Proteolysis Targeting Chimera (PROTAC)
Guest Editor
Dr. Matthias Baud E-Mail
Lecturer in Medicinal Chemistry and Chemical Biology, University of Southampton, Southampton, UK
Research Keywords: chemical biology; medicinal chemistry; small molecule; organic synthesis
About the Special lssue
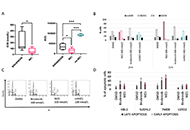
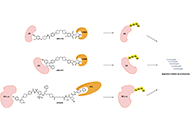
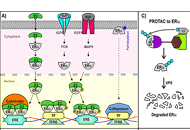
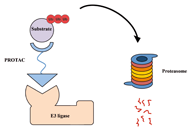
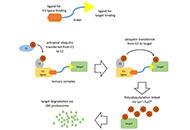
Proteolysis targeting chimeras (PROTAC) are heterofunctional, bispecific molecules where two protein-binding probes are connected via a linker. The mechanism of action involves ternary complex formation in which one fragment interacts with the protein of interest (POI) and the other binds to a component of an ubiquitin ligase. This results in the poly-ubiquitination of the POI, which then undergoes proteasomal degradation, releasing the catalytic PROTAC. This strategy to reduce cellular protein levels has generated huge interest and excitement, and at present, there is significant research aimed at understanding the factors that determine functional efficiency. This is a truly exciting time for this field, which progressively shifted from a chemical biology concept to a new Eldorado for anticancer drug discovery. We feel that this special issue is particularly timely, and aims to provide an overview of the recent developments in the field of PROTAC, and applications to the development of novel candidate anticancer therapies.
In this issue, we welcome Original Articles and Reviews spanning from the molecular sciences to advanced clinical work. Critical aspects include the development of novel molecular design principles and synthetic strategies for assembling PROTACs, structural biology and the thermodynamics of ternary complexes, the identification of novel anticancer targets, and the evaluation of new PROTACs in cancer cells and animal studies. In addition, structure activity relationship (SAR) studies and the correlation of molecular structures and properties with overall biological activity and selectivity profiles in cellular/animal studies will present a particular interest, as we believe that much is still to be done to derive useful design criteria for the rational design and optimization of PROTACs.
Keywords: PROTAC; targeted anticancer therapy; induced protein degradation; ubiquitin-proteasome system; E3 ubiquitin ligase
Published Articles