Editor's Picks
Open Access
Case Report
An unusual case of coexistence of Familial Mediterranean Fever with rheumatoid arthritis and Sjögren’s syndrome
We report a rare case of a female patient with multiple rheumatological conditions. The patient initially presented with periodic, diffuse abdominal pain. This complaint was not fully investigated because polyarthritic symptoms became the predominant ones. This led to the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Afterward, the patient complained of xerostomia, xerophthalmia, and diffuse rash. After investigations, she was diagnosed with Sjögren’s syndrome. Suspecting a case of methotrexate-induced vasculitis, her initial prescription was changed to azathioprine and then to etanercept. Eventually, her persistent abdominal pain, combined with her Armenian origin, prompted her physician to order a genetic analysis of the MEFV gene, which revealed the V726A/P369S mutation, giving rise to the diagnosis of Familial Mediterranean Fever. In her routine follow-up, the patient was in a stable condition, adherent to the medications, and showed improvement in her symptoms. Therefore, this case shows the importance of early genetic testing in similar cases, which in turn will allow timely diagnosis and treatment.
Open Access
Original Article
Evaluation of empiric therapy appropriateness, resistance patterns, and mortality in Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections in Jordan
Aim:
This study aimed to investigate the susceptibility patterns of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains, examine infection characteristics, and evaluate the appropriateness of empiric antibiotic therapy. Additionally, the study sought to identify factors influencing 30-day all-cause mortality in patients with Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections.
Methods:
This was a retrospective study conducted at Jordan University Hospital from January 2018 to March 2024. Adult patients (≥ 18 years) with confirmed Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections were included. Data were collected from medical records, focusing on demographics, infection characteristics, antibiotic treatment, and outcomes. The susceptibility patterns of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates were classified as multidrug-resistant (MDR) or non-MDR. Logistic regression was used to identify factors associated with 30-day mortality.
Results:
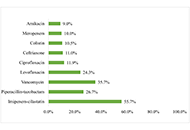
A total of 210 patients were included in the study, with 106 males (50.5%) and 104 females (49.5%). The majority of infections were community-acquired (n = 178, 84.8%), with the respiratory tract being the most common infection site (n = 81, 38.6%). Nearly half of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates were MDR (n = 99, 47.1%). Empiric antibiotic therapy was administered to all patients, with imipenem-cilastatin (55.7%), vancomycin (35.7%), and piperacillin-tazobactam (26.7%) being the most commonly used antibiotics. Of the 210 patients, 32.4% (n = 68) received inappropriate empiric therapy. The 30-day all-cause mortality rate was 4.9% (n = 10). Multivariate analysis revealed that non-localized infections, such as bacteremia and sepsis, were strongly associated with increased mortality [adjusted odds ratio (AOR) = 17.455, P < 0.001].
Conclusions:
This study highlights the high prevalence of MDR Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections, especially in community-acquired cases, and emphasizes the need for improved antimicrobial stewardship. The significant proportion of patients (32.4%) receiving inappropriate empiric therapy calls for better guidance in antibiotic prescribing practices. The key predictor of mortality was infection localization, indicating the importance of early intervention for systemic infections to reduce mortality rates.
Open Access
Original Article
Inflammatory mediators in nasal secretion in patients with bronchial asthma and allergic rhinitis with or without polyposis and hypertrophic sinonasal mucosa
Aim:
The pathogenetic mechanisms and predictors of the development of polyposis and hypertrophy of the sinonasal mucosa (SM) in patients with chronic allergic airway inflammation have not been clearly established. The concentration of inflammatory biomarkers in nasal secretions was determined in children and adolescents with a combined course of bronchial asthma (BA) and allergic rhinitis (AR) in the absence or presence of polyposis and hypertrophy of the SM.
Methods:
A single-centre observational cross-sectional pilot study was conducted. 93 patients with BA aged 8 to 17 years were studied. Total Nasal Symptom Score (TNSS), sinonasal symptoms (SNOT-22), and peak nasal inspiratory flow (PNIF) were assessed. Concentrations of eosinophil cationic protein (ECP), interleukin 4 (IL-4), IL-1, total immunoglobulin E (IgE), and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in nasal secretions were determined.
Results:
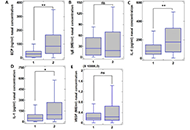
The levels of ECP, IL-4, and IL-1 in nasal secretions were statistically significantly higher in patients with the presence of polyposis and hypertrophic SM than in those without, amounting to 83.1 [31.4; 166.8] ng/mL for ECP vs. 29.5 [5.3; 49.9] ng/mL, P < 0.001, for IL-4 174.6 [68.6; 325.5] pg/mL vs. 79.5 [42.8; 146.01] pg/mL, P = 0.004, for IL-1 98.7 [33.7; 267.5] pg/mL and 48.8 [9.01; 108.2] pg/mL, P = 0.025. There were no statistically significant differences in IgE and VEGF levels in nasal secretions, all P > 0.05. Parameters such as ECP, IL-4, and IL-1 were found to be significant predictors of polyposis and hypertrophy in the formation of SM.
Conclusions:
In patients with a combined course of BA and AR, the presence of polyposis and hypertrophy of SM is associated with higher levels of ECP, IL-4, and IL-1 in nasal secretion. This may indicate that pathological remodelling of SM is associated with both the intensity of allergic inflammation and its relationship with local activation of innate immunity.
Articles
Latest
Most Viewed
Most Downloaded
Most Cited
Open Access
Case Report
An unusual case of coexistence of Familial Mediterranean Fever with rheumatoid arthritis and Sjögren’s syndrome
Fadi Altamimi ... Yasmeen Alabdallat
Published: April 27, 2025 Explor Med. 2025;6:1001313

