Lung Fibrosis—Models and Mechanisms
Guest Editor
Prof. Bernhard Ryffel E-Mail
Professor, INEM, UMR7355, CNRS, University of Orleans, Orleans, France
Research Keywords: Mechanisms of inflammation, innate immune danger sensing, inflammasome activation, IL-33 and Th17/Th22 differentiation
About the Special lssue
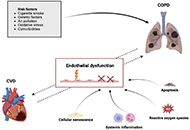
The lung is a critical organ for gas exchange and overall health. Chronic environmental exposures may cause injury to the respiratory barrier, leading to inflammation, emphysema, and progressive interstitial fibrosis, ultimately resulting in respiratory failure. This special issue will begin with an overview of human fibrotic diseases and then address the following key topics:
Aerosol and systemic exposure to particles, smoke, allergens, chemicals, ozone, radiation, as well as viral, bacterial, parasitic, and helminth infections.
Clinical perspectives on COPD, including rodent and in vitro models, and their predictive value for COPD.
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) and preclinical models.
Molecular mechanisms of fibrosis progression and cell death pathways.
The role of TLR, inflammasomes, DNA sensing, and cross-talk between pathways.
Inflammaging, senescence, and autophagy.
Inflammatory cytokines such as TNF and IL-1 family members, and growth factors.
The contribution of intestinal microbiota and metabolism, including SCFA, tryptophan, and serotonin.
Prevention and therapy: new therapeutic targets and drug candidates.
Keywords: TNF, IL-1, growth factors, NLRP, TLR, autophagy, senescence, pollution, microbiome, metabolites, disease models
Published Articles