Parkinson's Disease: Principal Targets and Interventional Mechanisms
Guest Editor
Prof. Mahesh Narayan E-Mail
Professor, Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, The University of Texas at El Paso, El Paso, TX 996 USA
Research Keywords: Parkinson’s; α-synuclein; dopamine; risk-factors; protein misfolding; cellular homeostasis; cellular dyshomeostasis; neurodegeneration; substantia nigra pars compacta; small-molecules; natural products; carbon quantum dots; carbon nano materials
About the Special lssue
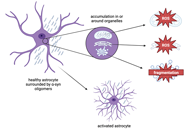
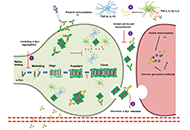
Parkinson's disease (PD) is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder after Alzheimer's disease. While age is a primary risk factor, environmental agents such as pesticides, weedicides, insecticides, cigarette smoke, industrial pollutants and drugs of abuse remain associated with the loss of dopaminergic neuronal homeostasis, neuronal injury, neuronal demise and disease onset. While α- synuclein is a central player in the pathogenesis of PD, other risk factors and targets include molecular chaperones, neuroinflammation, mitochondrial dysfunction, neuromelanin, ubiquitin-proteasome system, protein Abelson, synaptic vesicle glycoprotein 2C, and cocaine-amphetamine-regulated transcript. The need for novel intervention mechanisms has never been greater given the lack of suitable clinical regimens that satisfactorily address PD. Of late, the use of carbon nanomaterials has found some success in preclinical trials.
The proposed issue invites papers across, but not limited to, the following themes:
Novel targets in PD
Targeting α-synuclein in PD
Novel small-molecules in the treatment of PD
The role of carbon nanomaterials in PD intervention
Keywords: Parkinson’s; α-synuclein; dopamine; neuronal cells; dopaminergic cells; amyloid cross-talk; risk-factors; protein misfolding
Published Articles