Open Access
Original Article
Evaluation of empiric therapy appropriateness, resistance patterns, and mortality in Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections in Jordan
Savana Sobh ... Rana K. Abu-Farha
Published: April 23, 2025 Explor Med. 2025;6:1001312

Open Access
Original Article
Right ventricular echocardiographic parameters predict severe sleep apnea syndrome in patients with heart failure
Saoussen Antit ... Lilia Zakhama
Published: April 23, 2025 Explor Med. 2025;6:1001311
Open Access
Original Article
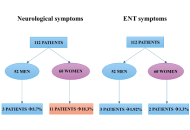
Long-term neurological and otolaryngological sequelae of COVID-19: a retrospective study
Wael Abu Ruqa ... Antonio Minni
Published: April 21, 2025 Explor Med. 2025;6:1001310
This article belongs to the special issue Emerging Infectious Diseases
Open Access
Original Article
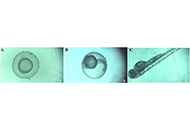
Cytocompatibility and bone regeneration potential of chitosan-thiocolchicoside-lauric acid nanogel with insights into zebrafish toxicology
Ameena Mustafa ... Giuseppe Minervini
Published: April 21, 2025 Explor Med. 2025;6:1001309
Open Access
Review
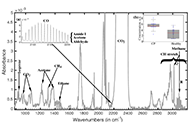
Breath analysis using FTIR spectroscopy
Andrei A. Bunaciu, Hassan Y. Aboul-Enein
Published: April 17, 2025 Explor Med. 2025;6:1001308
Open Access
Original Article
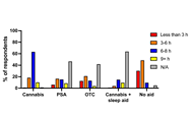
A large-scale survey of cannabis use for sleep: preferred products and perceived effects in comparison to over-the-counter and prescription sleep aids
Amanda Stueber, Carrie Cuttler
Published: October 25, 2023 Explor Med. 2023;4:709–719
This article belongs to the special issue Beyond Weed: Clinical Applications of Cannabis and Cannabinoids
Open Access
Review
The potential anti-cancer effects of melatonin on breast cancer
Naba Kumar Das, Saptadip Samanta
Published: February 25, 2022 Explor Med. 2022;3:112–127
Open Access
Review
3D printing in biomedicine: advancing personalized care through additive manufacturing
Kalyani Pathak ... Barbie Borthakur
Published: December 29, 2023 Explor Med. 2023;4:1135–1167
This article belongs to the special issue Exploration of 3D and 4D Printing in the Biomedical and Personalized Medicine Fields: Merits and Challenges
Open Access
Review
The gut microbiome and the immune system
Tenzin Choden, Nathaniel Aviv Cohen
Published: May 31, 2022 Explor Med. 2022;3:219–233
Open Access
Original Article
Cannabis use in cancer patients: acute and sustained associations with pain, cognition, and quality of life
Gregory Giordano ... Angela D. Bryan
Published: April 26, 2023 Explor Med. 2023;4:254–271
This article belongs to the special issue Beyond Weed: Clinical Applications of Cannabis and Cannabinoids
Open Access
Review
Reactive oxygen species in cancer progression and its role in therapeutics
Ranjeet Singh, Partha Pratim Manna
Published: February 22, 2022 Explor Med. 2022;3:43–57
