Editor's Picks
Articles
Latest
Most Viewed
Most Downloaded
Most Cited
Open Access
Review
Neoantigen-based immunotherapy: advancing precision medicine in cancer and glioblastoma treatment through discovery and innovation
Moawiah M Naffaa ... Valiko Begiashvili
Published: April 27, 2025 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2025;6:1002313

Open Access
Review
Cytokine-based immunotherapy for gastric cancer: targeting inflammation for tumor control
Mathan Muthu Chinakannu Marimuthu ... Hitesh Chopra
Published: April 26, 2025 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2025;6:1002312
Open Access
Review
Viral infections and immune modulation in bladder cancer: implications for immunotherapy
Lívia Bitencourt Pascoal ... Leonardo O. Reis
Published: April 24, 2025 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2025;6:1002311
This article belongs to the special issue Comprehensive Immunotherapy of Solid Tumors
Open Access
Review
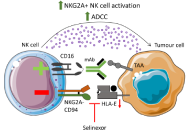
Modulation of anti-tumour immunity by XPO1 inhibitors
Jack G. Fisher ... Matthew D. Blunt
Published: April 23, 2025 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2025;6:1002310
This article belongs to the special issue Immune Checkpoint Therapy and Biomarkers in Cancer
Open Access
Case Report
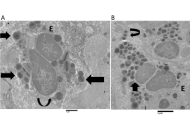
Eosinophil cytolysis with or without ETosis in four cases of human gastric cancer: a comparative ultrastructural study
Rosario Caruso ... Luciana Rigoli
Published: April 21, 2025 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2025;6:1002309
Open Access
Review
Nanoimmunotherapy: the smart trooper for cancer therapy
Suphiya Parveen ... Fahima Dilnawaz
Published: April 10, 2025 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2025;6:1002308
This article belongs to the special issue Comprehensive Immunotherapy of Solid Tumors

Open Access
Review
Current strategies for the design of PROTAC linkers: a critical review
Robert I. Troup ... Matthias G. J. Baud
Published: October 30, 2020 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2020;1:273–312
This article belongs to the special issue Proteolysis Targeting Chimera (PROTAC)
Open Access
Review
The impact of tumour pH on cancer progression: strategies for clinical intervention
Carol Ward ... Simon P Langdon
Published: April 28, 2020 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2020;1:71–100
Open Access
Review
Inhibitors of the Fanconi anaemia pathway as potential antitumour agents for ovarian cancer
Sarah J Taylor ... Simon P Langdon
Published: February 29, 2020 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2020;1:26–52
Open Access
Review
Development of PROTACs to address clinical limitations associated with BTK-targeted kinase inhibitors
Rachael Arthur ... Graham Packham
Published: June 29, 2020 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2020;1:131–152
This article belongs to the special issue Proteolysis Targeting Chimera (PROTAC)
Open Access
Review
Novel approaches for the rational design of PROTAC linkers
Almaz Zagidullin ... Emil Bulatov
Published: October 30, 2020 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2020;1:381–390
This article belongs to the special issue Proteolysis Targeting Chimera (PROTAC)
Open Access
Review
Early-stage triple negative breast cancer: the therapeutic role of immunotherapy and the prognostic value of pathological complete response
Pierluigi De Santis ... Palma Fedele
Published: February 28, 2024 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2024;5:232–250
This article belongs to the special issue Innovative Strategies to Target Triple-negative Breast Cancer
Open Access
Review
Current strategies for the design of PROTAC linkers: a critical review
Robert I. Troup ... Matthias G. J. Baud
Published: October 30, 2020 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2020;1:273–312
This article belongs to the special issue Proteolysis Targeting Chimera (PROTAC)

Open Access
Perspective
Encouraging probiotics for the prevention and treatment of immune-related adverse events in novel immunotherapies against malignant glioma
Sayuri Yoshikawa ... Satoru Matsuda
Published: December 27, 2022 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2022;3:817–827
This article belongs to the special issue Theranostic Frontiers in Neuro-Oncology
Open Access
Perspective
Potential tactics with vitamin D and certain phytochemicals for enhancing the effectiveness of immune-checkpoint blockade therapies
Ai Tsuji ... Satoru Matsuda
Published: June 30, 2023 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2023;4:460–473
This article belongs to the special issue Cancer Immunotherapy and Tumor Microenvironment
Open Access
Perspective
Potential tactics with certain gut microbiota for the treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma
Sayuri Yoshikawa ... Satoru Matsuda
Published: August 24, 2023 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2023;4:556–568
This article belongs to the special issue Cancer Immunotherapy and Tumor Microenvironment
Open Access
Review
The impact of tumour pH on cancer progression: strategies for clinical intervention
Carol Ward ... Simon P Langdon
Published: April 28, 2020 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2020;1:71–100

Open Access
Review
Novel approaches for the rational design of PROTAC linkers
Almaz Zagidullin ... Emil Bulatov
Published: October 30, 2020 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2020;1:381–390
This article belongs to the special issue Proteolysis Targeting Chimera (PROTAC)

Open Access
Review
Current strategies for the design of PROTAC linkers: a critical review
Robert I. Troup ... Matthias G. J. Baud
Published: October 30, 2020 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2020;1:273–312
This article belongs to the special issue Proteolysis Targeting Chimera (PROTAC)

