Editor's Picks
Articles
Latest
Most Viewed
Most Downloaded
Most Cited
Open Access
Original Article
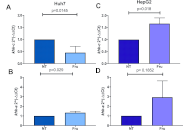
Fructose induces metabolic reprogramming in liver cancer cells, promoting aggressiveness and chemotherapy resistance
Lisette Chávez-Rodríguez ... Luis E. Gomez-Quiroz
Published: April 20, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. 2025;4:100572
Open Access
Perspective
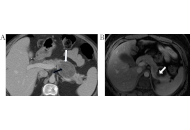
Molecular insights into pancreatic cysts: navigating diagnosis and precision management
Rudy El Asmar ... Samer AlMasri
Published: April 13, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. 2025;4:100571
This article belongs to the special issue Advances in Hepato-gastroenterology: Diagnosis, Prognostication, and Disease Stratification
Open Access
Perspective
Debugging surgical guidelines for acute diverticulitis
Valter Nilton Felix
Published: April 11, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. 2025;4:100570
This article belongs to the special issue Diverticulitis: Pathomechanism, Diagnosis and Treatment
Open Access
Review
The multiple mechanisms and modes of cell death after acetaminophen overdose
Hartmut Jaeschke, Anup Ramachandran
Published: April 07, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. 2025;4:100569
Open Access
Original Article
Immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients with advanced gastric cancer: a multi-institutional retrospective real-world study
Anastasia Rays ... Аlexey Tryakin
Published: March 27, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. 2025;4:100568
This article belongs to the special issue Immunotherapy for Cancer of Digestive System
Open Access
Letter to the Editor
Helicobacter pylori infection in the pathophysiology of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease and its complications
Jannis Kountouras ... Maria Tzitiridou-Chatzopoulou
Published: March 20, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. 2025;4:100567
Open Access
Review
Drug-induced cholestasis: causative agents and challenges in diagnosis and management
Jose M. Pinazo-Bandera ... Miren García-Cortés
Published: September 18, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. 2023;2:202–222
This article belongs to the special issue CHOLESTASIS
Open Access
Review
Etiopathogenesis and pathophysiology of cholestasis
Maitane Asensio ... Jose J. G. Marin
Published: October 31, 2022 Explor Dig Dis. 2022;1:97–117
This article belongs to the special issue CHOLESTASIS
Open Access
Review
Fructose, a trigger of metabolic diseases?—a narrative review
Anja Baumann ... Ina Bergheim
Published: August 29, 2022 Explor Dig Dis. 2022;1:51–71
Open Access
Review
Alcohol-related liver disease: also a question of what you drink?
Finn Jung ... Ina Bergheim
Published: June 30, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. 2023;2:118–132
Open Access
Review
Helicobacter pylori and gastric cancer: a critical approach to who really needs eradication
Elias Kouroumalis ... Argyro Voumvouraki
Published: April 16, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. 2024;3:107–142
This article belongs to the special issue Helicobacter Pylori and Infection: Genomics, Diagnosis, Pathogenesis, Antibiotic Resistance, Microbiota, Cancer, Prevention and Therapeutics
Open Access
Review
Hepatitis B virus: modes of transmission, immune pathogenesis, and research progress on therapeutic vaccines
Chunzheng Li ... Xianguang Yang
Published: October 14, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. 2024;3:443–458
This article belongs to the special issue Viral Hepatitis
Open Access
Review
Etiopathogenesis and pathophysiology of cholestasis
Maitane Asensio ... Jose J. G. Marin
Published: October 31, 2022 Explor Dig Dis. 2022;1:97–117
This article belongs to the special issue CHOLESTASIS

Open Access
Review
Drug-induced cholestasis: causative agents and challenges in diagnosis and management
Jose M. Pinazo-Bandera ... Miren García-Cortés
Published: September 18, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. 2023;2:202–222
This article belongs to the special issue CHOLESTASIS

Open Access
Review
Fructose, a trigger of metabolic diseases?—a narrative review
Anja Baumann ... Ina Bergheim
Published: August 29, 2022 Explor Dig Dis. 2022;1:51–71

Open Access
Review
Zebrafish as a model for drug induced liver injury: state of the art and beyond
Gulcin Cakan-Akdogan ... Ozlen Konu
Published: April 26, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. 2023;2:44–55
This article belongs to the special issue Drug-induced Liver Injury: From Bench to Clinical Application
Open Access
Review
Molecular mechanisms of metabolic disease-associated hepatic inflammation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
Chunye Zhang ... Ming Yang
Published: October 25, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. 2023;2:246–275
This article belongs to the special issue Cellular and Molecular Targets for NAFLD or MAFLD Treatments and Their Functions in Liver Fibrosis, Cirrhosis, and Cancer
Open Access
Review
Helicobacter pylori and gastric cancer: a critical approach to who really needs eradication
Elias Kouroumalis ... Argyro Voumvouraki
Published: April 16, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. 2024;3:107–142
This article belongs to the special issue Helicobacter Pylori and Infection: Genomics, Diagnosis, Pathogenesis, Antibiotic Resistance, Microbiota, Cancer, Prevention and Therapeutics

