Exploration of 3D and 4D Printing in the Biomedical and Personalized Medicine Fields: Merits and Challenges
Guest Editor
Dr. Nermeen A. Elkasabgy E-Mail
Cairo University Faculty of Pharmacy, Cairo, Egypt
Research Keywords: 3D printing; microfluidics; drug delivery; nanoplatforms; microparticles; sustained drug release; scaffolds; implants; tissue engineering; wound healing; brain targeting; pulmonary delivery; cancer; ocular delivery
About the Special lssue
3D printing, known as additive manufacturing, represents a breakthrough in the biomedical field. One of its prominent advantages is the compliance with the patients' specific medical needs through paving a new track for personalized medicine. Personalized medicine is considered an innovative paradigm in the biomedical field. Personalized medicine means tailoring an individualized treatment for diseases, which overcomes limitations encountered in traditional medicine's 'one-size-fits-all' approach. Avoiding severe side effects, enhancing the efficacy of drugs, saving time and cost as well as decreasing the failure rate of clinical experiments are all considered merits of personalized medicine.
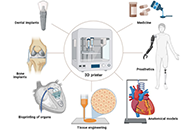
To construct a 3D print, several printers can be used such as stereolithography, selective laser sintering, fused deposition modeling, etc. 3D printing can be efficiently used in fabricating medical devices with customized shapes and architectures including stents, wound dressing, and limbs, etc. Additionally, 3D bioprinting has recently emerged as a magic option to develop tissue constructs capable of restoring lost or diseased tissues and minimizing the risk of tissue rejection by patients' immune system.
Fabricating 4D prints using stimuli-responsive polymers capable of shape alteration in response to external stimuli (e.g., light, temperature, electric/magnetic fields) has opened new avenues for advancing tissue regeneration, drug delivery, and biomedical device fabrication.
This special issue encourages researchers to submit their high quality research and review articles exploring the 3D and 4D printing in the biomedical and pharmaceutical fields.
The Editors believe that this special issue of Exploration of Medicine will allow the scientific community to reflect how far we have advanced in the frontiers of knowledge, where accepted knowledge of the system may need revision, and target the new frontiers of discovery in reaching ultimate knowledge of how hormones act to both regulate and dysregulate body homeostasis.
Keywords: 3D printing, 4D printing, personalized medicine, customized pharmaceutics, implants, scaffolds, medical devices, 3D bioprinting, stimuli-responsive polymers, shape memory polymers, 3D printers
Published Articles