This article belongs to the special issue Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) in Pathophysiological Conditions
Open Access
Perspective
Reactive oxygen species may influence on the crossroads of stemness, senescence, and carcinogenesis in a cell via the roles of APRO family proteins
Yuka Ikeda ... Satoru Matsuda
Published: October 31, 2021 Explor Med. 2021;2:443–454
This article belongs to the special issue Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) in Pathophysiological Conditions
Open Access
Perspective
A budding concept with certain microbiota, anti-proliferative family proteins, and engram theory for the innovative treatment of colon cancer
Yuka Ikeda ... Satoru Matsuda
Published: October 27, 2022 Explor Med. 2022;3:468–478
This article belongs to the special issue The Role of Gut Microbiota and its Metabolites in Gastrointestinal Diseases
Open Access
Review
Roles of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 and mitophagy in progeroid syndromes as well as physiological ageing
Naoko Suga ... Satoru Matsuda
Published: October 31, 2023 Explor Med. 2023;4:822–838
This article belongs to the special issue Determinants of Exceptional Longevity
Open Access
Review
The gut microbiome and the immune system
Tenzin Choden, Nathaniel Aviv Cohen
Published: May 31, 2022 Explor Med. 2022;3:219–233

Open Access
Review
Reactive oxygen species in cancer progression and its role in therapeutics
Ranjeet Singh, Partha Pratim Manna
Published: February 22, 2022 Explor Med. 2022;3:43–57
This article belongs to the special issue Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) in Pathophysiological Conditions

Open Access
Review
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and type 2 diabetes: pathophysiological mechanisms shared between the two faces of the same coin
Carlo Acierno ... Ferdinando Carlo Sasso
Published: October 30, 2020 Explor Med. 2020;1:287–306
This article belongs to the special issue Exploring NAFLD/NASH
Open Access
Review
3D printing in biomedicine: advancing personalized care through additive manufacturing
Kalyani Pathak ... Barbie Borthakur
Published: December 29, 2023 Explor Med. 2023;4:1135–1167
This article belongs to the special issue Exploration of 3D and 4D Printing in the Biomedical and Personalized Medicine Fields: Merits and Challenges

Open Access
Review
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and type 2 diabetes: pathophysiological mechanisms shared between the two faces of the same coin
Carlo Acierno ... Ferdinando Carlo Sasso
Published: October 30, 2020 Explor Med. 2020;1:287–306
This article belongs to the special issue Exploring NAFLD/NASH

Open Access
Review
Reactive oxygen species in cancer progression and its role in therapeutics
Ranjeet Singh, Partha Pratim Manna
Published: February 22, 2022 Explor Med. 2022;3:43–57
This article belongs to the special issue Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) in Pathophysiological Conditions

