Antibody-Drug Conjugates
Guest Editors
Dr. Francesco Bertoni E-Mail
Institute of Oncology Research, Faculty of Biomedical Sciences, USI, Bellinzona, Switzerland
Research Keywords: lymphoma; novel drugs; genomics; BET; PI3K
Dr. Anastasios Stathis E-Mail
Oncology Institute of Southern Switzerland (IOSI), Bellinzona, Switzerland; Faculty of Biomedical Sciences, USI, Bellinzona, Switzerland
About the Special lssue
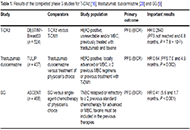
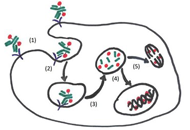
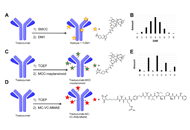
Antibody drug conjugates (ADCs) have become a potent modality to treat solid tumors and hematologic malignancies. The use of antibodies against antigens that are the most specific as possible for cancer cells and that bear particular biologic features allow the delivery of powerful payloads, which otherwise would be too toxic.
With some of the first-generation compounds already approved by regulatory agencies, there is still wide room for further improvements of this therapeutic approach. ADC-incorporating regimens, novel linkers, novel targets, novel payloads are all exciting fields of preclinical and clinical research.
This special issue of Exploration of Targeted Anti-tumor Therapy covers all the aspects of the use of ADCs, inviting investigators to submit their novel lab and clinical findings.
Keywords: Antibody drug conjugate; ADC; payload; linker; antibody
Published Articles