-
 Special Issue Topic
Special Issue TopicNutrition, Intestinal Barrier and Metabolic Liver Disease
Submission Deadline: July 31, 2023Guest Editors
Prof. Ina Bergheim E-Mail
Department of Nutritional Sciences, Molecular Nutritional Sciences, University of Vienna, Josef-Holaubek-Platz 2, 1090 Wien, Austria
Research Keywords: intestinal barrier, nutrition, bacterial endotoxin, alcoholic liver disease, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, aging
Dr. Annette Brandt E-Mail
Department of Nutritional Sciences, Molecular Nutritional Sciences, University of Vienna, Josef-Holaubek-Platz 2, 1090 Wien, Austria
Research Keywords: intestinal barrier, nutrition, PAMPs, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, aging
About the Special Issue
Metabolic liver diseases like non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases (NAFLD) and alcohol-related liver diseases (ALD) are by now among the leading liver diseases in the world. Results of studies performed in both humans and model organisms suggest that nutrition and herein both the intake of certain nutrients and the dietary pattern are critical in the development of NAFLD and ALD. Furthermore, it has been shown that alterations of intestinal microbiota composition and intestinal barrier function are also key factors in the development of NAFLD and ALD. Indeed, interventions targeting nutritional intake and/ or intestinal microbiota composition and barrier function have been suggested to improve existing and to prevent or delay the development of NAFLD and ALD. However, despite a marked progress in the in the understanding of molecular mechanisms involved in the onset and the progression of both NAFLD and ALD universally accepted therapies besides life-style intervention e.g., in the case of NAFLD weight reduction and increased physical activity and in the case of ALD abstinence, being in both cases afflicted with high relapse rates, are still lacking.
In this Special Issue, we invite experts in the field to cover a wide range of topics of interest in enhancing our current understanding of the interaction of nutrition, intestinal barrier dysfunction and the development and progression of metabolic liver diseases, from bench to bedside. Our aim for a collection of a state-of-the-art original and review articles that may stimulate multidisciplinary research in this critical field of basic and clinical liver research.
Keywords: Diet, dietary pattern, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, alcohol-related liver disease, gut microbiota, insulin resistance, fatty liver, PAMPs, intestinal permeability
Call for Papers
Published Articles
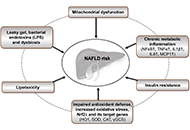 Ultra-processed food consumption and the risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease—What are the proposed mechanisms?Open AccessReviewA high consumption of ultra-processed food (UPF) is a hallmark of Western diets that has been related to increased risk of non-communicable diseases. As an underlying mechanism, UPF may promote non- [...] Read more.Franziska A. Hägele ... Anja Bosy-WestphalPublished: August 24, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. 2023;2:133–148
Ultra-processed food consumption and the risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease—What are the proposed mechanisms?Open AccessReviewA high consumption of ultra-processed food (UPF) is a hallmark of Western diets that has been related to increased risk of non-communicable diseases. As an underlying mechanism, UPF may promote non- [...] Read more.Franziska A. Hägele ... Anja Bosy-WestphalPublished: August 24, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. 2023;2:133–148
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/edd.2023.00023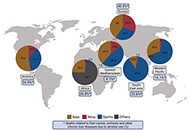 Alcohol-related liver disease: also a question of what you drink?Open AccessReviewExcessive alcohol intake is still among the leading causes of chronic liver diseases. Epidemiological studies suggest that per capita consumption of alcohol from various alcohol beverages e.g., beer [...] Read more.Finn Jung ... Ina BergheimPublished: June 30, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. 2023;2:118–132
Alcohol-related liver disease: also a question of what you drink?Open AccessReviewExcessive alcohol intake is still among the leading causes of chronic liver diseases. Epidemiological studies suggest that per capita consumption of alcohol from various alcohol beverages e.g., beer [...] Read more.Finn Jung ... Ina BergheimPublished: June 30, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. 2023;2:118–132
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/edd.2023.00022 -
-
Ongoing Special Issues
-
Completed Special Issues