in Health and Disease
Guest Editor
Marcello Iriti E-Mail
Plant Biology and Pathology at the Department of Biomedical, Surgical and Dental Sciences, Milan State University, Milan, Italy
Research Keywords: functional foods; nutraceuticals; mediterranean diet; nutritional therapy; pharmaconutrients; phytotherapeutics; bioactive phytochemicals; medicinal and food plants; food security
About the Special lssue
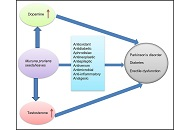
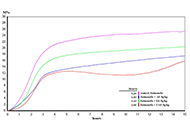
Plant organisms represent an unlimited source of bioactive secondary metabolites. In recent decades, an enormous amount of preclinical (i.e. in vitro and in vivo) studies have indicated that phytochemicals exert a plethora of biological and pharmacological activities in cell cultures and animal models, although the evidence in humans is less substantiated and still fragmentary. Nowadays, we know that bioactive phytochemicals possess antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant/prooxidant, cytotoxic and immunomodulating activities, among others, which make them promising antibiotic, cardioprotective, neuroprotective, anticancer, antidiabetic, anti-obesity and antiaging agents. In general, phytochemicals exert a multi-target mechanism of action which makes them suitable drugs for the prevention and treatment of both communicable and non-communicable diseases, although phytochemicals appear to be more effective in the prevention than in the treatment of chronic-degenerative diseases, as demonstrated by healthy diets rich in plant foods. Furthermore, phytochemicals can be developed as adjuvant and sensitizing agents in association with conventional antibiotic and anticancer therapies to improve their efficacy, decrease their adverse effects, reduce the risk of selecting resistant microbial strains or cancer cells, or even reverse resistance. However, the preclinical pharmacological activities of phytochemicals need to be further substantiated by clinical studies in healthy and unhealthy subjects on their effective dose, route of administration, possible adverse effects and drug interactions.
In this very wide context, we invite investigators to submit both original research and review articles that explore all these aspects.
Keywords: medicinal plants; botanicals; plant extracts; essential oils; marine drugs; nutraceuticals; herbal remedies; antimicrobials; antimicrobial resistance; anticancer drugs; antineoplastic resistance; cardioprotection; neuroprotection; antidiabetic agents; anti-obesity agents; antioxidant activity; ethnopharmacology; one health
Published Articles