Open Access
Review
The central role of mitochondrial metabolism in hepatic steatosis
Sanda Win ... Filbert Win Min Aung
Published: February 29, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. 2024;3:42–68
This article belongs to the special issue Mitochondria and Lipid Signalling in Liver Diseases
Open Access
Review
Extracellular vesicles in metabolic dysfunction associated fatty liver disease: mechanisms, diagnostic and therapeutic implications
Zongmei Wu ... Han Moshage
Published: July 13, 2022 Explor Dig Dis. 2022;1:4–20
Open Access
Editorial
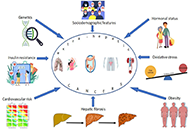
Extra-hepatic cancers in metabolic fatty liver syndromes
Amedeo Lonardo
Published: February 24, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. 2023;2:11–17
Open Access
Review
Helicobacter pylori and gastric cancer: a critical approach to who really needs eradication
Elias Kouroumalis ... Argyro Voumvouraki
Published: April 16, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. 2024;3:107–142
This article belongs to the special issue Helicobacter Pylori and Infection: Genomics, Diagnosis, Pathogenesis, Antibiotic Resistance, Microbiota, Cancer, Prevention and Therapeutics

Open Access
Review
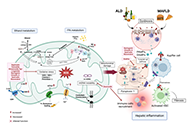
Mitochondrial ROS, a trigger for mitochondrial dysfunction and inflammasome activation and a therapeutic target in liver diseases
Hala Saeed Jaara, Sandra Torres
Published: December 10, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. 2024;3:474–503
This article belongs to the special issue Mitochondria and Lipid Signalling in Liver Diseases
Open Access
Review
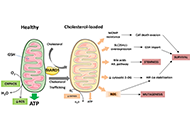
Role of cholesterol homeostasis in MASH-driven hepatocellular carcinoma: not just a neutral fat
Vicent Ribas
Published: June 14, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. 2024;3:203–225
This article belongs to the special issue Mitochondria and Lipid Signalling in Liver Diseases
Special Issues
Ongoing Special lssues
Completed Special lssues
Gastrointestinal Cancer
Prof. Nahum Mendez-Sanchez
August 31, 2025
Published Articles: 0

Prevention, Screening and Diagnosis for Primary Liver Cancer
Prof. Jian-Guo Chen
December 31, 2025
Published Articles: 0
Gut Microbiota towards Personalized Medicine in Metabolic Disease
Prof. Raquel Soares Dr. Carla Luís
June 30, 2025
Published Articles: 0

The Role of Gut Microbiota in Digestive Diseases: Exploring Pathogenesis to Clinical Applications
Prof. Lui Ng Prof. Manzhao Ouyang
October 31, 2025
Published Articles: 0
The Role of Gut Microbiota in the Pathogenesis and Management of Metabolic-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD)
Dr. Alfredo Caturano
October 31, 2025
Published Articles: 0

Diverticulitis: Pathomechanism, Diagnosis and Treatment
Prof. Roberto Cirocchi
October 31, 2025
Published Articles: 1
Immunotherapy for Cancer of Digestive System
Prof. Evgeny Imyanitov
October 31, 2025
Published Articles: 2
Gastrointestinal Diseases, Cholesterol, Oxysterols, and Bile Acids
Prof. Oren Tirosh
December 31, 2024
Published Articles: 0
Viral Hepatitis
Dr. Jinsheng Guo Prof. Youhua Xie
October 31, 2025
Published Articles: 4
Cirrhosis and Its Complications
Prof. Jean Francois D. Cadranel
August 31, 2025
Published Articles: 4
Chronic Hepatitis B and C
Prof. Ching Lung Lai
August 31, 2025
Published Articles: 2
Helicobacter Pylori and Infection: Genomics, Diagnosis, Pathogenesis, Antibiotic Resistance, Microbiota, Cancer, Prevention and Therapeutics
Prof. Tzi-Bun Ng
October 31, 2025
Published Articles: 4

Cellular and Molecular Targets for NAFLD or MAFLD Treatments and Their Functions in Liver Fibrosis, Cirrhosis, and Cancer
Prof. Ming Yang Prof. Chunye Zhang
January 31, 2025
Published Articles: 4

Mitochondria and Lipid Signalling in Liver Diseases
Prof. Carmen Garcia-Ruiz
May 30, 2025
Published Articles: 6

Latest Updates in the Endoscopic, Surgical and Medical Treatment of Resectable and Advanced Gastrointestinal Cancers
Dr. Michele Ghidini
October 31, 2025
Published Articles: 1

Advances in Hepato-gastroenterology: Diagnosis, Prognostication, and Disease Stratification
Prof. Amedeo Lonardo
October 31, 2025
Published Articles: 4

Fibrosis and Hepatobiliary Cancer
Prof. Fabio Marra Dr. Chiara Raggi
March 31, 2025
Published Articles: 3

Journal Information
Journal Indexing
Journal Metrics
Article Usage (total)
Views: 177,977
Downloads: 3,699










 Title: Unravelling the interplaybetween #Harmattan wind andbaroreflex functions: implicationon environmental health andcardiovascular #pathophys
Title: Unravelling the interplaybetween #Harmattan wind andbaroreflex functions: implicationon environmental health andcardiovascular #pathophys


