Role of the Monoaminergic Systems in the Pathogenesis and the Pathophysiology of Parkinson's Disease
Guest Editor
Dr. Abdelhamid Benazzouz E-Mail
Research Director, Team Leader, Neurochemistry, Deep brain stimulation & Parkinson’s disease, Neurodegenerative Diseases Institute, Bordeaux University, Bordeaux, France
Research Keywords: deep brain stimulation; monoaminergic systems; basal ganglia; animal models
About the Special lssue
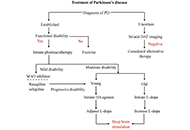
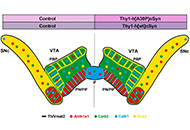
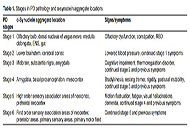
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a neurological condition representing the second most common neurodegenerative disorder after Alzheimer's disease. Although the cause of neuronal degeneration is not known, it is accepted that the motor symptoms of PD are due to the degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the pars compacta of the substantia nigra. In addition, PD is also characterized by the manifestation of non-motor symptoms that may occur even before the motor symptoms, which may be due to impaired function in the noradrenergic and/or serotonergic systems. However, the exact role and mechanisms of involvement of these systems in the pathogenesis and pathophysiology of the disease remain to be determined.
The proposed issue invites papers across, but not limited to, the following themes:
Is there a role of the noradrenergic and/or serotonergic system in the pathophysiology of motor symptoms
Is there a role of the noradrenergic and/or serotonergic system in the pathophysiology of non-motor symptoms
Are there any novel drugs targeting these monoaminergic systems in the treatment of PD
Is there any potential role of noradrenaline in neuroprotection against dopaminergic neurodegeneration
Are the noradrenergic and serotonergic systems involved in the mechanism of L-Dopa-induced dyskinesia in PD
Keywords: Parkinson’s disease; dopamine; noradrenaline; serotonin; cell death; neuroprotection; motor symptoms; non-motor symptoms; risk-factors in PD
Published Articles