Biomarkers for Personalized and Precise Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment
Guest Editor
Dr. Arun Seth E-Mail
Scientific Director of Molecular Diagnostics, Department of Laboratory Medicine and Molecular Diagnostics, Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre; Academic Director, Genomics Core Facility, Senior Scientist, Sunnybrook Research Institute; Professor, Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathobiology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Toronto, Toronto, Canada
Research Keywords: precision oncology; breast and prostate cancer biology; molecular diagnostics; genomic profiling; next-generation sequencing; targeted cancer therapy
About the Special lssue
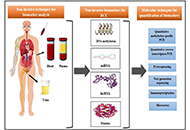
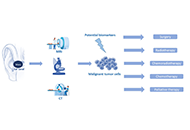
Biomarkers are biological molecules that can be evaluated as an indicator of a normal biological and pathogenic process, or a pharmacologic response to a drug. Identification of key cancer biomarkers is crucial for diagnosis, prognosis, treatment, and therapeutic responses. A wide range of technologies have been used to study and discover biomarkers including mass spectrometry, imaging, next generation sequencing.
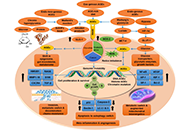
Cancer is a complex disease and develops due to the accumulation of genetic and epigenetic alterations. Precision cancer medicine promotes treatment options based on a patient's profile of genetic variations. This requires validated predictive and prognostic biomarkers that can guide the clinical management of individual cancer patients. The focus in precision and personalized cancer medicine is to identify effective approaches for patients based on genetic factors. Most tumors harbor genetic mutations unique to each patient’s cancer. A subset of these mutations drive oncogenesis by conferring a selective growth advantage to the tumor cell. Many cancers specific changes are druggable with highly specific anticancer agents such as small molecules or monoclonal antibodies. In certain cancer cases, companion diagnostic tests are used to identify safe and effective use of a corresponding targeted therapeutic. Precisely targeted mutated proteins can specifically inhibit cancerous cell growth and achieve remission with fewer side effects than traditional chemotherapies.
Keywords: Biomarkers; precision oncology; molecular diagnostics; companion diagnostics; patient profiling; personalized medicine; targeted therapy; genomics; transcriptomics; proteomics; metabolomics; imaging
Published Articles