Open Access
Review
The impact of tumour pH on cancer progression: strategies for clinical intervention
Carol Ward ... Simon P Langdon
Published: April 28, 2020 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2020;1:71–100

Open Access
Review
Diagnostic value of liquid biopsy in the era of precision medicine: 10 years of clinical evidence in cancer
Vincenza Caputo ... Stefania Napolitano
Published: February 28, 2023 Explor Target Antitumor Ther 2023;4:102–138
This article belongs to the special issue The Implementation of Liquid Biopsy in Clinical Practice for Different Solid Tumor
Open Access
Review
Novel approaches for the rational design of PROTAC linkers
Almaz Zagidullin ... Emil Bulatov
Published: October 30, 2020 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2020;1:381–390
This article belongs to the special issue Proteolysis Targeting Chimera (PROTAC)

Open Access
Review
Transforming growth factor-β signaling: from tumor microenvironment to anticancer therapy
Max Kam-Kwan Chan ... Patrick Ming-Kuen Tang
Published: April 28, 2023 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2023;4:316–343
This article belongs to the special issue Cancer Immunotherapy and Tumor Microenvironment
Open Access
Review
Genomic alterations in cholangiocarcinoma: clinical significance and relevance to therapy
Marianeve Carotenuto ... Nicola Normanno
Published: April 26, 2022 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2022;3:200–223
This article belongs to the special issue Precision Medicine for Cholangiocarcinoma
Special Issues
Ongoing Special lssues
Completed Special lssues
Artificial Intelligence Technology in Tumor Radiotherapy
Prof. Tuan D. Pham
September 30, 2025
Published Articles: 0

Liquid Biopsy: Has Already Changed the Clinical Decision-Making in Solid Tumors Treatment?
Dr. Giulia Martini
June 30, 2025
Published Articles: 0
Predictive and Prognostic Biomarkers in Cancer: Towards the Precision Medicine Era
Prof. Luca Falzone Dr. Antonio Rizzo Dr. Stefano Marletta Dr. Graziana Spoto
February 28, 2025
Published Articles: 2

Potential Clinical Applications of Inorganic Nanomaterials in Cancer
Prof. Javier Reguera
April 30, 2025
Published Articles: 1

Potential of Non-Coding RNAs in Cancer Research and Treatment
Prof. Francesco Bertoni Dr. Luciano Cascione
June 30, 2025
Published Articles: 0

Novel Biomarkers in the Immunotherapy Era
Dr. Carminia Maria Della Corte Dr. Floriana Morgillo Dr. Caterina De Rosa
December 31, 2024
Published Articles: 1
Comprehensive Immunotherapy of Solid Tumors
Dr. Michela Valeria Rita Starace
October 31, 2024
Published Articles: 4

Advances in Cancer Genomics and Therapeutic Targets
Prof. Apostolos Zaravinos
October 31, 2024
Published Articles: 2

Molecular Mechanisms and Intervention Options in Metastatic Spread of Cancer
Dr. Katrin Sak
June 30, 2025
Published Articles: 2

Immunotherapy Strategies for Non-small Cell Lung Cancer
Prof. Stergios Boussios Prof. Matin Sheriff
July 31, 2024
Published Articles: 5

Use of Different Radiation Treatment Modalities in Cancer Therapy: The Role of Inflammation and Immune Response
Prof. Alexandros Georgakilas
May 31, 2025
Published Articles: 1

Immune Checkpoint Therapy and Biomarkers in Cancer
Prof. Eyad Elkord
December 31, 2024
Published Articles: 7

Mechanisms of Targeted Therapy Resistance and Reversal Strategies
Prof. Pier Paolo Piccaluga
December 31, 2024
Published Articles: 3

Current Innovative Cancer Treatment
Prof. Salem Chouaib Dr. Ghazi Jerbi
February 29, 2024
Published Articles: 0

Cancer Epigenetics: Implications for Novel Therapeutic Strategies
Prof. Mingzhou Guo
February 01, 2025
Published Articles: 2

Novel Insights into Immunotherapy Targeting Tumor Microenvironment in Cancer
Prof. Hailin Tang
October 31, 2023
Published Articles: 4

Molecular Diagnosis and Personalized Therapy of Cancer
Prof. Monica Fedele Prof. Andrea Vecchione
May 31, 2024
Published Articles: 4

Innovative Strategies to Target Triple-negative Breast Cancer
Dr. Laura Cerchia Dr. Simona Camorani
May 31, 2023
Published Articles: 8

Posttranslational Modifications in Health and Disease
Prof. Oliver Krämer
December 31, 2024
Published Articles: 4

The Role of Bcl-2 Family Proteins in Cancer Progression and Their Relevance to Cancer Therapy
Dr. Donatella Del Bufalo Dr. Germain Gillet
November 30, 2021
Published Articles: 5

Journal Information
Journal Metrics
Article Usage (total)
Views: 858,708
Downloads: 24,755

































 Title: Unravelling the interplaybetween #Harmattan wind andbaroreflex functions: implicationon environmental health andcardiovascular #pathophys
Title: Unravelling the interplaybetween #Harmattan wind andbaroreflex functions: implicationon environmental health andcardiovascular #pathophys


