Endocrine Resistant Breast Cancer
Guest Editors
Dr. Simon Langdon E-Mail
Reader, School of Medicine, University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, UK
Research Keywords: ovarian cancer; breast cancer; estrogen signaling; HER signaling; DNA repair
Dr. Valerie Speirs E-Mail
Professor and Chair in Molecular Oncology, Institute of Medical Sciences, University of Aberdeen, Aberdeen, UK
Research Keywords: oestrogen receptor biology; endocrine resistant breast cancer; male breast cancer; in vitro models; biomarker
About the Special lssue
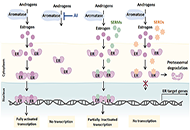
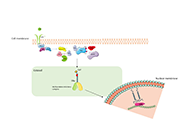
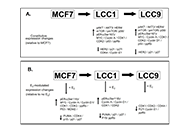
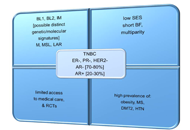
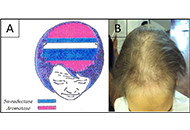
The majority of breast cancers are estrogen receptor alpha (ERa) positive and most will initially respond to endocrine therapy. Current therapies to treat ERa-positive disease include aromatase inhibitors, selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) and selective estrogen down-regulators (SERDs). However, resistance to these treatments will develop in many cancers and can be present either at the outset (de novo resistance) or develop on treatment (acquired resistance). Experimental and clinical investigations have demonstrated multiple mechanisms that can give rise to resistance and a range of therapeutic agents such as CDK4/6 inhibitors and other signalling inhibitors have been developed to circumvent these. Resistance mechanisms include changes in ER status (e.g. loss and mutation) and the involvement of compensatory pathways bypassing the dependence on estrogen activation particularly growth factor activation.
In this issue, we welcome Reviews and Original Articles encompassing experimental laboratory research studies of endocrine resistance through to clinical investigations in breast cancer.
Keywords: Breast cancer; resistance; endocrine; estrogen
Published Articles