Therapeutic Targeting of the Tumor Microenvironment
Guest Editor
Dr. Sufi Thomas E-Mail
Department of Otolaryngology, University of Kansas Medical Center, Kansas City, USA
Research Keywords: Tumor microenvironment; tumor associated stroma; cancer associated fibroblasts; immunosuppression; experimental therapeutics; tumor progression; cancer therapy
About the Special lssue
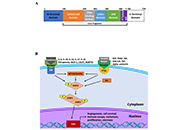
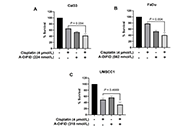
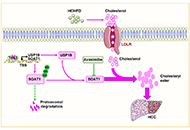
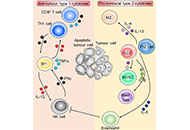
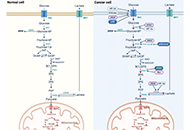
Cancer continues to be one of the most life threatening, and devastating pathologies faced by mankind. With an increasing incidence over time, there is a great need for effective therapies with minimal side effects. The role of the tumor microenvironment (TME) in tumor progression and response to therapy has become evident in the last few decades. From acellular components, immune cells, vascular and lymphatic endothelial cells, cancer associated fibroblasts, and more recently, neuronal cells, adipocytes and the microbiome, the complex tumor-stromal interactions open new possibilities for targeted therapies.
The advent of single cell sequencing and other medium to high throughput assays have accelerated the field uncovering key tumor-stroma molecular dependencies. Still in a relatively nascent phase, most of published literature includes studies with individual TME cell types or secreted components in relation to tumors. The concerted role of all TME players on tumor cells is an area that needs to be further developed. Preclinical animal models including transgenic, immunocompetent, and humanized mice coupled with xenograft, syngeneic and patient derived tumors provide platforms to test these new therapeutic approaches. The next few decades hold tremendous promise in the development of precision approaches for cancer therapy that target individual components of the TME.
Keywords: Tumor microenvironment; experimental therapeutics; cancer therapy; personalized medicine; targeted therapy; single cell sequencing; preclinical models; organotypic models
Published Articles