Novel Strategies and Targets for Immunotherapy of Cancer
Guest Editor
Prof. Seiji Okada E-Mail
Division of Hematopoiesis, Joint Research Center for Human Retrovirus Infection & Graduate School of Medical Sciences, Kumamoto University, Kumamoto, Japan
Research Keywords: Targeting therapy; cancer immunotherapy; precision medicine; animal model; Patient-derived xenograft (PDX)
About the Special lssue
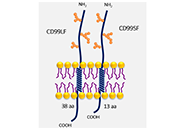
Immunotherapy is a type of cancer treatment that helps the patients’ immune system to fight with cancer by boosting the power of immune cells. Immunotherapy used to be the way to nonspecifically activate immune system by cytokines or immune stimulants such as BCG, and it was just an adjunctive therapy of surgery, chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Recently, immunotherapy is becoming the main actor of cancer therapy by developing various therapeutic approaches and therapies such as monoclonal antibodies, immune check point inhibitors, T-cell transfer therapy such as CAR-T therapy, etc. Immune system modulators such as interferons are also clinically in use and effective in some sort of cancers. These immunotherapies still have ample scope for improvement. The aim of this special issue is to discuss the latest progress and future direction of cancer immunotherapy. We accept original research articles, critical review papers and commentaries that provide novel approaches and highlight the promising targets for cancer immunotherapies.
Keywords: Immunotherapy; CAR-T; therapeutic monoclonal antibodies; immunomodulators; treatment vaccines; immune checkpoint inhibitors
Published Articles