Exploring Chronic Liver Disease
Guest Editor
Dr. Amedeo Lonardo E-Mail
Director of Simple Operating Unit, Ospedale Civile di Baggiovara, Azienda Ospedaliero-Universitaria di Modena, Modena, Italy
Research Keywords: NAFLD, NASH, cirrhosis, HCC
About the Special lssue
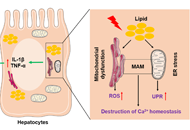
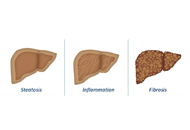
Chronic liver disease (CLD) defines an etiologically diverse group of disorders spanning from viral hepatitis to non-communicable diseases due to alcoholic, metabolic (i.e. nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, NAFLD), genetic, auto-immune and other causes. From a clinico-pathological perspective, the spectrum is also heterogeneous and includes such phenotypically variable entities as steatosis, steatohepatitis, chronic hepatitis, liver cirrhosis and cancer.
The burden of CLD varies across different countries and over time. A recent study conducted in Texas, USA, found that, compared to prevalent chronic conditions, such as either congestive heart failure or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, patients with CLD had increased rates of hospitalization, longer hospital stays, and more readmissions. It was noted that, despite these adverse outcomes, CLD individuals also had less access to post-acute care (1).
Since 1990, the Global Burden of Disease (GBD) consortium has employed more than 3,600 researchers in approximately 150 countries, to register data regarding health loss from more than 350 diseases in 195 countries (2). A recent analysis of the GBD database has demonstrated that the global burden of liver cancer and cirrhosis has steadily increased from 2012 to 2017: although viral hepatitis remains the most common cause of liver deaths, NAFLD is the most rapidly growing contributor to liver mortality and morbidity (3).
CLD poses a menace not only to health systems in the western world, but also in China. Data from the 2016 GBD Study evaluating the burden of CLD in 33 Chinese provinces found that cirrhosis and other CLD impose a huge health burden in China, with Hepatitis B virus remaining the leading cause of disease (4).
For clinicians and health care providers CLD represents a formidable challenge owing to the need for inter- and multi-disciplinary competences. Typically, CLD patients, further to accurate medical history, physical examination (a routine extension of which will modernly also include first-line ultrasonography in many areas of the world) will often need extensive laboratory evaluation; elastometry; accurate imaging studies with “heavy” techniques such as CT scanning and MR imaging; histological characterization whenever indicated; assessment of portal hemodynamics through either invasive or non-invasive techniques; and digestive endoscopy. Many medical specializations are typically involved: not only hepatologists (of various cultural areas such as internal medicine, gastroenterology and infectious diseases) but also diabetologists, lipidologists; molecular virologists; clinical pharmacologists; oncologists; geneticists and others.
Given the complexity of this vivid and rapidly evolving scenario, novel disease management models are greatly needed to handle the anticipated increase in hospitalizations for CLD (2). Therefore, the Editor has chosen to dedicate a single-topic issue of Exploration of Medicine to CLD, entitled “Exploring Chronic Liver Disease”. This special issue is addressed to an audience of, and open to contributions from, a large variety of writers, mainly but not limited to clinicians; radiologists; virologists; geneticists; pharmacologists; researchers in the drug industry; basic scientists; nurses; biotechnicians; patients; health authorities; and medical students, all of whom are encouraged to propose their studies. The following categories will be considered for publication: Original Article and Review (Meta-Analysis, Systematic Review); Case Report, Commentary, and Perspective articles.
References
1. Asrani SK, Kouznetsova M, Ogola G, Taylor T, Masica A, Pope B, et al. Increasing health care burden of chronic liver disease compared with other chronic diseases, 2004-2013. Gastroenterology. 2018;155:719-29.e4.
2. About GBD. Available from: http://www.healthdata.org/gbd/about. [Last accessed on 19 Aug 2020].
3. Paik JM, Golabi P, Younossi Y, Mishra A, Younossi ZM. Changes in the global burden of chronic liver diseases from 2012 to 2017: the growing impact of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2020;[Epub ahead of print].
4. Li M, Wang ZQ, Zhang L, Zheng H, Liu DW, Zhou MG. Burden of cirrhosis and other chronic liver diseases caused by specific etiologies in China, 1990-2016: findings from the global burden of disease study 2016. Biomed Environ Sci. 2020;33:1-10.
Keywords: Biomarkers, cardiometabolic risk, clinical chemistry, endoscopy, genetics, geriatrics gut-liver-axis, imaging techniques, infectious diseases, liver failure, lifestyle changes, liver histology, liver transplantation, medicinal chemistry, metabolic disorders, pediatrics, personalized medicine, portal hypertension, ultrasonography, viral hepatitis
Published Articles