Intervention of Neuroimmune Responses
Guest Editor
Prof. Raymond Chuen-Chung Chang E-Mail
Laboratory of Neurodegenerative Diseases, School of Biomedical Sciences, LKS Faculty of Medicine, and State Key Laboratory of Brain and Cognitive Sciences, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China
Research Keywords: neuroinflammation; neurodegeneration; microglia; exercise; herbal medicine
About the Special lssue
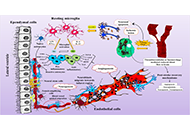
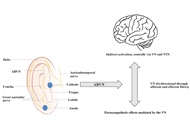
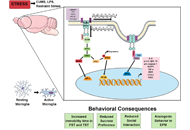
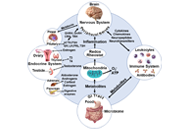
It has been considered that the brain is an immune-privileged site. However, with the new findings of lymphatic vessels in the dural sinus and infiltration of activated macrophages as well as lymphocytes, the concept of immune-privileged site should be totally revised. In fact, immune responses occur when we get an infection in childhood and adulthood, chronic pain, surgery, high fat, polluted environment, aging. Neuroimmune responses often affect progressive neurodegenerative diseases (Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, Huntington’s disease, Dementia with Lewy Bodies), acute neurological disorders (stroke, brain trauma, spinal cord injury, pain, epilepsy), and mental disorders (depression, post-traumatic injury, stress, psychosis, schizophrenia). Our brain usually does not welcome neuroimmune responses. Therefore, we have to understand more about the basic mechanisms of neuroimmune responses and any potential interventions. Therapeutic strategies can be pharmacological (anti-inflammatory, potential herbal medicine and healthy food/natural products, gut microbiota, immunotherapy, miRNA), non-pharmacological (different exercises, environmental enrichment, acupuncture), and even cell therapy (stem cells, stimulation of endogenous stem cells, modification of immune stem cells).
This special issue aims to collect studies from different types of therapeutic interventions or prevention by all the above methods/strategies. We welcome review article, original laboratory work, clinical study, drug trial, case study and systematic review. This special issue provides a platform for the science community to discuss and share strategies of intervention and prevention of neuroimmune responses.
Keywords: neuroimmune; therapeutic intervention; preventive medicine; herbal medicine; exercise; acupuncture; miRNA
Published Articles