Open Access
Review
PNPLA3 gene and kidney disease
Alessandro Mantovani, Chiara Zusi
Published: February 29, 2020 Explor Med. 2020;1:42–50
Open Access
Review
Oxidative stress in obesity and insulin resistance
Anastasija Panic ... Esma R. Isenovic
Published: February 23, 2022 Explor Med. 2022;3:58–70
This article belongs to the special issue Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) in Pathophysiological Conditions
Open Access
Review
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and portal hypertension
Marvin Ryou ... Gyorgy Baffy
Published: June 29, 2020 Explor Med. 2020;1:149–169
This article belongs to the special issue Exploring NAFLD/NASH
Special Issues
Ongoing Special lssues
Completed Special lssues
Practical Tips for Cancer Care: Guidance for Patients, Caregivers, and Healthcare Professionals
Prof. Patricia Tai
September 30, 2025
Published Articles: 0

Assessment of Atrial and Ventricular Volumes and Functional Properties: Novel Insights
Prof. Attila Nemes
August 31, 2025
Published Articles: 0

Lipid Peroxidation and Cancer
Prof. Neven Zarkovic
July 31, 2025
Published Articles: 0
Innovative Approaches to Chronic Pain Management: from Multidisciplinary Strategies to Artificial Intelligence Perspectives
Prof. Marco Cascella
April 30, 2025
Published Articles: 2

Global Perspectives on the Clinical Diagnosis, Treatment, and Functional Cure of HIV Infection in the Post-ART Era
Prof. Hongzhou Lu
July 31, 2025
Published Articles: 0

Disrupted Cytokine Signaling Pathways in Autoimmunity
Prof. Alister C. Ward
May 31, 2025
Published Articles: 0

Molecular Diagnostics in Oncology
Prof. Evgeny Imyanitov
December 31, 2024
Published Articles: 1

Advances in Oral Cancer: Prevention, Diagnosis, and Therapeutics
Dr. Luca Fiorillo
December 31, 2024
Published Articles: 3

Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Cardiovascular Medicine
Prof. Zhong Wang Dr. Ienglam Lei Dr. Liu Liu
August 31, 2025
Published Articles: 0

Oral Health Interconnections and Multidisciplinary Approaches
Dr. Giuseppe Minervini
December 31, 2024
Published Articles: 10

Prostate Specific Membrane Antigen (PSMA) in Prostate Cancer
Dr. Finn Edler von Eyben
June 30, 2025
Published Articles: 0
Neurophysiological Mechanisms of Aging and Dementia
Prof. Fabrizio Vecchio
June 30, 2024
Published Articles: 4

Personalized Medicine in Cancer Therapy
Prof. Haim Werner Prof. Ilan Bruchim
June 30, 2025
Published Articles: 0

Spotlight on Cervical Cancer: Prevention, Early-Diagnosis, and Treatments
Dr. Andrea Giannini Dr. Giorgio Bogani
February 29, 2024
Published Articles: 4

Advances in the Identification and Mechanisms of Action of Luminal Compounds Involved in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
Dr. Francois Blachier
September 30, 2024
Published Articles: 1

Drug Adherence in Hypertension
Prof. Sverre E. Kjeldsen
April 30, 2025
Published Articles: 6

Emerging Infectious Diseases
Prof. Marcos Roberto Tovani-Palone
June 30, 2025
Published Articles: 3

Gut Microbiota Derived Metabolites and Chronic Inflammatory Diseases
Dr. Zeneng Wang
May 30, 2025
Published Articles: 4
Lung Fibrosis—Models and Mechanisms
Prof. Bernhard Ryffel
June 30, 2025
Published Articles: 4

Focus
Exploration of 3D and 4D Printing in the Biomedical and Personalized Medicine Fields: Merits and Challenges
Dr. Nermeen A. Elkasabgy
Dec. 6, 2024
1793


Cerebrovascular Disease Modeling, Mechanistic Study and Therapy Development
Prof. Hua Su
Jun. 9, 2023
1147


Journal Information
Journal Metrics
Speed 2024
From First decision to Acceptance: 83.9 days
From Acceptance to Publication: 14 days
Article Usage (total)
Views: 982,052
Downloads: 24,377
Acceptance Rate
36%

































 Title: Unravelling the interplaybetween #Harmattan wind andbaroreflex functions: implicationon environmental health andcardiovascular #pathophys
Title: Unravelling the interplaybetween #Harmattan wind andbaroreflex functions: implicationon environmental health andcardiovascular #pathophys


